Apprentice/Associate Level Certification through AHIMA or AAPC
Comparing Apprentice Associate Level Certification through AHIMA or AAPC: Which to Choose?
Deciding between an apprentice associate level certification through AAPC and AHIMA can significantly impact your career in medical coding. This article will compare these certifications to help you choose the one that fits your career goals, whether you aim to work in outpatient or inpatient settings.
Key Takeaways
AHIMA’s CCA certification is tailored for inpatient coding, while AAPC’s CPC-A is focused on outpatient coding, guiding candidates based on their desired work environment.
Both certifications offer unique career paths, with AHIMA preferred in hospital settings and AAPC in outpatient clinics, impacting job opportunities, salary potential, and the value of a medical coding certification.
Certification preparation involves financial planning and comprehensive study programs, with varying exam structures and costs influencing candidate decisions.
Comparing Apprentice Associate Level Certification through AHIMA or AAPC: Which to Choose?
Medical coding professionals seeking to enhance their career opportunities can acquire certifications from two leading bodies in the field, AHIMA and AAPC. These organizations not only provide professional certification, but also offer relevant educational resources. Established over a century ago, in 1928, AHIMA specializes in health information management and focuses on providing certifications tailored for inpatient coding roles. In contrast, founded 60 years later in 1988, AAPC prioritizes outpatient coding with particular emphasis on its Certified Professional Coder designation.
The distinctions between these certifying bodies are significant due to their specialization areas: healthcare employers often prefer candidates with AHIMA’s credentials for hospital-based positions that require expertise in managing patient records and overseeing compliance within an acute care context. Conversely, AAPC’s certifications cater more towards individuals pursuing careers at outpatient facilities like clinics or physician’s offices where billing accuracy is paramount. AAPC also offers multiple certifications, allowing professionals to specialize in various areas of medical coding.
Grasping both the historical significance and specialties of these institutions plays a crucial role when selecting which pathway might best suit one’s professional goals. While AHIMA has cemented its position as an authority on comprehensive health information management since nearly the inception of medical recordkeeping itself. Meanwhile, AAPC provides robust support for those focusing predominantly on outpatient settings—making each institution indispensable based upon individual career objectives within the domain of medical coding.
Introduction
The health care industry provides a plethora of career opportunities, and making a choice between AHIMA and AAPC certifications can pose quite the dilemma due to the broad spectrum they cover. This decision is largely influenced by one’s personal career objectives along with the preference for specializing in either outpatient or inpatient coding scenarios.
Each specific certification brings with it its own advantages, equipping a medical coder with tailored skills needed for distinct positions within the realm of medical coding. For example, while AHIMA offers the Certified Coding Associate (CCA) focusing on broader aspects of medical coding, AAPC provides individuals with an opportunity to become a Certified Professional Coder-Apprentice (CPC-A), honing their expertise primarily towards ambulatory settings as well as hospitals and different healthcare entities.
Understanding these multifaceted certifications, including what areas they target, how their exams are structured, and what professional pathways they open up, is crucial when discerning which path aligns most closely with your vocational aspirations. Through this blog post, we aim to elucidate these key distinctions aiding you in selecting a certification that best matches your future ambitions in certified coding.
Understanding Entry-Level Medical Coding Certifications
Aspiring medical coders and medical billers can begin their journey with entry-level certifications, which serve as crucial building blocks for a successful career in the healthcare industry. Such credentials establish an essential base of knowledge and proficiency needed to thrive in medical coding and billing roles. Both AHIMA and AAPC provide these introductory level certifications that are tuned to different aspects of the healthcare sector.
Certifications like AHIMA’s Certified Coding Associate (CCA) or AAPC’s Certified Professional Coder (CPC) along with their Certified Professional Biller (CPB) recognition stand out among advanced qualifications within this field. These endorsements not only confirm your capabilities, but also bolster your marketability, allowing you to demonstrate your specialized knowledge effectively to prospective employers.
Whereas AHIMA zeroes in on health information management alongside inpatient coding, the focus for AAPC is predominantly on outpatient coding, offering specialty certificates tailored towards various niches within the coding domain. This provides professionals with options so they may select a certification path that best fits their specific aspirations within the healthcare workforce.
Overview of AHIMA and AAPC
The American Health Information Management Association (AHIMA) and the American Academy of Professional Coders (AAPC) are two prominent organizations in the healthcare industry that offer certifications for medical coders. Both organizations aim to promote excellence in health information management and medical coding, but they have distinct focuses and approaches.
AHIMA, established in 1928, primarily focuses on inpatient coding and health information management. It offers certifications that are highly regarded in hospital settings, where managing patient records and ensuring compliance with healthcare regulations are critical. AHIMA certifications, such as the Certified Coding Associate (CCA) and Certified Coding Specialist (CCS), are designed to equip professionals with the skills needed to excel in these environments.
On the other hand, AAPC, founded in 1988, is dedicated to outpatient coding. It provides certifications that are widely recognized in outpatient facilities, including clinics and physician’s offices. AAPC’s Certified Professional Coder (CPC) and Certified Outpatient Coder (COC) certifications focus on the accuracy of billing and coding in ambulatory settings. Understanding the differences between these two organizations is essential for aspiring medical coders to make informed career decisions and choose the certification that aligns with their career goals.
AHIMA's Certified Coding Associate (CCA)
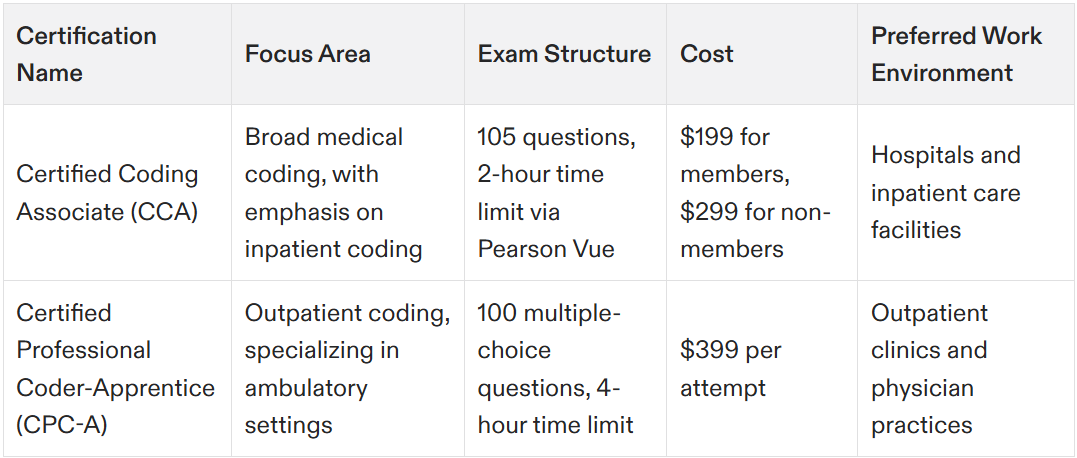
The AHIMA Certified Coding Associate (CCA) credential is tailored for individuals at the beginning of their medical coding career. It acts as a standard measure of competence in coding and enjoys recognition from employers across various healthcare realms.
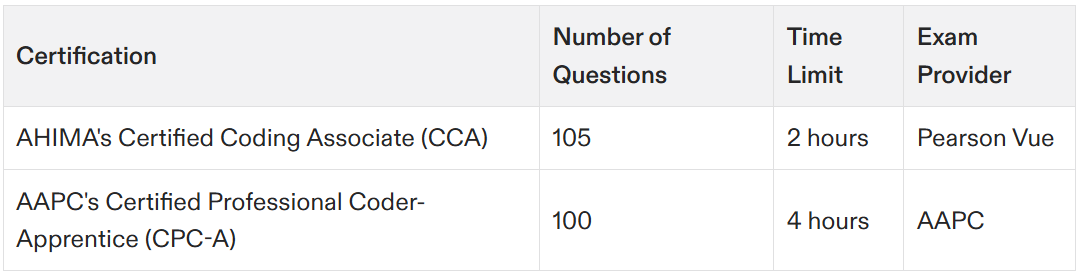
Comprising 105 questions—90 that contribute to the final score and 15 pretest questions—the CCA examination grants candidates two hours for completion, delivered through Pearson Vue’s computer-based test centers. Achieving certification necessitates attaining a minimum score of 300, reflecting the exam’s thorough assessment of an individual’s expertise in coding practices and knowledge.
Those preparing to take on the CCA exam engage with fundamental topics such as clinical classification systems and methods pertaining to reimbursement. The extensive nature of this preparation confirms that certified professionals possess robust capabilities, positioning them effectively for addressing complex medical coding tasks within any health service setting. Achieving the CCA certification can also open doors to advanced roles such as a coding manager, providing greater responsibilities and higher salaries.
AAPC's Certified Professional Coder-Apprentice (CPC-A)
An entry-level credential that is recognized for its prestige within the field of medical coding is the Certified Professional Coder-Apprentice (CPC-A) certification, awarded by AAPC. This particular credential is ideal for individuals aiming to concentrate on outpatient coding.
The CPC-A examination involves a comprehensive 4-hour test with 100 multiple-choice questions aimed at evaluating an examinee’s proficiency and understanding in the domain of medical coding. With each attempt priced at $399, pursuing this certification represents a significant investment towards one’s professional development. AAPC also offers advanced certifications in specialized areas such as cardiology and anesthesia, further enhancing career opportunities.
With AAPC certifications extending across various specialized areas such as cardiology, anesthesia, and oncology coding among others, professionals have the opportunity to adapt their knowledge and skillset to cater specifically to different branches of medicine. Such specialization can significantly boost career advancement opportunities for those who are certified.
Key Differences Between AHIMA and AAPC Certifications
AHIMA and AAPC certifications have distinct differences in terms of their focus, requirements, and benefits. AHIMA certifications, such as the Certified Coding Specialist (CCS) and Certified Coding Associate (CCA), are geared towards inpatient coding and require a strong foundation in health information management. These certifications are often preferred by hospitals and healthcare systems, where comprehensive knowledge of patient records and compliance is crucial.
In contrast, AAPC certifications, such as the Certified Professional Coder (CPC) and Certified Outpatient Coder (COC), are focused on outpatient coding. These certifications require expertise in medical coding guidelines and regulations specific to ambulatory care settings. AAPC certifications are highly valued in physician practices and outpatient facilities, where accurate billing and coding are essential for financial operations.
Additionally, the requirements for obtaining these certifications differ. AHIMA certifications typically require a combination of education and experience in health information management, while AAPC certifications emphasize practical knowledge of medical coding and billing. Understanding these key differences can help aspiring medical coders choose the certification that best fits their career aspirations and the type of healthcare environment they wish to work in.
AHIMA Certification Requirements
To become certified through AHIMA, medical coders must meet specific requirements, including education, experience, and examination. AHIMA offers various certifications, such as the CCA, CCS, and Certified Coding Specialist-Physician-based (CCS-P), each with its own set of requirements.
For example, the CCA certification requires a high school diploma and completion of a coding course. This certification is ideal for individuals at the beginning of their medical coding career, providing a solid foundation in coding practices. On the other hand, the CCS certification is more advanced, requiring a bachelor’s degree and two years of coding experience. This certification is designed for professionals who have a deeper understanding of coding and health information management.
All AHIMA certifications require passing a certification exam, which tests a coder’s knowledge and skills in medical coding, health information management, and data analysis. The exams are rigorous and comprehensive, ensuring that certified professionals are well-prepared to handle complex coding tasks in various healthcare settings. By meeting these requirements, medical coders can demonstrate their expertise and commitment to excellence in the field.
Comparing CCA and CPC-A
When evaluating the distinctions between CCA and CPC-A medical coding certification, it’s clear that there are several notable differences. The fee for undertaking the CCA certification exam is set at $199 for those with membership status and increases to $299 for individuals without membership. In contrast, each attempt at the CPC certification exam comes with a cost of $399. Such variation in price can significantly influence the decision-making process of prospective candidates.
These exams differ markedly in their structure. While candidates are given four hours to navigate through 100 multiple-choice questions on the CPC exam, they must tackle 105 questions within a span of just two hours when sitting for the CCA certification test. These contrasting testing formats underscore how AHIMA and AAPC assess coding skills using different methodologies.
Preferences among employers based on certifications also play a role—hospitals typically lean towards professionals holding AHIMA’s credentials whereas outpatient settings often look more favorably upon those with AAPC-certified training under their belts. This preference should steer aspirants toward selecting a certification pathway that best suits their anticipated career environment.
Exam Preparation and Resources
Undertaking rigorous study sessions is essential for those aspiring to become certified professional coders. It’s imperative that individuals are knowledgeable in areas like anatomy, pathophysiology, and medical terminology, which are fundamental components of the CPC exam. AAPC provides multiple certifications, allowing candidates to choose from a variety of specialized areas in medical coding.
As part of preparing for the certification exam, it’s equally critical to consider financial readiness. The combined cost for one attempt at both AAPC exams is $798. Hence candidates must strategically manage their finances as they navigate through the certification journey. Institutions such as the Advanced Medical Billing and Coding Institute (AMBCI) alleviate this burden by offering payment schemes starting from a modest $189 per month to support prospective coders.
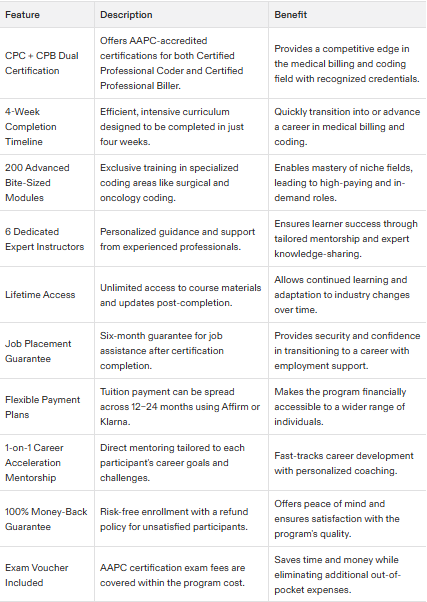
Completable within four weeks, AMBCI presents an extensive program featuring over 200 advanced modules designed with intensive training strategies tailored for swift learning. With accreditation from AAPC under its belt, AMBCI aligns its curriculum with industry benchmarks while also bolstering student confidence by backing their educational pursuits with a solid 100% money-back guarantee should they not succeed.
Maintaining Certification through Continuing Education
Both AHIMA and AAPC require certified coders to complete continuing education (CE) units to maintain their certification. CE units can be earned through various formats, including courses, webinars, and workshops. These units are essential for staying current with industry developments, advancements, and changes in medical coding guidelines and regulations.
AHIMA requires certified coders to complete 20 hours of CE every two years. This ensures that professionals remain updated with the latest practices in health information management and inpatient coding. Similarly, AAPC requires 36 hours of CE every two years, focusing on outpatient coding and billing practices.
By completing CE units, certified coders can maintain their expertise, stay competitive in their field, and ensure continued recognition and credibility. Continuing education is a vital component of professional development, allowing coders to adapt to the evolving healthcare industry and maintain their certification status.
Career Paths with CCA and CPC-A
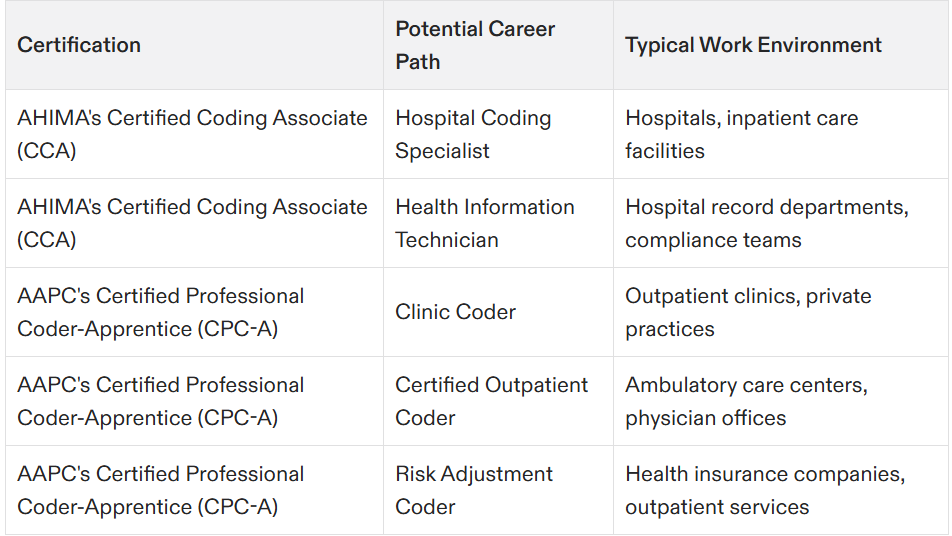
Securing a CCA or CPC-A medical coding certification can unlock numerous job opportunities within the healthcare industry. Certifications from AAPC are commonly sought after in outpatient environments such as clinics and private practices, whereas AHIMA certifications are typically preferred by hospital employers.
Individuals who have earned their CCA or CPC-A credentials often find employment in settings ranging from hospitals to insurance companies, fulfilling roles that may include clinic coder, risk adjustment coder, and certified outpatient coder. Professionals with these qualifications from either AAPC or AHIMA usually receive higher wages than those without certification.
As of 2023, professionals holding the CPC-A credential had an average hourly income of $29 while those possessing the CCA designation averaged at $22 per hour. These certifications offer substantial financial advantages and enhance employability significantly—making them an essential asset for advancing one’s career trajectory in this sector.
Choosing the Right Certification for Your Goals
Making an informed decision about which certification to pursue is vital and should be in line with your career ambitions and areas of interest. For those who are inclined towards working within outpatient settings, the CPC (Certified Professional Coder) certification provided by AAPC might be more appropriate, particularly if you already have some healthcare experience or relevant educational background.
Conversely, for individuals aspiring to secure a position within hospital surroundings, certifications offered by AHIMA could potentially serve as a better fit. It’s critical that you assess the specific job roles and designations that each certification targets. AAPC provides specialty certifications tailored for niche fields such as cardiology, offering Considerations based on your distinct career trajectory. AAPC also offers advanced certifications in specialized areas, providing further opportunities for career growth.
When determining whether to choose from among AACPC’s or AHIMA’s offerings, it will largely depend on your preference between outpatient versus inpatient care facilities employment opportunities. A thorough comprehension of what each certificate entails regarding professional objectives will guide you toward making a choice that best suits your intended path.
Benefits of Certification in Medical Coding
Securing a medical coding certification through organizations like AHIMA or AAPC can lead to significant career benefits, such as increased opportunities for advancement and greater attractiveness to potential employers. Holding a certification is seen as an indicator of dedication and professionalism within the field, which can significantly enhance one’s employment prospects.
Individuals who are certified in medical coding typically experience an easier path toward career progression. Certifications act as evidence of their knowledge and skills, making them more desirable to employers looking for qualified medical coders with verified expertise.
To uphold the CCA credential offered by these organizations, professionals must pursue continuing education units (CEUs) every year. This requirement ensures that they remain current with evolving industry standards and methodologies in the realm of medical coding.
Summary
To summarize, depending on your professional ambitions, both the AHIMA’s Certified Coding Associate (CCA) and AAPC’s Certified Professional Coder-Apprentice (CPC-A) medical coding certification offer unique benefits. For those interested in hospital-based inpatient coding roles, AHIMA certifications tend to be more sought after. Conversely, outpatient settings often prefer professionals with AAPC certifications.
The process of selecting an appropriate certification requires careful reflection upon your career objectives and the types of positions you desire as well as understanding the precise focus areas each certification caters to. Both sets of credentials hold considerable merit and can substantially bolster your chances within the job market.
Committing to a certified coding qualification represents not just an investment into one’s skillset, but also serves as leverage for better opportunities within the healthcare sector. Deliberate over what you wish to achieve professionally before deciding which pathway aligns most closely with your desired trajectory in this field.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the duration of the Advanced CPC + CPB certification program at AMBCI?
The Advanced CPC + CPB certification program at AMBCI is designed to be completed in just 4 weeks.
What type of accreditation does the Advanced Medical Billing and Coding Institute have?
The Advanced Medical Billing and Coding Institute is accredited by AAPC.
What is the starting payment plan for the AMBCI program?
The AMBCI program offers starting payment plans as low as $189 per month. This makes it an accessible option for many interested participants.
What guarantee does AMBCI offer for their program?
AMBCI provides participants with a guarantee of complete satisfaction, offering a full refund for their program.
How many advanced modules are included in the AMBCI program?
The AMBCI program includes over 200 advanced modules. This extensive range ensures comprehensive coverage of topics for participants.