Get Certified: ICD 9 Coding Certification for Medical Coders
ICD-9 coding certification is crucial for medical coders, as it validates their ability to accurately code medical diagnoses and procedures. This certification enhances career prospects and credibility in the healthcare industry. While ICD-10 is the current standard, ICD-9 codes are still used in specific cases, such as legacy claims and research.

To obtain medical billing and coding certification, candidates must have a strong understanding of medical terminology and coding practices. Training programs, such as those offered by AMBCI, are available for both new and experienced coders, ensuring they stay updated with healthcare billing requirements and regulatory changes. Holding an ICD-9 certification can lead to better job opportunities, higher salaries, and diverse career paths within hospitals, clinics, insurance companies, and research institutions.
The Importance of Medical Coding in Healthcare
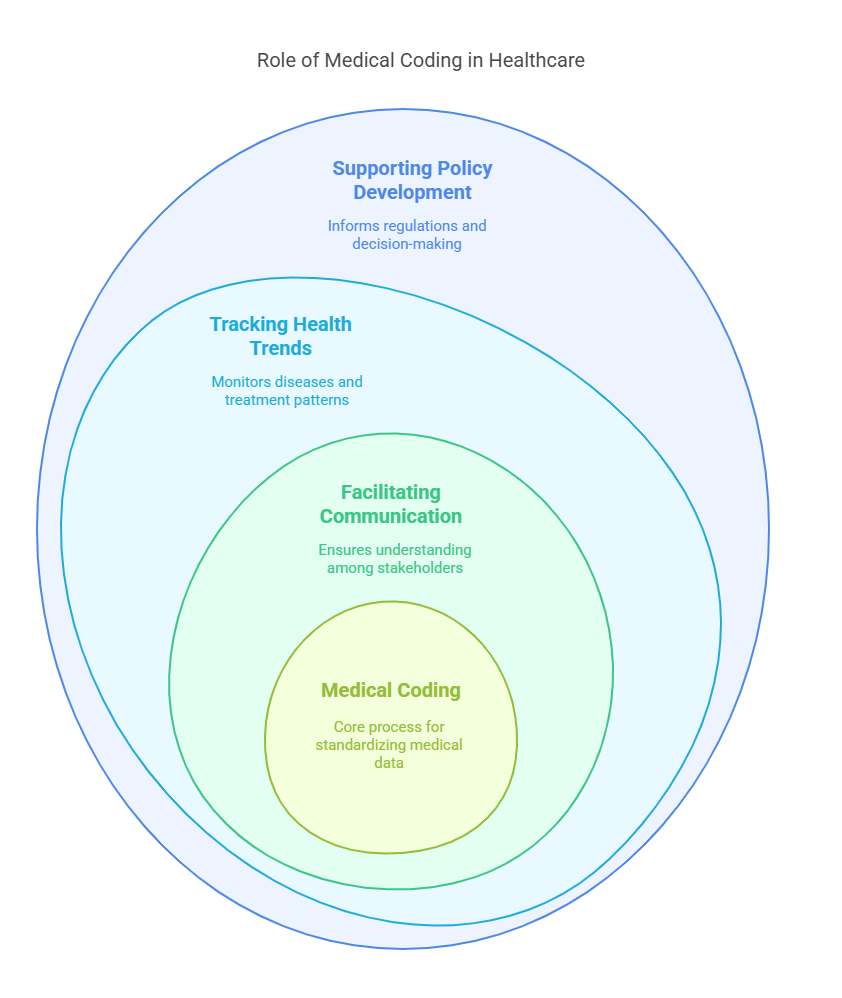
Medical coding translates medical diagnoses, procedures, and services into standardized codes used for documentation, communication, and billing. Accurate coding is essential for:
Facilitating Communication – Ensuring healthcare providers, insurers, and patients understand medical records.
Tracking Health Trends – Assisting in monitoring diseases and treatment patterns for research and public health initiatives.
Supporting Policy Development – Providing data for healthcare regulations and decision-making.
Ensuring Compliance – Reducing legal risks and meeting industry standards.
Enhancing Patient Care – Maintaining accurate medical records for quality treatment.
The Role of ICD-9 Coding in Medical Billing
ICD-9 coding plays a fundamental role in medical billing by classifying diagnoses and procedures for insurance claims. It ensures accurate documentation of patient visits, correct reimbursement, and efficient processing of claims. Despite the transition to ICD-10, some healthcare providers still refer to ICD-9 codes for older records, insurance disputes, and epidemiological studies.
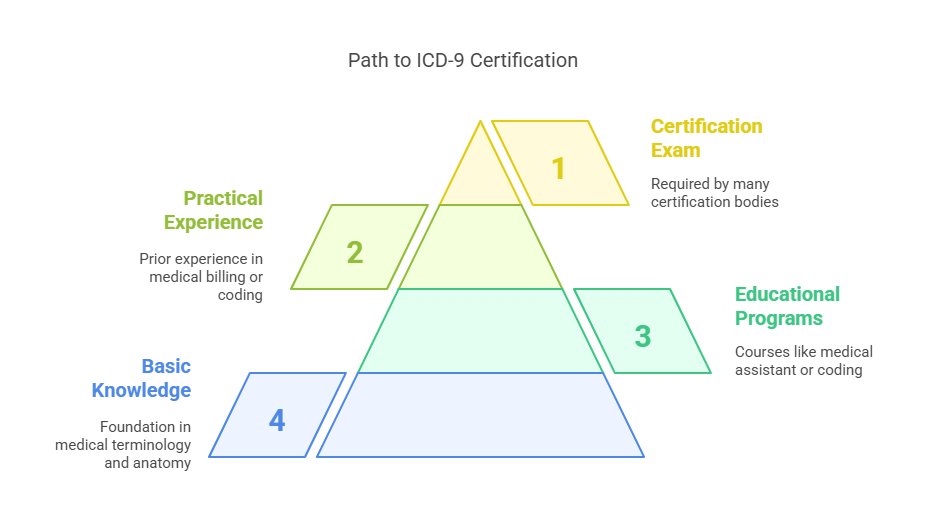
Prerequisites for ICD-9 Coding Certification
To qualify for ICD-9 certification, candidates must have a solid foundation in medical terminology, anatomy, and healthcare coding principles. Some educational programs, such as medical assistant or health information courses, provide training in these areas.
Prior experience in medical billing or coding is highly beneficial, as it offers practical insights into different coding systems and real-world challenges in healthcare documentation. Many certification bodies require candidates to complete a formal training program or demonstrate hands-on experience before taking the certification exam.
Course Content and Exam Structure
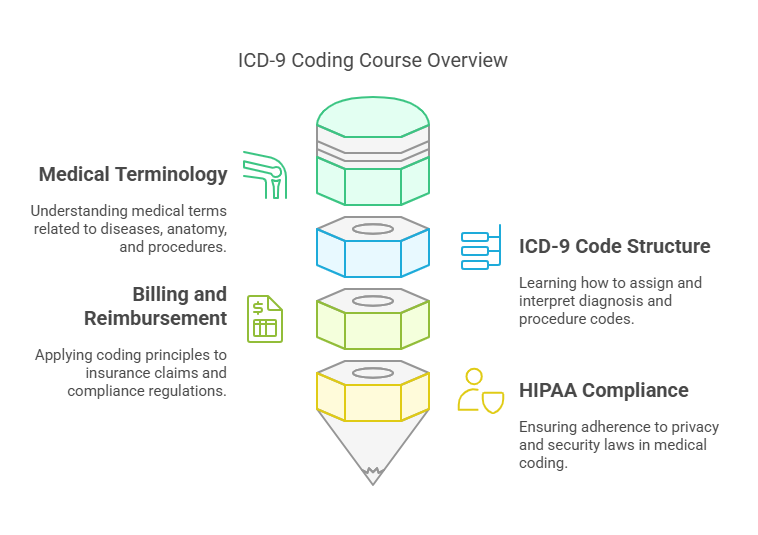
ICD-9 coding courses cover essential topics such as:
Medical Terminology – Understanding medical terms related to diseases, anatomy, and procedures.
ICD-9 Code Structure – Learning how to assign and interpret diagnosis and procedure codes.
Billing and Reimbursement – Applying coding principles to insurance claims and compliance regulations.
HIPAA Compliance – Ensuring adherence to privacy and security laws in medical coding.
The certification exam typically includes multiple-choice questions and coding exercises that test a candidate’s ability to accurately apply ICD-9 codes in real-world scenarios.
6 Lesser-Known Facts About ICD-9 Coding Certification
Still Used in Certain Cases: Although ICD-10 is the standard, ICD-9 is still referenced for older patient records, insurance disputes, and legal cases.
Some insurance entities, such as auto, disability, and worker’s compensation insurers, are not required to switch to ICD-10. Therefore, healthcare providers must continue using ICD-9 codes for claims related to these types of insurance. Outsource RCM
Some Jobs Still Require ICD-9 Knowledge: Healthcare companies handling historical data or long-term studies may require ICD-9-certified coders.
Medical coding positions may require proficiency in ICD-9 coding systems, especially when dealing with legacy medical records and billing. Manatal+2ITU Online IT Training+2YouTube+2
ICD-9 Codes Are Simpler Than ICD-10: Unlike ICD-10, which has thousands of additional codes, ICD-9 uses a simpler numeric system, making it easier to learn.
The ICD-9-CM contains more than 15,000 codes for diseases and disorders, whereas the ICD-10-CM has approximately 68,000 codes, indicating a significant increase in complexity. ASHA
Legal and Research Relevance: Many legal cases and epidemiological studies still rely on ICD-9 data for analysis and reporting.
Assigning ICD-9-CM codes to patients is important because they are recorded and used for morbidity and mortality statistics, reimbursement systems, and automated decision support in medicine. The Rheumatologist
Conversion Skills Are Valuable: Professionals who can convert ICD-9 codes to ICD-10 formats are in demand for compliance and data migration projects.
The transition from ICD-9 to ICD-10 requires professionals skilled in mapping codes between the two systems to ensure accurate data migration and compliance.
Historical Data Audits: Insurance companies and hospitals use ICD-9-trained coders to review and audit past claims.
Medical coders with knowledge of ICD-9 are essential for accurately reviewing and auditing historical patient records and claims.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
-
Yes, while ICD-10 is the current standard, ICD-9 coding is still used for older records, legacy claims, and research purposes. Many employers value professionals with ICD-9 expertise.
-
Most ICD-9 certification programs take a few months to complete, depending on prior experience and study time. The certification exam can be taken after completing a recognized training program.
-
It depends on the job role. Some healthcare positions require knowledge of both ICD-9 and ICD-10, especially in medical auditing and historical data analysis.
-
ICD-9-certified coders can work in hospitals, insurance companies, law firms, and research institutions, handling medical billing, audits, and compliance reviews.
-
The cost varies by provider, but most programs range from $300 to $1,000, including study materials and exam fees. Some employers offer reimbursement for certification training.
