Understanding Certified Medical Assistant Exam Requirements: A Guide
Becoming a Certified Medical Assistant
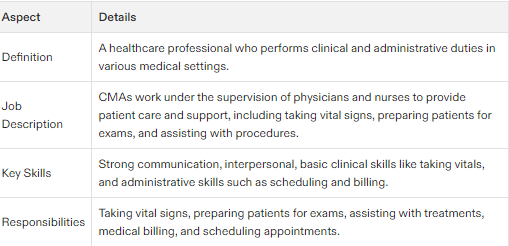
Definition and Job Description
A certified medical assistant (CMA) is a healthcare professional who performs clinical and administrative duties in medical offices, clinics, and other healthcare settings.
Medical assistants work under the supervision of physicians, nurses, and other healthcare professionals to provide patient care and support.
They are responsible for taking vital signs, preparing patients for exams, and assisting with treatment procedures. Obtaining a high school diploma or GED is a fundamental prerequisite for pursuing a career as a medical assistant.
Key Skills and Responsibilities
Medical assistants must have strong communication and interpersonal skills to work effectively with patients, families, and healthcare teams.
They must also have basic clinical skills, such as taking vital signs and preparing patients for exams.
Administrative duties, such as medical billing and scheduling appointments, are also important responsibilities.
Importance of Certification
Certification demonstrates a medical assistant’s expertise and commitment to their profession.
Many employers prefer to hire certified medical assistants, as it ensures they have the necessary skills and knowledge to perform their job duties effectively.
Ethical and Legal Considerations in Medical Assisting
As a medical assistant, it is essential to understand the ethical and legal considerations that govern the profession. Medical assistants must adhere to a code of ethics that prioritizes patient confidentiality, respect, and dignity. They must also be aware of the laws and regulations that govern medical practice, including HIPAA, OSHA, and state-specific laws.
Some key ethical considerations for medical assistants include:
Maintaining patient confidentiality and respecting patient autonomy
Providing culturally sensitive care and avoiding discrimination
Reporting any suspected abuse or neglect
Respecting patient boundaries and avoiding conflicts of interest
Maintaining accurate and complete medical records
In terms of legal considerations, medical assistants must be aware of their scope of practice and the laws that govern medical assisting in their state. They must also be familiar with the laws and regulations that govern medical billing, coding, and reimbursement.
Some key legal considerations for medical assistants include:
Understanding the laws and regulations that govern medical assisting in their state
Maintaining accurate and complete medical records
Reporting any suspected abuse or neglect
Respecting patient boundaries and avoiding conflicts of interest
Complying with HIPAA and OSHA regulations
By understanding the ethical and legal considerations that govern medical assisting, medical assistants can provide high-quality care while minimizing the risk of legal and ethical issues.
Education and Training
Medical Assisting Program Options
Medical assisting programs are available at community colleges, vocational schools, and online institutions.
Programs may lead to a certificate, diploma, or associate’s degree in medical assisting.
Certificate Program
Certificate programs in medical assisting typically take 9-12 months to complete.
They provide basic training in clinical and administrative duties, as well as medical terminology and anatomy.
Associate Degree Program
Associate degree programs in medical assisting, which are a form of medical assistant training, typically take 2 years to complete.
They provide more comprehensive training in clinical and administrative duties, as well as general education courses.
Continuing Education and Professional Development
As a medical assistant, it is essential to stay up-to-date with the latest developments in medical assisting and healthcare. Continuing education and professional development are critical for maintaining certification, staying current with industry developments, and providing high-quality patient care.
Some ways that medical assistants can engage in continuing education and professional development include:
Attending conferences and workshops
Participating in online courses and webinars
Joining professional organizations, such as the American Association of Medical Assistants (AAMA)
Reading industry publications and journals
Participating in peer review and quality improvement initiatives
By engaging in continuing education and professional development, medical assistants can:
Stay current with industry developments and advancements
Maintain certification and licensure
Enhance their skills and knowledge
Provide high-quality patient care
Advance their careers and increase their earning potential
Eligibility Criteria for Medical Assistant Certification
Education Requirements
To be eligible for certification, medical assistants must graduate from an accredited program, which is essential for taking the certification exam and obtaining certification in the medical assistant field.
Programs must be accredited by a recognized accrediting agency, such as the Commission on Accreditation of Allied Health Education Programs (CAAHEP).
Work Experience Requirements
Some certification exams require medical assistants to have a certain amount of work experience before they can take the exam.
This experience can be gained through internships, volunteer work, or paid employment.
Alternative Paths (Military, Instructor)
Military personnel and medical assisting instructors may be eligible for certification through alternative paths.
These paths may require additional education or training, but can provide a faster route to certification.
Certification Options
Certified Medical Assistant (CMA) Exam
The CMA exam is offered by the American Association of Medical Assistants (AAMA).
It is a comprehensive exam that tests medical assistants’ knowledge and skills in clinical and administrative duties.
Other Certification Options (CCMA, RMA)
The Certified Clinical Medical Assistant (CCMA) exam is offered by the National Healthcareer Association (NHA).
The Registered Medical Assistant (RMA) exam is offered by the American Medical Technologists (AMT).
These exams are also comprehensive and test medical assistants’ knowledge and skills in clinical and administrative duties.
Exam Preparation and Registration
Study Materials and Resources
Study materials and resources are available from the certifying organizations and other sources.
These materials can help medical assistants prepare for the exam and improve their chances of passing.
Application and Fee Submission
Medical assistants must submit an application and fee to take the certification exam.
The application and fee must be submitted to the certifying organization before the exam can be scheduled.
Scheduling the Exam
Once the application and fee have been submitted, medical assistants can schedule their exam.
Exams are typically scheduled through a testing center or online.
What to Expect on the Exam
Exam Format and Content
The certification exam is a multiple-choice exam that tests medical assistants’ knowledge and skills in clinical and administrative duties.
The exam format and content may vary depending on the certifying organization.
Question Types and Difficulty
The exam questions may be multiple-choice, true/false, or fill-in-the-blank.
The difficulty level of the questions may vary, but they are designed to test medical assistants’ knowledge and skills.
Time Limit and Scoring
The exam is typically timed, and medical assistants must complete it within the allotted time.
The exam is scored based on the number of correct answers, and a passing score is required for certification.
After the Exam
Results and Certification
Medical assistants will receive their exam results and certification status after the exam.
If they pass the exam, they will be awarded certification and can use the certified medical assistant (CMA) credential.
Retesting and Appeals
If medical assistants do not pass the exam, they can retest after a certain period of time.
They can also appeal their exam results if they believe there was an error in the scoring process.
Maintaining Certification
Certification must be maintained through continuing education and professional development.
Medical assistants must complete continuing education requirements and adhere to the certifying organization’s code of ethics to maintain their certification.
Career Opportunities and Job Settings
Common Work Settings for Medical Assistants
Medical assistants can work in a variety of settings, including medical offices, clinics, hospitals, and nursing homes.
They can also work in specialized settings, such as dermatology or cardiology clinics.
Job Outlook and Growth Prospects
The job outlook for medical assistants is excellent, with a high demand for certified medical assistants.
The Bureau of Labor Statistics predicts a 23% growth in employment opportunities for medical assistants through 2028.
Specialized Roles and Advancement Opportunities
Medical assistants can specialize in areas such as medical billing, medical coding, or medical transcription.
They can also advance to leadership roles, such as medical office manager or clinical coordinator.
Technological Skills and Tools in Medical Assisting
In today’s healthcare environment, technological proficiency is a crucial skill for medical assistants. Familiarity with various tools and software used in medical offices and healthcare facilities can significantly enhance patient care and operational efficiency.
Some key technological skills and tools for medical assistants include:
Electronic health records (EHRs) and practice management systems (PMS)
Medical billing and coding software
Telehealth platforms and virtual communication tools
Medical imaging and diagnostic equipment
Point-of-care testing and laboratory equipment
By mastering these technological tools, medical assistants can:
Enhance patient care and safety
Improve communication and collaboration with healthcare providers
Increase efficiency and productivity
Reduce errors and improve accuracy
Stay current with industry developments and advancements
Benefits of Medical Assistant Certification
Career Advancement Opportunities
Certification can provide medical assistants with career advancement opportunities, such as promotions or higher salaries.
It can also provide them with specialized roles, such as medical billing or medical coding.
Increased Earning Potential
Certified medical assistants can earn higher salaries than non-certified medical assistants.
According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, the median annual salary for medical assistants is $34,800, but certified medical assistants can earn up to $50,000 or more per year.
Enhanced Job Security
Certification can provide medical assistants with enhanced job security, as it demonstrates their expertise and commitment to their profession.
It can also provide them with a competitive edge in the job market, as many employers prefer to hire certified medical assistants.
Impact of Certification on Patient Care Quality
Certification as a medical assistant can have a significant impact on patient care quality. Certified medical assistants have demonstrated a higher level of knowledge, skills, and competence in medical assisting, which can lead to:
Improved patient outcomes and satisfaction
Enhanced patient safety and reduced risk of errors
Increased efficiency and productivity in medical offices and healthcare facilities
Better communication and collaboration with healthcare providers
Greater confidence and trust in medical assistants among patients and healthcare providers
By hiring certified medical assistants, healthcare providers can:
Improve patient care quality and outcomes
Enhance patient safety and reduce risk of errors
Increase efficiency and productivity
Improve communication and collaboration with patients and healthcare providers
Demonstrate a commitment to excellence and quality in patient care
Conclusion
Summary of Key Points
Medical assistant certification is a valuable credential that demonstrates a medical assistant’s expertise and commitment to their profession.
It can provide career advancement opportunities, increased earning potential, and enhanced job security.
Medical assistants can prepare for the certification exam by studying and using resources from the certifying organizations.
Final Tips and Recommendations
Medical assistants should research the certifying organizations and their certification exams to determine which one is best for them.
They should also prepare thoroughly for the exam by studying and using resources from the certifying organizations.
Certification can provide medical assistants with a competitive edge in the job market and enhance their career prospects.