CBCS vs CPC: Which Medical Coding Certification Offers the Best Career Growth?
Choosing between CBCS and CPC for a career in medical coding can be a challenging decision. Both certifications play vital roles in the healthcare industry, but they target different skill sets and career paths. This article will help you understand the differences between the CBCS (Certified Billing and Coding Specialist) and CPC (Certified Professional Coder) certifications to help you make an informed decision on which one aligns best with your career goals and offers better growth opportunities.

Key Takeaways for CBCS vs CPC Certification Comparison
The CBCS certification is primarily for individuals starting their career in medical billing and coding certification, offering foundational skills in both billing and coding. On the other hand, the CPC certification is aimed at professionals with more experience who specialize in outpatient coding. CPC professionals earn higher average salaries compared to CBCS-certified individuals, with CPC salaries averaging around $59,605 annually, compared to $50,100 for CBCS professionals. Advanced certifications can also enhance career growth and earning potential, with CPC-certified professionals having access to specialized qualifications that lead to higher-paying opportunities. AMBCI provides comprehensive training and resources to help individuals obtain these valuable certifications.
Overview of CBCS and CPC Certifications
Both CBCS and CPC certifications hold significant value in the medical coding and billing industry. The CBCS is designed for entry-level professionals looking to gain foundational knowledge in coding and billing practices. The CPC, however, is meant for those specializing in outpatient coding and requires more experience in the field. Both certifications are highly respected, but each focuses on different areas of expertise in the healthcare sector.
The Certified Coding Associate (CCA) certification is another entry-level certification that prepares individuals for coding and billing positions within healthcare. While CBCS focuses on foundational skills for various healthcare settings, CPC targets outpatient coding, which is particularly relevant for those working in physician offices or outpatient care centers. Achieving either certification demonstrates a high level of proficiency, but the CPC certification offers more specialized knowledge and a broader scope in the healthcare industry.
What is CBCS?
The Certified Billing and Coding Specialist (CBCS) certification is aimed at individuals who are starting their careers in medical coding and billing. This certification verifies that the holder is proficient in both coding and billing tasks, which are crucial to ensuring healthcare providers are properly compensated for their services. The CBCS certification covers essential skills across different healthcare environments, helping individuals understand the revenue cycle and compliance guidelines necessary for efficient management in healthcare.
Obtaining the CBCS serves as an entry-level certification that showcases an individual's commitment to the field of medical billing and coding. It's ideal for those who are just beginning their careers in this industry, offering foundational knowledge in medical coding and billing practices.
What is CPC?
The Certified Professional Coder (CPC) certification signifies an advanced level of expertise in medical coding, particularly in outpatient coding. This certification demonstrates that the holder has a deep understanding of medical terminology, coding procedures, and the ability to apply appropriate codes to various clinical services, especially in outpatient settings like physician offices.
CPC-certified professionals are highly sought after in the healthcare industry due to their proficiency in ensuring accurate medical billing practices and maintaining precise medical records. The CPC certification, offered by the American Academy of Professional Coders (AAPC), is one of the most recognized credentials in the field and provides significant career advancement opportunities.
Eligibility Requirements for CBCS and CPC Certifications
To pursue either CBCS or CPC certification, individuals must meet certain educational and professional requirements. For both certifications, candidates must be at least 18 years old and possess a high school diploma or equivalent. However, the requirements for obtaining each certification differ.
CBCS Certification Prerequisites
The CBCS certification serves as an entry-level credential, so the prerequisites are minimal. Candidates need either a formal medical billing and coding education or at least one year of supervised professional experience in the field. Candidates who meet these criteria can sit for the CBCS exam, which serves as a gateway into the medical billing and coding profession.
CPC Certification Prerequisites
The CPC certification requires more experience compared to CBCS. To be eligible, candidates need a high school diploma, an active membership with AAPC, and some relevant experience or education. Those who lack two years of experience can take the CPC exam and, if they pass, will be granted the title Certified Professional Coder-Apprentice (CPC-A), marking their entry-level status.

Exam Structure and Content
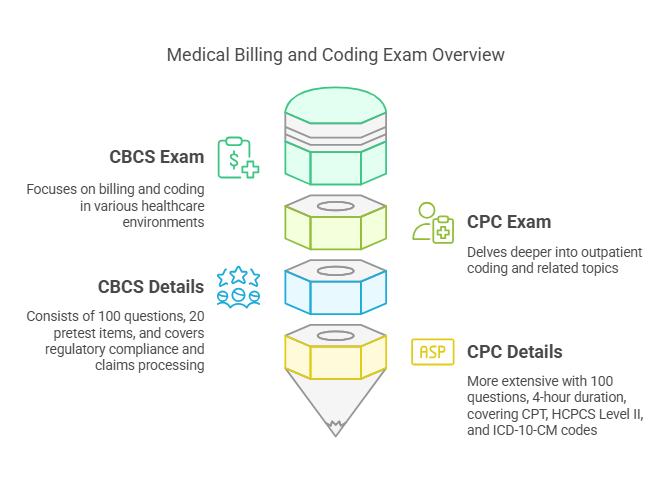
Both the CBCS and CPC exams assess an individual's understanding of medical billing and coding principles, but they differ in structure and content. The CBCS exam is more focused on billing and coding principles in a variety of healthcare environments, while the CPC exam delves deeper into outpatient coding and related topics.
CBCS Exam Details
The CBCS exam consists of 100 multiple-choice questions, along with an additional 20 pretest items, which candidates must complete within two hours. It covers topics such as regulatory compliance, claims processing, coding knowledge, and payment adjudication. Recommended study resources include coding manuals, online courses, and practice exams.
CPC Exam Details
The CPC exam is a more extensive exam that lasts for four hours. It consists of 100 multiple-choice questions, and candidates must score at least 70% to pass. The exam covers a wide range of coding topics, including CPT, HCPCS Level II, and ICD-10-CM codes, with a specific focus on outpatient care.
Career Opportunities and Salary Expectations
Certification in medical coding opens up a range of career opportunities, with both CBCS and CPC-certified professionals finding work in hospitals, clinics, insurance companies, and other healthcare settings.
Jobs for CBCS Holders
CBCS-certified professionals can pursue roles in medical billing, coding, and insurance claims processing across various healthcare environments. Common job titles include medical billing and coding specialist, insurance claims processor, and medical records coordinator.
Jobs for CPC Holders
CPC-certified professionals can secure positions in outpatient coding, including roles such as medical coding auditor, coding specialist, and compliance auditor. Many employers prefer hiring CPC-certified coders due to their expertise in outpatient care and ability to ensure accurate billing practices.
Salary Expectations
CPC-certified professionals earn a higher average salary compared to CBCS-certified professionals. On average, CPC-certified individuals make around $59,605 annually, while CBCS-certified professionals earn an average of $50,100 per year. These figures can vary depending on experience, location, and additional certifications.
Less Known Facts
CPC is highly regarded for outpatient coding:
The Certified Professional Coder (CPC) certification, offered by the American Academy of Professional Coders (AAPC), focuses on outpatient coding and is highly valued in physician-based settings. OnlineDegree.com+3Penn Foster+3Nurse.org+3
Advanced certifications can significantly increase salary potential:
Pursuing advanced certifications like Certified Coding Specialist (CCS) or Certified Professional Coder-Payer (CPC-P) can lead to higher salaries, with some professionals experiencing substantial pay increases. AAPC
CPC holders have more career advancement opportunities:
The CPC certification is widely respected and often leads to more job prospects and higher-level roles in medical coding and auditing.
CPC certification is more comprehensive:
While the Certified Billing and Coding Specialist (CBCS) certification is suitable for entry-level coders, the CPC covers a broader range of coding topics and is considered more advanced. AMBCI
CBCS is often the first step toward higher certifications:
Many professionals begin with the CBCS certification and later pursue advanced certifications like the CPC to enhance their expertise and career prospects.
CPC-certified professionals often work in both outpatient and inpatient settings:
Although the CPC focuses on outpatient coding, many professionals with this certification also work in inpatient settings, depending on their employer and the healthcare facility..
Frequently Asked Questions
-
To qualify for both the CBCS and CPC certifications, candidates must be at least 18 years old and possess a high school diploma or equivalent. CBCS has less stringent experience requirements, making it an entry-level option, while CPC requires more experience.
-
The CBCS exam focuses mainly on medical billing and coding basics, while the CPC exam covers a wider range of topics, with a strong emphasis on outpatient coding and medical record management.
-
CBCS-certified individuals can work in medical billing, coding, and insurance claims processing roles across various healthcare settings such as hospitals, clinics, and insurance companies.
-
The average annual salary for CPC-certified professionals is around $59,605, with potential for higher earnings depending on experience and additional certifications.
-
CPC holders can pursue advanced certifications such as the Certified Inpatient Coder (CIC) or Certified Outpatient Coder (COC) to increase their expertise and open up additional career opportunities.
