Understanding the Cost of Medical Coding Certification
Medical coding is a crucial aspect of the healthcare industry, and obtaining certification in this field can lead to rewarding job opportunities. However, like many professional certifications, the cost of medical coding certification can vary significantly depending on several factors, including the type of institution you choose, whether the program is online or in-person, and additional costs like study materials and exam fees. In this article, we will break down these expenses to help you understand what to expect when budgeting for medical coding certification in 2025.

Key Takeaways on Medical Coding Certification Costs
The primary costs associated with obtaining a medical billing and coding certification are tuition fees, study materials, and exam fees. These costs can vary based on the institution offering the program, with online programs generally being more affordable than in-person options. Financial aid, such as scholarships and federal financial assistance, can also help ease the financial burden of pursuing a medical billing and coding certification. Organizations like AMBCI provide certification programs that can enhance career opportunities in the medical billing and coding field.
Breakdown of Medical Coding Certification Costs
To embark on a career as a medical coder, it’s essential to understand the total financial investment required. The cost of certification is typically broken down into three main categories: tuition fees, study materials, and exam fees. The total cost can vary based on where and how you pursue your education, so it's important to evaluate each of these components carefully.
Medical coders play a vital role in the healthcare system by ensuring accurate coding of services provided, which helps maximize reimbursements for healthcare facilities. Therefore, understanding the costs involved in becoming a certified medical coder is crucial for effective financial planning.
Tuition Fees
The cost of tuition for medical coding certification programs can vary widely depending on the institution. Generally, online programs tend to be more affordable than traditional in-person programs due to lower overhead costs. It's important to verify the most up-to-date tuition rates, as these can change from year to year.
Full-time medical coding programs typically span around 38 weeks, with students expected to dedicate at least 24 hours per week to their studies. Some online programs may include the cost of certification exams, such as the Certified Professional Coder (CPC) or Certified Billing and Coding Specialist (CBCS) exams, in the tuition fees. However, tuition usually does not cover additional costs like textbooks, software, and other materials, so it’s essential to budget for these extra expenses.
Study Materials
In addition to tuition, students should budget for study materials, including textbooks, coding software, and other resources necessary for understanding medical terminology and coding procedures. Online students may also need to invest in reliable technology, such as a computer and internet connection. These costs can range from $6 to $114 per credit hour, depending on the program.
Study materials are critical for passing certification exams, and many programs offer access to these resources as part of the tuition package. However, it's important to factor in any additional expenses for software, textbooks, and other tools that may not be included in the program.
Exam Fees
One of the most significant expenses associated with medical coding certification is the exam fee. Non-members of professional organizations like the AAPC (American Academy of Professional Coders) may face fees of around $711.85 for the CPC certification exam. However, members of these organizations often pay reduced fees, with the cost dropping to about $499. Joining professional associations not only lowers exam fees but also provides additional resources and networking opportunities that can be beneficial for career advancement.
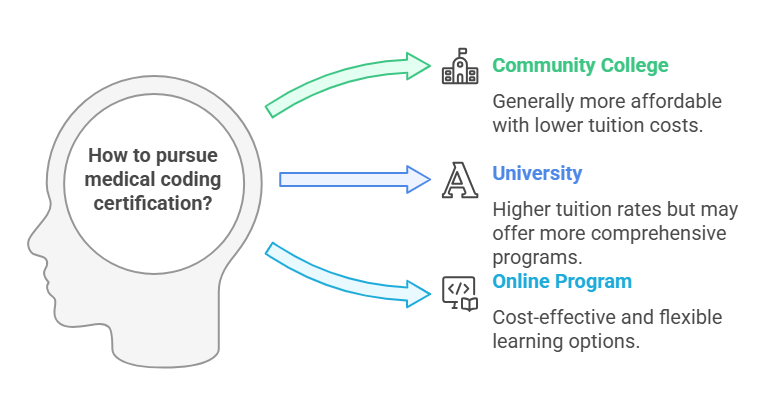
Comparing Costs Across Institutions
The costs of medical coding certification programs can vary significantly depending on whether you choose a community college, university, or an online program. Community colleges are often more affordable, with programs typically costing around $4,192 for tuition and fees. Universities may have higher tuition rates, and it’s essential to evaluate the costs of both community colleges and universities before making a decision.
Online programs tend to be less expensive than in-person programs due to reduced operational costs. These programs also offer greater flexibility, allowing students to learn at their own pace. However, when choosing between online and in-person programs, it's important to consider the learning style that best suits your needs and career goals.
Financial Aid Options for Medical Coding Students
Various financial aid options are available to help students cover the costs of medical coding certification. Scholarships, federal financial aid, and payment plans are some of the ways students can manage their expenses.
Scholarships
Scholarships are an excellent way to reduce the financial burden of obtaining a medical coding certification. Numerous scholarships are available at both national and regional levels, with funding typically awarded based on factors like academic achievement, financial need, and demographic criteria. It's important to actively research and apply for these scholarships to help cover the costs of tuition and study materials.
Federal Financial Aid
Students pursuing medical coding certification may also be eligible for federal financial aid through grants, loans, and work-study programs. To determine eligibility, students must fill out the Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA). Federal financial aid can help students pay for tuition, study materials, and other educational expenses, making medical coding certification more accessible.
Payment Plans
Many educational institutions offer payment plans that allow students to pay for their medical coding programs in installments. This can help alleviate the financial strain by spreading tuition costs over several months, making the program more affordable for a broader range of students.
Additional Costs to Consider
In addition to tuition, study materials, and exam fees, there are other costs associated with medical coding certification that students should be aware of.
Membership Fees
Joining professional organizations like the AAPC often requires paying annual membership fees. These fees can range up to $210 per year, depending on the organization. Membership provides benefits such as access to networking opportunities, study resources, and discounts on exam fees.
Continuing Education
To maintain certification, medical coders must engage in continuing education. This can include additional courses, seminars, and workshops, which may come with extra fees. Staying up-to-date with the latest coding practices and regulations is essential for maintaining certification.
Miscellaneous Costs
Students should also consider other incidental expenses, such as transportation costs, administrative fees, and fees for technology use. These costs can add up, so it's important to budget for them as part of your overall educational expenses.
Return on Investment (ROI) for Medical Coding Certification
Despite the upfront costs of obtaining certification, the return on investment for medical coding certification is substantial. Certified medical coders typically earn higher salaries and have more job opportunities than their non-certified counterparts. According to recent data, certified medical coders earn an average salary of $58,895 annually, compared to $45,035 for non-certified coders.
The demand for medical coders is expected to grow by 9% by 2033, driven by an aging population and advancements in healthcare technology. This growth in demand makes medical coding certification a valuable investment for those looking to secure a stable and rewarding career.

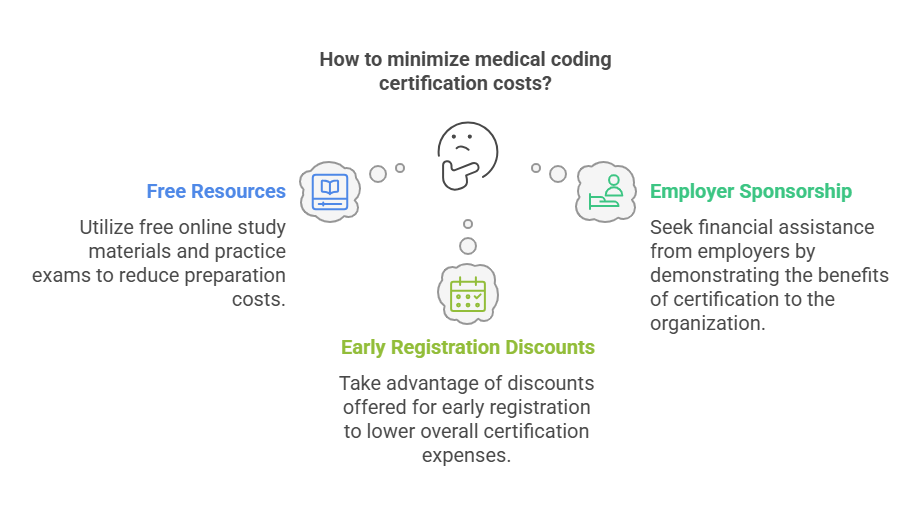
Tips to Minimize Certification Costs
There are several strategies you can use to reduce the costs associated with medical coding certification:
Utilize Free Resources: Many online resources offer free study materials and practice exams. These can help reduce the cost of preparing for the certification exam.
Seek Employer Sponsorship: Some employers offer financial assistance for certification programs, viewing it as an investment in employee skills. Presenting a compelling case for how certification will benefit the organization can increase your chances of securing employer sponsorship.
Take Advantage of Early Registration Discounts: Many institutions offer discounts for students who register for courses and exams early. Taking advantage of these discounts can help reduce overall costs.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
-
The main costs include tuition, exam fees, study materials, membership dues, and other incidental expenses like technology and commuting.
-
Yes, many scholarships are available for medical coding students, often based on academic achievement, financial need, or specific demographic criteria.
-
You can reduce costs by utilizing free resources, seeking employer sponsorship, and taking advantage of early registration discounts.
-
Certified medical coders earn higher salaries and have better job opportunities than non-certified coders, making certification a valuable investment.
-
The demand for medical coders is projected to grow by 9% by 2033, indicating strong job prospects in the field.
6 Less-Known Facts About Medical Coding Certification
Medical coders can specialize: Medical coding certifications offer various specialties, such as inpatient coding, outpatient coding, and oncology coding, which can lead to higher-paying opportunities.
The American Academy of Professional Coders (AAPC) offers specialty certifications, including Certified Ambulatory Surgery Center Coder (CASCC)™ and Certified Evaluation and Management Coder (CEMC)™. AAPC
Specializing in areas like radiology, oncology, or emergency department coding can potentially lead to higher salaries. Penn Foster
Certification maintenance is required: Certification holders must complete continuing education courses regularly to maintain their credentials.
The AAPC requires certified professionals to earn and submit Continuing Education Units (CEUs) within a two-year renewal period to maintain their certifications. AAPC+2AAPC+2ahima.org+2
The American Health Information Management Association (AHIMA) also mandates earning a specified number of CEUs during a two-year certification cycle for recertification. ahima.org
Coding systems vary by region: Different countries use distinct coding systems, such as ICD-10 in the U.S. and ICD-11 in other parts of the world.
The World Health Organization (WHO) introduced ICD-11 to replace ICD-10, with implementation beginning on January 1, 2022. Countries can continue using ICD-10 but are encouraged to adopt ICD-11 promptly. World Health Organization (WHO)
As of October 2024, 35 countries are actively using ICD-11, with 64 countries in various stages of implementation. Better Health+1World Health Organization (WHO)+1
Job flexibility: Many medical coders work remotely, offering greater work-life balance and flexibility.
Remote medical coding positions are available, providing flexibility in work hours and location. Reddit+5Indeed+5AAPC+5
Working remotely as a medical coder offers benefits such as flexibility, cost savings, and increased productivity. Coding Clarified
Coding impacts healthcare outcomes: Accurate coding ensures proper reimbursement for healthcare services and helps healthcare facilities maintain financial stability.
Accurate medical coding leads to clean claims, prompt reimbursements, and a positive bottom line for healthcare facilities. RCCS
Proper coding reduces claim denials and rejections, improving cash flow and financial stability. lutz.us+1medicalhealthcaresolutions.com+1
Medical coders work across industries: Beyond hospitals, medical coders are employed in insurance companies, law firms, and government agencies, broadening career opportunities.
Insurance companies hire medical coders to review claims for accuracy and determine coverage. Brundage Group+5Gwinnett College+5Goodwin University+5
Law firms employ medical coders to examine records for billing irregularities, assisting in identifying potential fraud. Home
Government agencies at state and federal levels hire medical coders for administrative duties, including summarizing claims information and auditing.
Understanding the cost and requirements of medical coding certification helps prospective coders prepare financially and set realistic goals for their educational journey. With proper planning and the right resources, achieving certification in medical coding is both an attainable and rewarding career move.
