Understanding Eligibility for Medical Coding Course: A Complete Guide
Medical coding is the process of assigning standardized codes to diagnoses, procedures, and services to ensure accurate billing and record-keeping. Medical coders use medical terminology and coding systems to translate patient information into standardized codes. One of the key coding systems is the Current Procedural Terminology (CPT), which is essential for ensuring accurate billing and reimbursement.

Medical coding plays a crucial role in the healthcare industry by organizing patient data using precise medical codes. These codes help streamline medical records, making it easier for healthcare providers and insurance companies to track treatments, process claims, and maintain efficient healthcare services.
Benefits of a Career in Medical Coding
A career in medical coding offers competitive salaries, job security, and flexibility. The field is rapidly growing, with increasing job prospects due to the expanding healthcare industry. Medical billing and coding certification through AMBCI can provide the qualifications needed to excel in this field. Medical coders can work in various settings, including hospitals, clinics, insurance companies, and remote positions. Additionally, medical coding is a great option for individuals looking for a stable career with the opportunity to work from home.
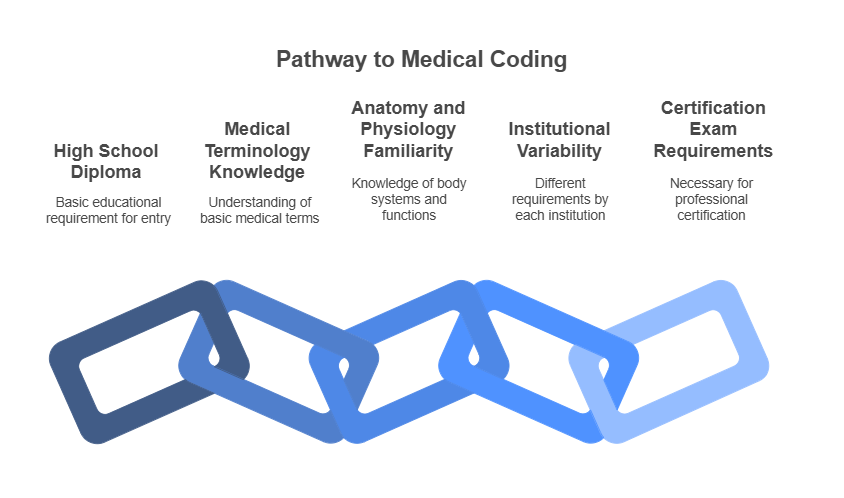
Eligibility Requirements for a Medical Coding Course
Most medical coding programs require a high school diploma or equivalent. While no prior experience in healthcare is necessary, having a basic understanding of medical terminology can be beneficial. Some courses may have additional prerequisites, such as familiarity with anatomy and physiology, which helps in understanding medical codes.
The eligibility criteria for medical coding courses vary by institution. It's also important to check the requirements for certification exams, as passing these exams is necessary to work professionally as a medical coder.
Medical Coding Course Curriculum
Medical coding courses cover a broad range of topics, including:
Medical coding principles
Anatomy and physiology
Medical terminology
Billing procedures
Healthcare compliance and ethics
ICD (International Classification of Diseases) and CPT coding systems
Understanding medical procedures is crucial in medical coding, as it ensures accurate coding for claim processing and reimbursement in the healthcare system.
Types of Medical Coding Certifications
Several certifications are available for medical coders, each providing different career opportunities:
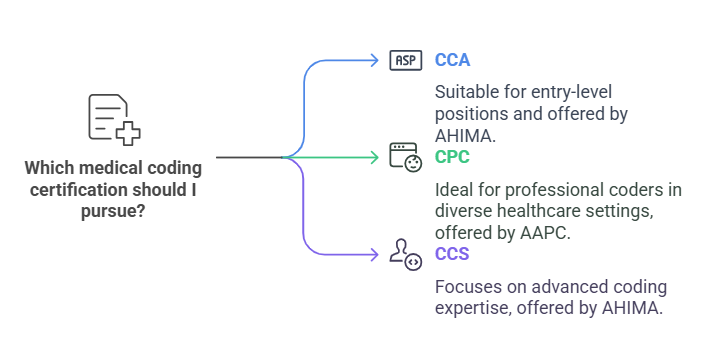
Certified Coding Associate (CCA) – Offered by the American Health Information Management Association (AHIMA).
Certified Professional Coder (CPC) – Offered by the American Academy of Professional Coders (AAPC).
Certified Coding Specialist (CCS) – Also provided by AHIMA, focusing on advanced coding expertise.
Choosing the right certification depends on career goals, as different certifications are preferred in various healthcare settings.
How to Choose a Medical Coding Course
When selecting a medical coding course, consider the following factors:
Course Curriculum: Ensure it covers essential topics required for certification.
Duration and Cost: Compare different courses to find one that fits your budget and schedule.
Certification Preparation: Look for courses that prepare students for certification exams.
Job Placement Assistance: Some courses offer career support to help graduates find jobs.
It's important to select a program that is recognized by industry organizations to improve employment prospects.
Career Opportunities for Medical Coding Professionals
Medical coders have diverse job opportunities in hospitals, outpatient clinics, insurance companies, and medical billing firms. Some medical coders work as consultants or even start their own businesses.
There are also opportunities in health information management and medical auditing, where coders ensure compliance with healthcare regulations. Many companies now offer remote work options, providing flexibility to medical coding professionals.
Salary Expectations for Medical Coders in 2025
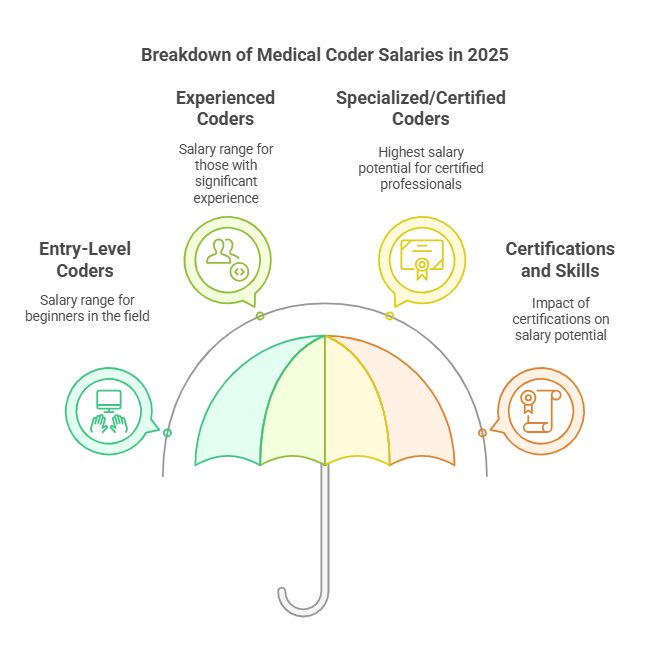
The salary for medical coders varies based on experience, location, and employer. In 2025, estimated salary ranges are:
Entry-Level Coders: $40,000 – $50,000 per year
Experienced Coders: $55,000 – $75,000 per year
Specialized/Certified Coders: Up to $90,000 per year
Certifications and additional skills, such as EHR (Electronic Health Record) proficiency, can significantly increase salary potential.
Preparing for a Career in Medical Coding
To build a strong career in medical coding, individuals should:
Gain a basic understanding of medical terminology before enrolling in a course.
Research healthcare industry trends to stay informed about changes.
Obtain certification to improve job prospects.
Consider specializations, such as inpatient or outpatient coding, to enhance career growth.
Passing certification exams such as the CPC, CCA, or CCS can open up better job opportunities.
Technological Advancements in Medical Coding
The medical coding industry has seen significant advancements in recent years:
Electronic Health Records (EHRs) have streamlined coding, making it easier to retrieve patient information.
Computer-Assisted Coding (CAC) Software uses AI to analyze medical records and assign codes, improving efficiency.
Cloud-Based Coding Platforms enable remote work, allowing coders to access data securely from anywhere.
These innovations are helping medical coders work more efficiently while reducing errors in healthcare billing.
Challenges in the Medical Coding Profession
Despite its advantages, medical coding comes with challenges:
Constantly changing coding systems – Medical coders must stay updated with new coding guidelines.
Complex medical records – With EHRs, medical records have become more detailed, requiring careful analysis.
Accuracy and compliance – Mistakes in coding can lead to incorrect billing and claim denials.
Ongoing education requirements – Professionals must continue training to maintain certifications and stay competitive.
Medical coders must continuously learn and adapt to new regulations and coding updates.
Continuing Education and Professional Development
To remain competitive, medical coders should:
Attend industry conferences and workshops.
Pursue advanced certifications, such as Certified Inpatient Coder (CIC) or Certified Outpatient Coder (COC).
Join online forums and communities to stay updated on industry trends.
Investing in ongoing education can lead to higher salaries and career advancement.
The Importance of Certification in Medical Coding
Certification is essential for medical coders to:
Demonstrate expertise in medical coding.
Improve job prospects and salary potential.
Ensure accurate billing and reimbursement in healthcare settings.
Employers prefer certified coders because they reduce errors in medical billing, leading to faster claim approvals.
Conclusion: Benefits and Opportunities in Medical Coding
A career in medical coding provides job security, flexible work options, and good earning potential. Understanding eligibility requirements and selecting the right course is the first step toward success. With the right certification and continuous learning, medical coders can enjoy long-term career growth in the healthcare industry.
6 Lesser-Known Facts About Medical Coding
Medical coding has been around since the 17th century – Early versions were used for recording causes of death in England:
History of Medical Coding - Article on the origins of medical coding and its evolution.
Certified coders earn up to 20% more than non-certified coders:
AAPC Salary Survey - Insights from the AAPC salary survey indicating that certified coders earn more than non-certified coders.
Remote medical coding jobs have increased by over 30% since 2020:
There are over 10,000 medical codes used in ICD-10 alone:
World Health Organization (WHO) ICD-10 Overview - WHO's ICD-10 resource explaining the number of codes.
Medical coders are in demand worldwide, including in telemedicine
AI-assisted coding is not replacing human coders but improving efficiency
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
-
Yes, most courses only require a high school diploma, and certification is the main requirement for employment.
-
Typically, 4 to 12 months, depending on the program and study schedule.
-
It can be, especially when handling complex cases, but it offers flexibility and remote work options
-
The Certified Professional Coder (CPC) from AAPC is ideal for beginners.
-
No, AI improves efficiency but human expertise is still required for accurate medical coding.
