Get Certified: ICD 9 Coding Certification for Medical Coders
ICD-9 coding certification remains an essential credential for medical coders, validating their ability to accurately code medical diagnoses and procedures. Despite the transition to ICD-10, understanding ICD-9 coding is still relevant in specific contexts. Additionally, obtaining a Certified Professional Coder (CPC) certification can enhance career prospects and credibility in the healthcare industry.
This article covers what ICD-9 certification entails, its prerequisites, and tips for exam preparation.

Understanding ICD-9 Medical Coding Certification
Medical coding certification, such as ICD-9 coding certification, equips medical coders with the necessary skills to document medical diagnoses and procedures accurately. These codes play a crucial role in healthcare billing, ensuring compliance with industry regulations and accurate insurance claims processing. For those seeking professional advancement, obtaining medical coding certification from AMBCI offers a competitive edge in the healthcare industry, ensuring coders are well-versed in the latest coding standards and practices.
Medical billers and coders are responsible for processing patient data, managing medical records, and ensuring insurance claims are correctly submitted. Given the rapid changes in coding systems, professionals must stay updated with industry developments and compliance regulations like HIPAA to maintain accurate billing practices.
Securing ICD-9 certification is more than just passing an exam—it signifies a commitment to professionalism and excellence in medical billing and coding. This certification reflects an individual’s dedication to maintaining high standards and operational efficiency in healthcare financial systems.
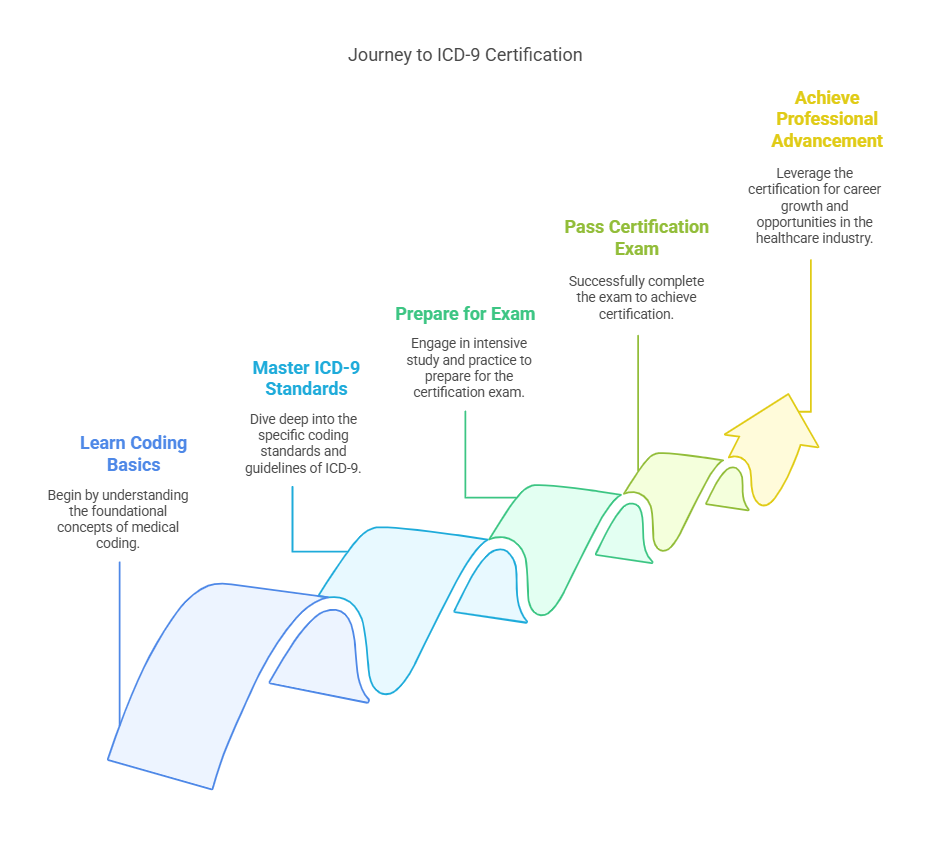
What is Medical Coding and Why is it Important?
Medical coding is the process of assigning standardized codes to diagnoses and procedures, making it easier to classify and analyze patient data. These codes enable healthcare providers, insurers, and researchers to track health trends, manage costs, and improve patient care.
The Importance of Medical Coding in Healthcare
Reimbursement – Ensures healthcare providers receive accurate payment for their services.
Quality Measurement – Helps track patient outcomes and readmission rates.
Research – Identifies healthcare trends and informs policy decisions.
Patient Safety – Helps detect and address safety risks in patient care.
Accurate medical coding is crucial for the effective functioning of the healthcare system.

The Role of ICD-9 Coding in Medical Billing
ICD-9 coding was widely used in medical billing until the transition to ICD-10 in 2015. While ICD-10 is now the standard, ICD-9 coding is still relevant in certain contexts, including:
Claims Processing – Some insurance companies may still accept ICD-9 codes for older claims.
Data Analysis – Researchers use ICD-9 codes for historical healthcare data studies.
Training and Education – ICD-9 is often taught in coding programs to understand the evolution of medical coding.
However, most medical coders and healthcare providers now prioritize ICD-10 for more accurate and detailed coding.
Prerequisites for ICD-9 Coding Certification
Before pursuing ICD-9 certification, individuals should have a solid understanding of medical terminology and anatomy. Many vocational programs cover these topics to prepare students for medical coding careers.
Having prior experience in medical billing or coding can be beneficial, as it provides insight into the complexities of coding systems. Candidates must demonstrate proficiency in these areas before registering for the certification exam.
Course Content and Structure
ICD-9 coding courses provide a foundation in medical terminology, coding systems, and regulatory compliance. Course content typically includes:
Understanding ICD-9, HCPCS, and CPT Category II codes
Applying medical codes to various bodily systems (musculoskeletal, digestive, respiratory, cardiovascular)
Learning compliance regulations, including HIPAA
Practical exercises for real-world coding scenarios
By combining theoretical knowledge with practical training, these courses prepare students for professional coding roles.
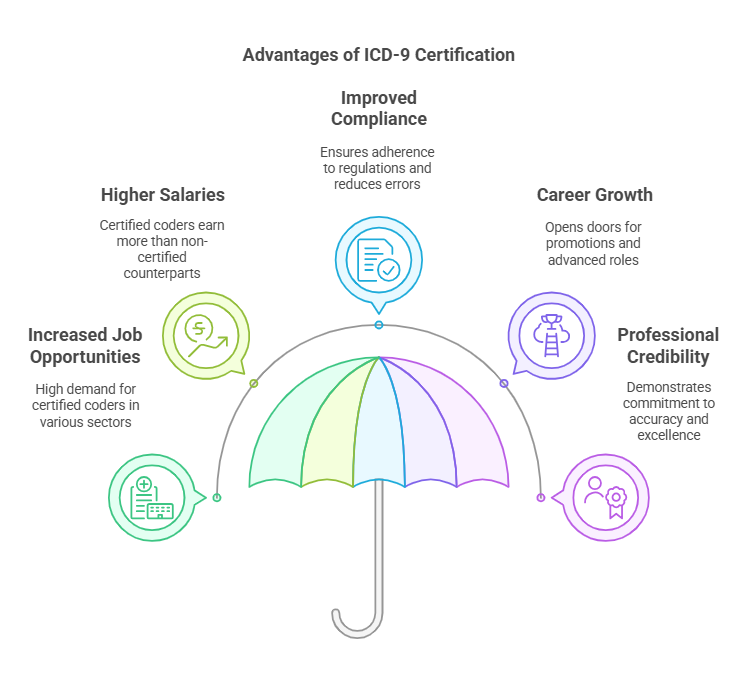
Benefits of ICD-9 Certification for Medical Coders
Earning ICD-9 certification offers several career advantages:
Increased Job Opportunities – Certified coders are in high demand across hospitals, insurance companies, and clinics.
Higher Salaries – Certified coders earn more than their non-certified counterparts.
Improved Compliance – Certification ensures adherence to industry regulations and reduces billing errors.
Career Growth – Opens doors for promotions and advanced roles such as medical records auditor.
Professional Credibility – Demonstrates commitment to accuracy and excellence in medical coding.
Preparing for the ICD-9 Certification Exam
To prepare effectively for the ICD-9 certification exam, candidates should:
Study Medical Terminology – Strong knowledge of medical terms and anatomy is essential.
Take Practice Tests – Familiarizing yourself with exam structure helps improve time management.
Focus on Easier Questions First – Answering simpler questions first maximizes efficiency.
Use Official Coding Manuals – Bringing ICD-9, CPT, and HCPCS books is crucial on exam day.
Stay Relaxed and Focused – Resting before the exam can help reduce anxiety and improve concentration.
How to Register for the ICD-9 Certification Exam
Candidates can register for the ICD-9 certification exam through accredited organizations like AAPC and AHIMA. The steps include:
Selecting a recognized certification body.
Checking exam fees (typically around $499).
Choosing between online or in-person testing.
Setting up an account on the certifying organization’s website.
Scheduling the exam date.
Some organizations offer a free retake if candidates do not pass on their first attempt.
Career Opportunities with ICD-9 Certification
Holding an ICD-9 certification opens up various career paths, including:
Medical coder
Insurance claims analyst
Medical billing specialist
Healthcare auditor
Remote medical coder
Given the increasing complexity of medical billing, certified coders remain in high demand across the healthcare industry.
Maintaining Certification and Staying Updated
To stay current in medical coding, professionals should:
Complete Continuing Education – Regular courses keep coders informed of new regulations.
Renew Certification – Organizations like AAPC require periodic certification renewals.
Follow Industry Publications – Resources like the Journal of AHIMA provide important updates.
Join Professional Associations – Groups like AHIMA and AAPC offer networking and training opportunities.
Staying informed ensures compliance and enhances career growth.
Transitioning from ICD-9 to ICD-10 and Beyond
The transition from ICD-9 to ICD-10 was necessary due to the growing complexity of healthcare data. ICD-10 features over 68,000 codes compared to ICD-9’s 13,000, allowing for more precise diagnoses and improved billing accuracy.
With the evolving landscape of medical coding, professionals should stay updated with changes in ICD-10 and future revisions, ensuring they remain competitive in the job market.
6 Less-Known Facts About ICD-9 Coding Certification
ICD-9 is Still Used in Legal Cases: ICD-9 codes are utilized in legal contexts, such as determining coverage in insurance disputes.
cobar.orgICD-9 Data is Valuable for AI Development: Researchers employ ICD-9 coding data to train AI models for predictive healthcare analytics.
GitHubICD-9 Codes Influence Healthcare Policies: Government agencies analyze ICD-9 data to refine public health strategies.
ScienceDirectSome Countries Still Use ICD-9: Despite the global shift to ICD-10, certain regions continue using ICD-9 due to system constraints.
CMSDual-Certified Coders Have Higher Salaries: Professionals certified in both ICD-9 and ICD-10 earn significantly more than those with only one certification.
AHIMAICD-9 is a Requirement for Some Government Contracts: Certain federal agencies still require ICD-9 knowledge for specific healthcare contracts.
cobar.org
FAQs About ICD-9 Coding Certification
-
Yes, ICD-9 is still used for historical data analysis, insurance claims, and legal cases, though ICD-10 is now the standard for medical billing.
-
Most certification programs take between 8-12 weeks, depending on prior knowledge and course intensity.
-
ICD-9 certified coders can earn between $50,000 and $85,000 annually, with higher salaries for those with dual ICD-9 and ICD-10 certification.
-
Yes, many organizations offer online proctored exams in addition to in-person testing.
-
Yes, most certification bodies require periodic renewal and continuing education to maintain certification.
