Essential Continuing Education for Medical Coders: Boost Your Career
Understanding Medical Coding CEUs
What are Medical Coding CEUs?
Medical Coding CEUs (Continuing Education Units) are required for medical coders to maintain their certification and stay up-to-date with the latest coding guidelines and regulations.
CEUs demonstrate a coder’s commitment to ongoing education and professional development.
Medical coding CEUs are essential for career advancement and specialization in the field.
Types of Medical Coding CEUs
Pre-approved CEUs are offered by organizations such as AAPC and AHIMA.
CEUs can be earned through online courses, webinars, in-person seminars, and publications. Upon course completion, learners may receive vouchers for certification exams, emphasizing the importance of completing the coursework to advance in their professional certification journey.
Medical coding CEUs can be submitted through the AAPC website, and CEU requirements are clearly outlined for easy tracking and reporting.
Medical Billing and Coding Career Overview
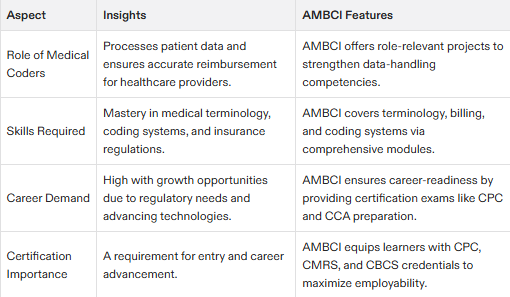
What is Medical Billing and Coding?
Medical billing and coding involves processing patient data, including medical records and insurance claims.
Medical billers and coders play a crucial role in ensuring healthcare providers are quickly and accurately paid for patient treatment.
Medical billing and coding requires a strong understanding of medical terminology, coding systems, and health insurance regulations.
Career Requirements and Outlook
Entry-level positions in medical billing and coding typically require a certificate or associate degree.
Medical billing and coding professionals must understand HIPAA and maintain certification through ongoing education.
The demand for medical billers and coders is high, with job prospects expected to grow in the coming years.
Medical Terminology Fundamentals
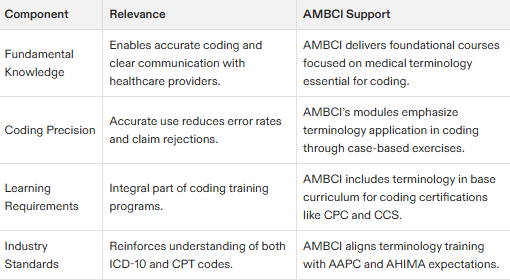
Importance of Medical Terminology
Medical terminology is essential for accurate coding and billing.
Understanding medical terminology is critical for effective communication between healthcare providers and medical billers and coders.
Medical terminology is a fundamental component of medical billing and coding education.
Certification and Continuing Education
Certification Exams (CPC, CCA, and CBCS)
Certification exams, such as the CPC, CCA, and CBCS, demonstrate competencies in medical billing and coding.
Certification is valuable for career goals and provides confidence in making informed decisions.
Certification exams are offered by organizations such as AAPC and AHIMA.
Benefits of Certification and Continuing Education
Certification and continuing education enhance career prospects and advancement opportunities.
Certification demonstrates a commitment to ongoing education and professional development. Course completion is a key milestone that can provide significant materials and benefits, such as vouchers for certification exams.
Continuing education helps medical coders stay current with changing regulations and coding guidelines.
Career Advancement and Specialization
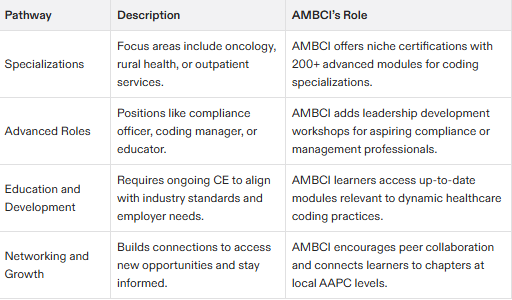
Specializing in Medical Coding
Specializing in medical coding can lead to career advancement opportunities and increased earning potential.
Medical coders can specialize in areas such as physician practices, rural health clinics, or medical facilities.
Specialization requires ongoing education and training in specific areas of medical coding.
Career Advancement Opportunities
Career advancement opportunities in medical billing and coding include leadership roles, consulting, and education.
Experienced medical coders can move into roles such as coding manager or compliance officer.
Career advancement requires ongoing education, certification, and professional development.
Conclusion
Summary of Key Points
Medical billing and coding is a high-demand occupation in the healthcare field, with a wide range of job opportunities available in various industries, including medical facilities, health insurance companies, and physician practices. To become a medical biller and coder, one typically needs to complete a certificate or associate degree program in medical billing and coding, and pass a certification exam, such as the CPC, CCA, or CBCS. Medical coders translate patient care into current procedural terminology (CPT) codes, while medical billers create a claim based on the codes provided by the medical coder. Many professionals in this area do both medical billing and medical coding.
Medical billing and coding professionals must understand the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) and stay current with industry developments through continuing education, including medical coding CEUs. The American Academy of Professional Coders (AAPC) and the American Health Information Management Association (AHIMA) have specific CEU requirements for their certifications. Medical coding CEUs can be obtained through various formats, including online courses, in-person seminars, and self-study materials.
To maintain certification and licensure, medical coding professionals must submit their CEUs to the AAPC or other certifying organizations. The Medicare Learning Network (MLN) offers pre-approved CEUs for medical coders, and the American Medical Billing Association (AMBA) requires completion of 15 continuing education units (CEUs) annually to maintain CMRS certification. By staying current with industry developments and meeting CEU requirements, medical billing and coding professionals can advance their career goals and maintain their hard-earned credentials.