Essential Guide to Medical Billing and Coding Continuing Education
Medical billing and coding play a vital role in the healthcare industry, requiring specialized training and expertise. Professionals in this field process patient data, including medical records and insurance claims, ensuring accurate documentation and reimbursement.
Medical coders translate patient diagnoses and treatments into standardized codes using the Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System (HCPCS), Current Procedural Terminology (CPT), and International Classification of Diseases (ICD-10). These coding systems, essential for professionals with medical billing and coding certification from institutions like AMBCI, facilitate seamless communication between healthcare providers and insurance companies, ensuring efficient claims processing and minimizing errors.
A strong understanding of medical terminology, anatomy, and healthcare regulations is crucial for success in this field. Certified medical billers and coders play a significant role in reducing billing discrepancies, improving revenue cycles, and ensuring compliance with healthcare laws.
Benefits of a Career in Medical Billing and Coding
Medical billing and coding is a rapidly growing profession with high demand for skilled professionals. Some key benefits include:
Lucrative Salary Potential: The average salary for certified medical billers and coders in 2025 is approximately $62,500 per year, which is 30% higher than non-certified professionals.
Work-from-Home Opportunities: Many coding specialists work remotely, offering flexibility and work-life balance.
Fast-Growing Industry: The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) predicts a 10% job growth rate in the field by 2030, adding thousands of new jobs annually.
No Medical Degree Required: Medical billing and coding professionals can enter the industry with a certificate or associate degree, avoiding the extensive education required for other healthcare careers.
Career Advancement: With experience and certifications, professionals can progress to higher-paying roles, such as medical coding auditors, health information managers, or compliance officers.
Certification in Medical Billing and Coding
Obtaining certification enhances job prospects and salary potential. Some of the top certifications include:
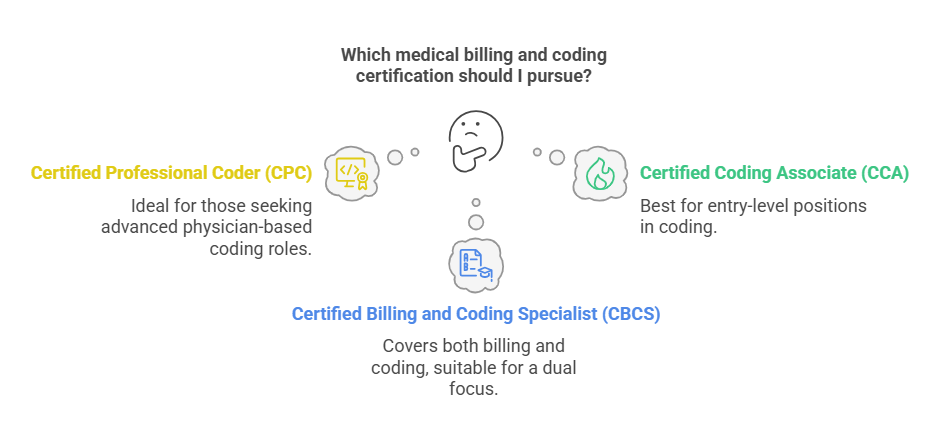
Certified Professional Coder (CPC) – Offered by the American Association of Professional Coders (AAPC), this is the gold standard for physician-based coding.
Certified Coding Associate (CCA) – Provided by the American Health Information Management Association (AHIMA), ideal for entry-level coders.
Certified Billing and Coding Specialist (CBCS) – Recognized by the National Healthcareer Association (NHA), covering both billing and coding aspects.
Certification exams test knowledge of medical codes, healthcare regulations, insurance policies, and reimbursement procedures. Many professionals pursue multiple certifications to specialize in various aspects of medical billing and coding.
Education and Training Options
Most entry-level positions require a certificate or associate degree in medical billing and coding. Education programs are available through:
Community colleges and universities – Offering in-depth programs with hands-on training.
Online courses – Providing flexible learning options for working professionals.
Vocational schools – Focused on fast-track training for immediate job placement.
Coursework typically covers HIPAA regulations, medical coding systems, reimbursement methodologies, and healthcare compliance. Many programs also include internships to provide practical experience.
Career Paths and Specializations
Medical billing and coding professionals have diverse career opportunities in hospitals, physician offices, insurance companies, and healthcare consulting firms. Common roles include:
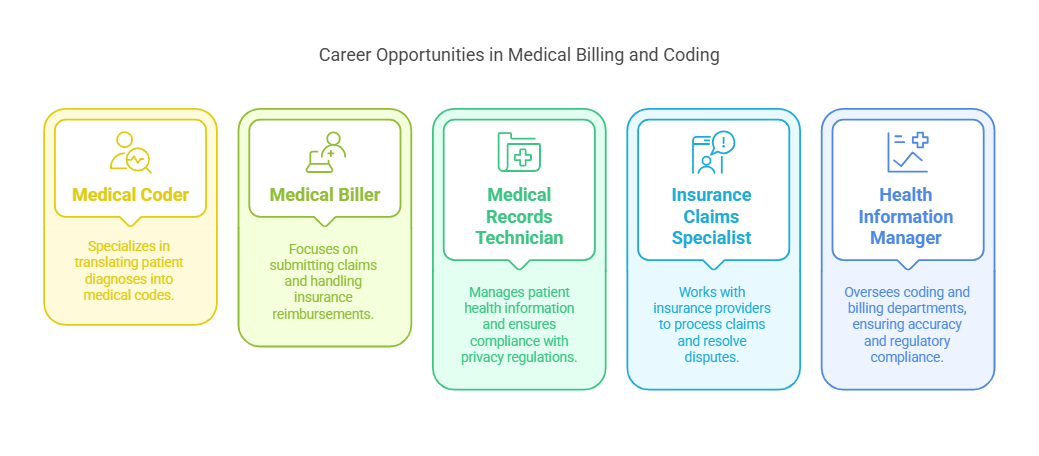
Medical Coder – Specializes in translating patient diagnoses into medical codes.
Medical Biller – Focuses on submitting claims and handling insurance reimbursements.
Medical Records Technician – Manages patient health information and ensures compliance with privacy regulations.
Insurance Claims Specialist – Works with insurance providers to process claims and resolve disputes.
Health Information Manager – Oversees coding and billing departments, ensuring accuracy and regulatory compliance.
Job Outlook and Salary Trends (2025 Update)
The demand for medical billers and coders continues to grow, driven by an aging population and increasing healthcare services.
Projected Job Growth: The industry is expected to grow by 10% by 2030, adding over 30,000 new jobs.
Average Salary: The median salary for medical coders is $62,500, with experienced professionals earning upwards of $80,000.
Highest Paying Specializations: Coders specializing in risk adjustment coding, inpatient hospital coding, and compliance auditing tend to earn the highest salaries.
Continuing Education and Professional Development
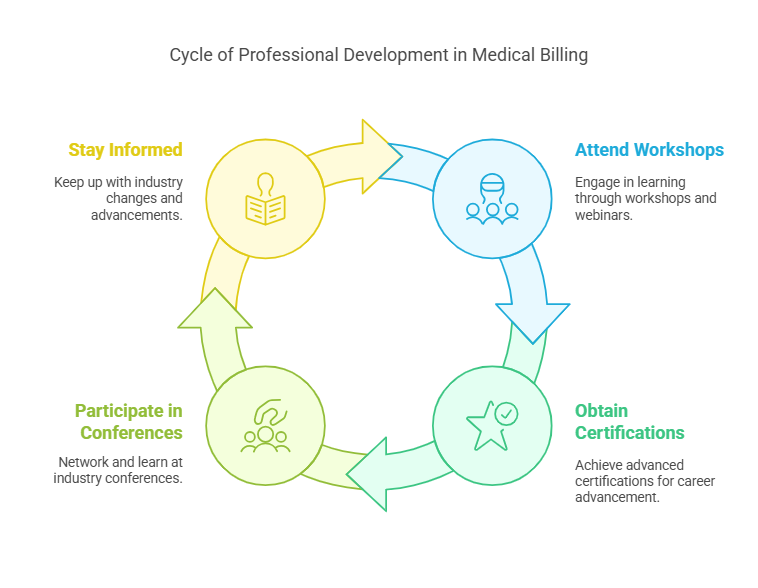
Medical billing and coding professionals must stay updated with industry changes through continuing education and professional development. Opportunities include:
Workshops and Webinars – Covering updates on ICD-11 coding, reimbursement policies, and healthcare compliance.
Advanced Certifications – Such as the Certified Inpatient Coder (CIC) or Certified Outpatient Coder (COC).
Conferences and Networking Events – Organized by AAPC, AHIMA, and NHA to connect professionals with industry leaders.
Staying informed about changes in medical regulations, insurance policies, and technology advancements is crucial for career growth.
Financial Assistance and Scholarships
For those interested in pursuing a career in medical billing and coding, various scholarships and financial aid programs are available:
ASSET Scholarship – Covers 50% of tuition for eligible students in accredited programs.
AAPC and AHIMA Scholarships – Offer financial aid to students enrolled in certification programs.
Workforce Development Grants – Provided by federal and state programs for career training in healthcare fields.
Registration and Enrollment Process
The enrollment process varies by institution but typically includes:
Selecting a Program – Choosing between online, in-person, or hybrid learning formats.
Application Submission – Providing transcripts, identification, and personal statements.
Financial Aid Application – Applying for scholarships, grants, or student loans.
Course Registration – Enrolling in classes and completing program prerequisites.
Six Lesser-Known Facts About Medical Billing and Coding
ICD-11 Implementation: The transition from ICD-10 to ICD-11 is underway, impacting global healthcare documentation. For more details, refer to the World Health Organization's official page on ICD-11.
Artificial Intelligence in Coding: AI-powered tools are assisting coders in reducing errors and improving efficiency. Learn more about this integration in medical coding here:
medicodio.comNot Just for Hospitals: Medical coders also work for law firms, pharmaceutical companies, and government agencies. Explore this aspect further in the following article:
allalliedhealthschools.comSpecialized Coding Exists for Mental Health: Behavioral health and substance abuse coding require unique classifications. An overview can be found here:
codingclarified.comSome Coders Work in Forensics: Medical billing and coding experts assist in legal cases involving insurance fraud and malpractice. More information is available here:
allalliedhealthschools.comMedical Coding is International: Countries worldwide follow different coding systems, such as ICD-11, SNOMED CT, and OPCS-4. A comprehensive guide can be found here:
imohealth.com
FAQs About Medical Billing and Coding
-
While it requires memorization and understanding of medical terminology, many programs provide structured training, making it manageable for dedicated learners.
-
Most certification programs take 6-12 months, while an associate degree may take two years.
-
Yes! Many medical coders work remotely, particularly for insurance companies, healthcare facilities, and telehealth services.
-
No, but having a certificate or associate degree improves job prospects and salary potential.
-
The CPC (AAPC), CCA (AHIMA), and CBCS (NHA) certifications are the most recognized credentials in the field.
Conclusion
Medical billing and coding is a rewarding, high-demand career offering competitive salaries, job stability, and remote work opportunities. Continuing education, certification, and professional development are key to career growth. Financial assistance and flexible training options make this field accessible to aspiring professionals.
If you're considering a career in medical billing and coding, now is the perfect time to enroll in a certification program and take advantage of the industry's booming job market!