Advanced Medical Coding Certifications: Which One is Right for You?
The world of medical coding is evolving rapidly, and with it comes a growing demand for skilled professionals who hold recognized certifications. For those pursuing a career in advanced medical coding, earning a relevant certification is more than just a resume booster—it's a critical step toward higher earning potential, career advancement, and professional credibility.
But with so many certification options available, how do you know which one is the right fit for your goals? In this blog, we’ll explore the top certifications in advanced medical coding, what each entails, and how to choose the best one based on your experience and career path.
Why Certifications Matter in Advanced Medical Coding
Medical coding is an essential function in the healthcare system. It ensures that providers are properly reimbursed for services rendered, and that patient records are accurately documented. With stricter regulations, frequent audits, and increasing complexity in billing, having an advanced certification helps coders prove their expertise and stand out in a competitive job market.
Key Benefits of Certification:
Validates your expertise in coding systems (ICD-10, CPT, HCPCS)
Enhances job prospects and salary potential
Demonstrates a commitment to industry standards
Prepares you for leadership roles and specialized coding jobs
Helps maintain compliance in billing and documentation
Top Certifications in Advanced Medical Coding
In the world of health information management and medical coding, the Certified Coding Specialist (CCS) credential stands out as a prestigious and highly sought-after certification. Offered by the American Health Information Management Association (AHIMA), the CCS credential validates the skills of professionals who are proficient in medical coding for hospital settings—particularly inpatient coding. This credential holds significant weight across healthcare systems in the United States and internationally, as it demonstrates a coder’s ability to transform complex medical documentation into standardized codes used for billing, research, and statistical analysis.
Whether you’re a seasoned medical coder or an aspiring health information professional, earning the CCS credential could be a game-changer for your career.
What is the CCS Certification?
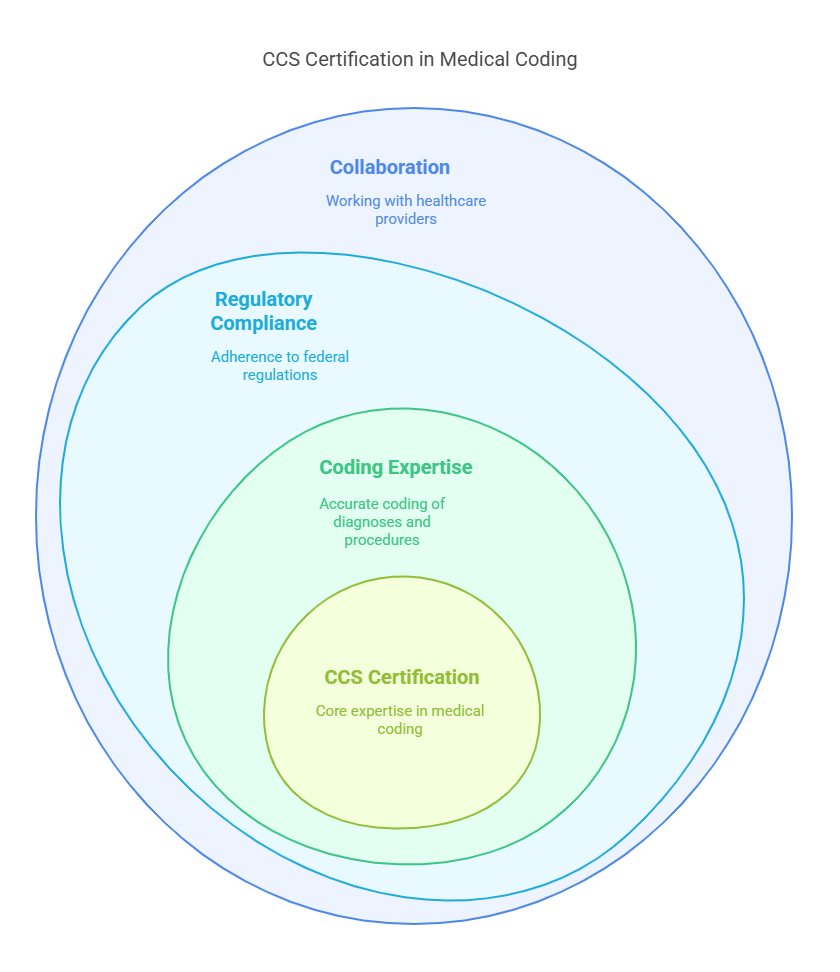
The Certified Coding Specialist (CCS) credential is designed for individuals who specialize in classifying medical data from patient records—especially in hospital or inpatient settings. This certification focuses on coding diagnoses and procedures using the ICD-10-CM (International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, Clinical Modification) and ICD-10-PCS (Procedure Coding System) code sets. These codes are essential for documenting patient diagnoses, surgical procedures, treatments, and other aspects of care.
Professionals who earn the CCS credential demonstrate their expertise in:
Reviewing patient records and assigning accurate codes for diagnoses and procedures
Understanding and applying coding guidelines
Ensuring compliance with federal regulations
Maintaining the accuracy of patient records for reimbursement and data quality purposes
Collaborating with physicians and healthcare providers to clarify documentation
The CCS is not an entry-level certification; instead, it’s tailored for professionals with real-world coding experience and formal training. It distinguishes experts from generalists and is often considered a stepping stone into more advanced or leadership roles in the medical coding profession.
Who Should Pursue the CCS?
The CCS credential is best suited for experienced medical coders who work or plan to work in hospital-based or inpatient care settings. These individuals are typically already familiar with the day-to-day coding processes but want to take their expertise to the next level.
Ideal candidates include:
Medical coders with 2+ years of experience in inpatient coding
Coding specialists currently working in acute care hospitals or similar facilities
Health Information Management (HIM) professionals who want to specialize in coding
Certified coders (e.g., CPC, RHIT, RHIA) looking to expand their credentials
Foreign-trained coders aiming for a credential that is globally recognized and respected
Because the CCS certification focuses heavily on ICD-10-CM and ICD-10-PCS, candidates should be comfortable handling complex inpatient records, which often include a variety of surgical procedures, comorbidities, and multifaceted treatment plans.
Prerequisites: What You Need Before Taking the Exam
While AHIMA doesn’t mandate a specific degree to sit for the CCS exam, candidates are strongly encouraged to have formal training and coding experience. This is not a beginner’s test—it’s designed for professionals who are already confident in their abilities and looking for formal recognition of their skills.
Typical prerequisites include:
Completion of a medical coding training program (from a college, university, or online training provider)
Hands-on experience working with medical records in a hospital or similar healthcare environment
Proficiency in medical terminology, pharmacology, disease processes, anatomy, and physiology
Strong knowledge of the ICD-10-CM and ICD-10-PCS coding systems
Familiarity with compliance and regulatory standards, such as HIPAA and Medicare billing guidelines
AHIMA offers a self-assessment tool that can help you determine if you’re ready to take the CCS exam. If you feel confident in your ability to code from inpatient medical records without relying on automated suggestions or software tools, you’re likely a good candidate.
What Does the Exam Cover?
The CCS exam is a rigorous assessment that tests a coder’s ability to assign codes accurately in real-world scenarios. The exam is divided into two sections:
1. Multiple-Choice Questions:
This section tests theoretical knowledge on areas such as:
Coding guidelines (ICD-10-CM/PCS)
Medical terminology
Disease pathology
Pharmacology
Legal and compliance issues
Reimbursement methodologies
2. Medical Scenario Section:
One key component of the CCS exam is the practical portion, which includes clinical cases where the candidate must assign accurate codes based on real medical documentation. It simulates tasks a coder would face on the job, requiring detailed analysis of patient records and procedural notes. How can you best prepare for this hands-on portion of the CCS exam? The answer lies in understanding coding guidelines, practicing with real case scenarios, and staying updated with the latest ICD-10-CM and PCS standards.
The entire test is administered through Pearson VUE testing centers and typically takes four hours to complete. As of 2025, the exam consists of approximately 115 to 140 questions split between multiple-choice and scenario-based items.
Benefits of CCS Certification
There are many compelling reasons to pursue the CCS credential. Here are some of the key advantages:
Higher earning potential: Certified Coding Specialists often command better salaries than their non-certified peers. Employers value the CCS credential as proof of advanced coding knowledge.
Career advancement: With a CCS, coders are more likely to move into lead, supervisory, or auditing roles.
Recognition and credibility: AHIMA is one of the most respected organizations in the healthcare information space. A CCS credential carries weight with employers, making your resume stand out.
Increased job opportunities: Many hospitals and healthcare systems specifically require or prefer CCS certification for coding positions.
Global recognition: The CCS credential is not just limited to the U.S.—many international employers accept or prefer AHIMA-certified coders.
Real-World Use and Demand
Hospitals, long-term care facilities, and specialized surgical centers are consistently in search of CCS-certified professionals. The demand for skilled inpatient coders is high, especially given the complexity of ICD-10-PCS and the precision required for insurance billing and data tracking.
With the ongoing digitization of healthcare and an increased focus on accurate documentation and compliance, CCS-certified coders are more important than ever. As healthcare organizations search for the Best Medical Billing and Coding Certification Programs in 2025, the demand for qualified professionals continues to rise. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, employment for medical records and health information specialists is expected to grow by 8% through 2032, faster than average for most occupations.
Preparation Tips
If you’re preparing for the CCS exam, here are a few tips to help you succeed:
Study daily using coding scenarios—focus especially on inpatient cases
Use AHIMA’s official prep materials, including the CCS exam prep book
Practice time management, as both the multiple-choice and scenario sections are timed
Join a study group or online community to learn from peers
Take full-length practice exams under real test conditions
Remember, this exam is challenging because it’s meant to certify only the most competent coders in the field. Give yourself ample time to prepare thoroughly.
2. Certified Professional Coder (CPC) – Offered by AAPC
The CPC is the most popular medical coding certification in the U.S. It focuses on coding outpatient procedures using CPT, ICD-10-CM, and HCPCS Level II codes.
Who It’s Best For:
Coders working in physician offices, outpatient clinics, or ambulatory settings.
Prerequisites:
AAPC recommends 1-2 years of professional coding experience, although it’s not mandatory
3. Certified Outpatient Coder (COC) – Offered by AAPC
Formerly known as CPC-H, the COC is designed for coders specializing in facility-based outpatient services such as ER, ambulatory surgical centers, and hospital outpatient departments.
Who It’s Best For:
Coders working in outpatient hospital departments or ERs.
Prerequisites:
Similar to CPC; recommended to have some outpatient experience
4. Certified Inpatient Coder (CIC) – Offered by AAPC
The CIC focuses on inpatient facility coding and includes training in complex medical procedures, surgical coding, and ICD-10-PCS usage.
Who It’s Best For:
Coders aiming for careers in hospitals and acute care facilities.
Prerequisites:
Advanced knowledge of anatomy, physiology, and inpatient coding systems
5. Certified Risk Adjustment Coder (CRC) – Offered by AAPC
This certification focuses on risk adjustment models, such as those used in Medicare Advantage programs. It’s ideal for coders interested in the financial side of coding and data analytics.
Who It’s Best For:
Coders working with risk adjustment data, chronic conditions, or Medicare plans.
Prerequisites:
Understanding of ICD-10-CM and chronic condition coding
How to Choose the Right Certification
1. Evaluate Your Work Environment
Are you working in a hospital, clinic, or outpatient center? Choose a certification aligned with your current or desired work setting.
2. Consider Your Experience Level
If you're newer to coding, the CPC might be a great start. For those already coding in an inpatient setting, the CCS or CIC may be more appropriate.
3. Look at Your Career Goals
Do you want to specialize in auditing, compliance, or analytics? Certifications like CRC or even additional credentials in healthcare compliance could give you a competitive edge.
4. Check Employer Requirements
Different healthcare organizations prefer different certifications. It's always helpful to check job listings in your area to see what certifications employers value most.
Maintaining Your Certification
Getting certified is only half the journey. Most coding certifications require continuing education units (CEUs) to remain valid. This ensures coders stay up to date with:
Annual code updates
New regulations
Technological advancements in medical billing
Regular learning not only keeps your certification active but also makes you more valuable to employers.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
-
While it’s possible to get an entry-level job without certification, most employers prefer or require certification, especially for advanced roles.
-
Certifications like CCS, CIC, and CRC are typically associated with higher salaries due to their specialized focus.
-
On average, it takes 3–6 months of preparation, depending on your prior experience and study schedule.
-
Yes! Many advanced coders pursue multiple certifications to expand their knowledge and career options.
-
Yes, many reputable organizations, including AMBCI, offer online training and certification preparation.
5 Lesser-Known Facts About Coding Certifications
1. CCS Is Recognized Globally
The Certified Coding Specialist (CCS) credential by AHIMA is highly regarded by international employers, especially in hospital settings. AHIMA certifications are considered the gold standard in health information management and medical coding.
2. CPC-A vs. CPC
New coders who pass the Certified Professional Coder (CPC) exam receive the CPC-A (Apprentice) designation until they gain professional experience. The "A" is removed after fulfilling specific experience requirements.MedCerts+1Ultimate Medical Academy+1AAPC
3. You Can Specialize Further
Beyond basic certifications, coders can specialize in areas like cardiology, radiology, dermatology, and more through niche certifications. These specialty certifications validate expertise in specific medical fields.
4. CEUs Are Industry Gold
Continuing Education Units (CEUs) are essential for maintaining your credential and staying competitive in the medical coding field. They ensure coders remain updated with industry changes and enhance their skills.MarTech Munch
5. Some Employers Sponsor Exams
Many healthcare employers cover the cost of certification exams and training, especially if you commit to working with them. This support can include paying for study materials, memberships, and even higher education.Reddit
Conclusion: Get Certified with AMBCI
At AMBCI, we believe that the right certification can open doors to rewarding opportunities in medical coding and billing. Our advanced medical coding programs are built for real-world success, designed by experts, and aligned with industry standards. Whether you're eyeing the CPC, CCS, or a more specialized credential, we’ve got the course for you.
We offer flexible online certification programs in medical coding and billing to help you build a successful career—whether you're a newcomer or a working professional looking to upskill.
Join AMBCI today and take your career in medical coding to the next level!