Affordable Billing and Coding Classes Cost: What to Expect
If you're considering a career in medical billing and coding, understanding the cost of education is crucial. The price of these programs varies based on multiple factors, including the type of institution, program length, and additional expenses beyond tuition. This guide will help you understand what to expect when budgeting for medical billing and coding education in 2025.

Understanding Medical Billing and Coding Careers
Medical billing and coding professionals are vital to the healthcare industry. They ensure accurate processing of patient records and insurance claims, which directly affects the financial stability of healthcare providers. Obtaining a medical billing and coding certification through organizations like AMBCI ensures professionals have the necessary skills and knowledge to maintain high standards in this critical role.
Medical billing involves submitting claims to insurance companies to secure reimbursements for medical services. Meanwhile, medical coding assigns standardized codes to diagnoses, procedures, and treatments for accurate documentation and billing. With increasing healthcare regulations and a growing demand for precise medical records, the need for trained medical billers and coders continues to rise.
A career in this field is stable and rewarding, offering flexible work environments, including remote opportunities. Many professionals work in hospitals, private practices, insurance companies, and government healthcare agencies.
Cost of Billing and Coding Classes in 2025
The cost of a medical billing and coding program varies widely, depending on the institution and the type of program. In 2025, students can expect to pay:
Certificate Programs: $1,000 - $5,000 (6 months to 1 year)
Associate Degree in Medical Billing and Coding: $4,500 - $12,000 (2 years)
Bachelor’s Degree in Health Information Management (Optional): $10,000 - $30,000 (4 years)
The price range depends on factors such as the institution’s reputation, program length, and location. Online programs tend to be more affordable than in-person classes, and community colleges typically offer lower tuition than universities.

Additional Costs to Consider
Beyond tuition, students should factor in extra costs associated with their education. These include:
Textbooks & Study Materials: $200 - $600
Coding Software: $100 - $500
Certification Exam Fees: $300 - $500 per exam (CPC, CCS, etc.)
Professional Membership Fees: $100 - $200 annually (AAPC, AHIMA, etc.)
Lab Fees (for Hands-on Training Programs): $100 - $300
Budgeting for these additional expenses ensures that students are financially prepared for the full cost of their education.
Payment and Financial Aid Options
Medical billing and coding education can be expensive, but various payment options help make it more accessible:
Installment Plans – Many institutions offer flexible payment plans to break tuition into smaller monthly payments.
Scholarships & Grants – Organizations like AAPC and AHIMA provide scholarships for students entering the healthcare field.
Employer Tuition Reimbursement – Healthcare employers often cover tuition costs for employees who wish to advance their careers.
Federal Financial Aid – Students who qualify can apply for federal grants and student loans through FAFSA.
Workforce Development Programs – Government programs offer financial aid to individuals pursuing in-demand healthcare careers.
Exploring these options can significantly reduce the financial burden of education.

Certification and Career Growth
Obtaining a Certified Professional Coder (CPC) or Certified Coding Specialist (CCS) credential enhances job prospects and earning potential. Certification exams require thorough preparation, and passing them can lead to higher salaries and career advancement.
In 2025, certified medical coders earn an average salary of $60,000 - $75,000 per year, compared to non-certified professionals who typically earn $45,000 - $50,000 per year. Specialized certifications, such as Risk Adjustment Coding (CRC) or Inpatient Coding (CIC), can further increase earning potential.
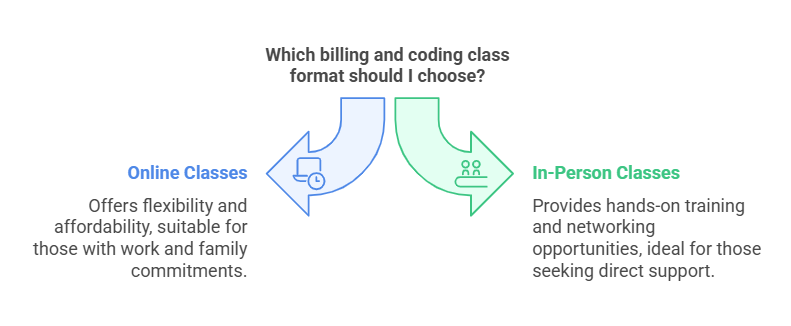
Online vs. In-Person Billing and Coding Classes
Choosing between online and in-person classes depends on individual learning preferences and circumstances.
Online Classes – More flexible and affordable, ideal for students balancing work and family responsibilities. Programs like those at Penn Foster, Ashworth College, and BMCC offer self-paced coursework.
In-Person Classes – Provide hands-on training, networking opportunities, and direct instructor support. Available at community colleges and universities.
Both options offer quality education, but students should consider their schedules, budgets, and preferred learning styles before enrolling.
Return on Investment (ROI): Is Medical Billing and Coding Education Worth It?
Medical billing and coding is a high-demand field with steady job growth. The Bureau of Labor Statistics projects a 9% increase in jobs by 2030, ensuring a stable career path.
Entry-level professionals can expect salaries ranging from $40,000 to $50,000, while experienced coders with advanced certifications can earn $75,000+ per year.
For those seeking job security, remote work options, and opportunities for career advancement, investing in medical billing and coding education is a worthwhile decision.
6 Less-Known Facts About Medical Billing and Coding
Not Just Hospitals: Medical coders work in various settings, including insurance companies, law firms, and government agencies.
No Degree Required: While degrees can be beneficial, many employers hire certified professionals with only a diploma or certification.
Global Demand: Medical coders are in demand worldwide, with opportunities for remote work across different countries.
AI and Automation Impact: While AI assists in billing processes, human coders remain essential for ensuring accuracy and compliance.
Specialized Fields Pay More: Niche certifications like Certified Inpatient Coder (CIC) or Certified Outpatient Coder (COC) lead to higher salaries.
Rapid Career Growth: With just 6-12 months of training, professionals can start working and earning competitive salaries.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
-
The total cost ranges from $3,000 to $7,000, depending on the program, certification fees, and additional expenses like textbooks and software.
-
Yes, students can apply for FAFSA, scholarships, employer reimbursement programs, and flexible payment plans to lower education costs.
-
Absolutely! Many reputable institutions offer fully online programs, allowing students to learn at their own pace while preparing for certification exams.
-
The field is growing steadily, with a 9% job growth projection, making it a recession-proof career with high demand.
-
No, a certification (like CPC or CCS) is sufficient for most entry-level jobs. However, an Associate or Bachelor’s Degree can lead to better opportunities and higher pay.
Conclusion
Medical billing and coding is a promising career choice with affordable education options, high job demand, and flexible work opportunities. While tuition varies, financial aid and scholarships can make it more accessible. Whether choosing an online or in-person program, students can expect a rewarding career with strong earning potential in the healthcare industry.
For those interested in becoming a Certified Professional Coder (CPC) or Certified Coding Specialist (CCS), investing in education now can lead to long-term career success.
