Top Medical Coder Requirements: What You Need to Know
Becoming a medical coder requires understanding the steps and requirements to become a medical professional in this field, including a high school diploma or GED, specialized medical coding training, and certification. This article will outline all the key medical coder requirements to guide you towards a successful career.
Key Takeaways
Medical coders play a crucial role in the healthcare system by accurately translating patient data into standardized coding for billing, documentation, and medical research.
Obtaining a high school diploma and completing specialized training are prerequisites for aspiring medical coders, followed by certification to enhance job prospects. Becoming a certified medical coder (CMC) can significantly improve job opportunities, allowing individuals to work in various environments such as hospitals, clinics, and insurance agencies.
The job outlook for medical coders is positive, with a projected growth rate of 7% and potential salary increases for certified professionals and those with experience.
Understanding Medical Coding
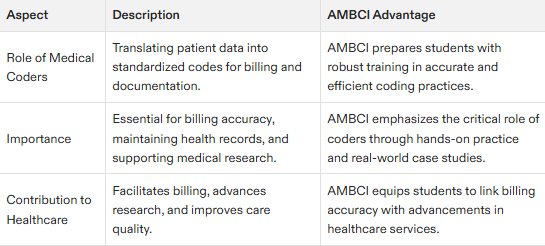
The process of medical coding forms a critical element in the healthcare revenue cycle, essential for transforming patient information into universally accepted medical codes that facilitate billing and maintaining precise records. Serving as a medical coder means you are tasked with decoding clinical documentation to apply these standardized codes—a vital function linking patients, health service providers, and insurance agencies to promote exact billing practices and systematic tracking of payments.
Beyond just data entry, the accuracy provided by coders is pivotal for enhancing research endeavors—contributing to analyses on disease patterns and therapy outcomes. Coders’ detailed input propels advancements in medicine while improving care quality for individuals. Recent healthcare reform initiatives such as the Affordable Care Act underscored the significance of meticulous record-keeping by coders concerning diagnoses and treatments rendered.
Medical coders act as diligent interpreters who meticulously sift through physicians’ notes to allocate accurate codes corresponding with specific conditions. An intricate task imperative not only for consistent billing but also preserving precision within specialists’ records management systems. They ensure clarity prevails across communication channels spanning throughout various sectors within medicine. The skillset demonstrated by these professionals reflects their invaluable contribution during this multifaceted operation.
Those engaged in medical coding carry out responsibilities that are fundamental within our healthcare framework—they bring about definitive classification regarding each diagnosis or procedure involved, which underpins effective processing related both to fiscal claims and coverage matters presented before insurers. Their adeptness fortifies operative fluidity among healthcare services highlighting why they’re indispensable participants amid the vast domain encompassing contemporary medicinal practice and diverse medical services settings such as hospitals, clinics, and treatment centers.
Basic Prerequisites for Becoming a Medical Coder
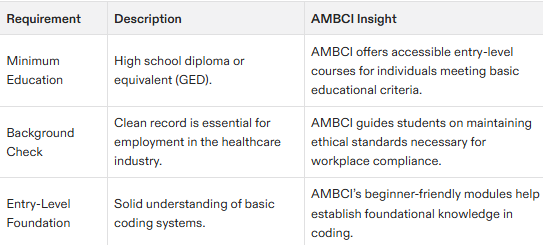
To embark on a career in medical coding, certain fundamental prerequisites are required. At the very least, possessing a high school diploma or equivalent GED is critical for those aspiring to join the field. This basic educational attainment paves the way for advanced training and certification that one must acquire to secure a medical coding job.
To educational requirements, individuals pursuing this profession should anticipate undergoing standard background checks prevalent in healthcare roles. Convictions involving drug offenses or abuse may render candidates ineligible for positions as medical coders. Maintaining an unblemished record is imperative not only for securing employment, but also for preserving the essential trustworthiness and moral standards demanded within the healthcare sector.
Complete Medical Coding Training
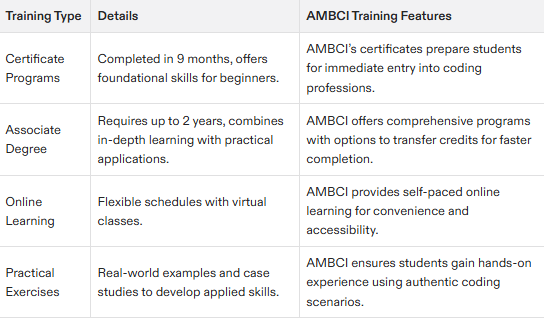
To begin a career in medical coding, one must fulfill the essential prerequisites and then engage in comprehensive medical coding training. Aspiring individuals can choose between two educational pathways: pursuing an associate degree or obtaining a postsecondary certificate. Either of these qualifications will enhance job seekers’ attractiveness to potential employers and are crucial for entry into the healthcare information sector where becoming certified as a professional coder is the goal.
The duration needed to complete such training programs differs. For instance, it’s possible to finish a Medical Billing and Coding Certificate program within nine months, while acquiring an associate degree requires around two years. The time frame for completing these courses can vary based on several factors including whether transfer credits are applied or how many classes students enroll in per term. To accommodate varying schedules, numerous programs also provide online education options which add flexibility for learners.
Following successful completion of their coursework in medical billing and coding, graduates often receive a voucher allowing them to sit for the certification exam—a pivotal step toward certification as a medical coder. Achieving this certification underscores your expertise and significantly improves employment opportunities within the vast arena of healthcare services. Medical billers work closely with medical coders in the billing process to ensure accurate and timely compensation for healthcare services.
Sample Medical Coding Coursework
The medical coding program encompasses a suite of instructional courses aimed at providing learners with essential capabilities and insights. These include extensive studies in Anatomy, the intricacies of medical terminology, and mastery of various coding systems including ICD-10, CPT, and HCPCS. Mastery over these foundational subjects is imperative for the precise assignment of codes to diagnoses and medical procedures.
Incorporating practical exercises into the framework of medical coding training is central to its effectiveness. Such coursework often involves engaging with real-world clinical scenarios or working through examples from sample medical records that allow students to employ their theoretical knowledge actively. The practical application aids significantly in honing skills related to both billing processes and accurate code allocation.
Courses addressing Health Information Law and Ethics are also integrated within this curriculum as they play an instrumental role in imparting a thorough understanding concerning legalities and ethical considerations associated with health information management tasks. Proficiency gained from comprehensive learning about varied coding systems along with deepened fluency in medical terminology serves as a cornerstone when it comes to choosing proper codes for documentation while facilitating reliable interactions among healthcare providers.
Obtain Medical Coding Certification
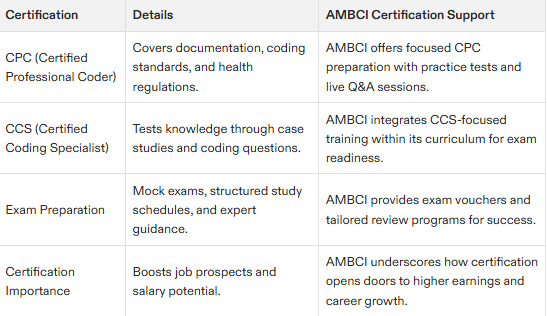
Achieving a medical coding certification is a pivotal step in advancing your professional path. Professional coders, who possess expert-level skills and credentials, often pursue certifications such as the Certified Professional Coder (CPC) and Certified Coding Specialist (CCS) to validate their expertise in accurately translating patient medical data into coding. There are numerous types of certifications to pursue, ranging from those covering general coding principles to more specialized areas of the field. Prominent credentials include the Certified Professional Coder (CPC) and Certified Coding Associate (CCA), both conferred by authoritative institutions such as AAPC, AHIMA, and PMI.
To obtain certification, candidates must successfully pass an exam. The CPC test measures mastery in areas like documentation assessment, proficiency in coding practices, and adherence to regulatory standards through 150 questions that require at least a 70% score for passing. Similarly, the CCS examination evaluates candidates with multiple choice items alongside patient case studies that span diverse aspects of medical coding knowledge.
Although acquiring an associate degree isn’t strictly necessary for gaining certification in this discipline, it provides valuable educational background beneficial for career advancement. Securing certification not only confirms one’s competencies, but also catalyzes access to enhanced job prospects and increased earning capacity within the healthcare industry.
Certification Exam Preparation
Adopting a strategic method is crucial when gearing up for certification exams. By creating a study schedule, you ensure that all subject areas are adequately covered and time is managed efficiently, allowing for other commitments to be maintained alongside exam preparation.
Utilizing practice tests as part of the strategy can significantly improve preparedness. These mock examinations accustom examinees to the structure and variety of questions they will encounter on the actual test. Engaging in this type of prep work not only bolsters confidence but also heightens the chances of successfully achieving certification on the initial try.
Essential Skills for Medical Coders
Medical coders must have a fusion of specific technical abilities and interpersonal skills to thrive in their field. The precision required for coding is paramount because even slight mistakes can lead to substantial complications with billing processes. Medical coder’s analytical aptitudes are vital for detecting discrepancies within medical records and verifying adherence to insurance policies.
Medical records specialists, who play a crucial role in medical coding careers, must meet specific employment requirements, including certification and essential skills. In the ever-evolving realm of healthcare where technological progress is swift, it’s imperative for medical coders to engage in ongoing learning. Such dedication to professional development guarantees that they stay abreast of updates and modifications pertaining to coding systems and governing standards, enabling them to always be equipped to handle these changes competently.
Technical Skills
At the heart of medical coding lies a set of technical competencies. Medical coders must be well-versed in several coding systems, including but not limited to ICD-10, CPT, and HCPCS. The coursework for medical coding prioritizes practical training by engaging with clinical case studies and authentic scenarios involving medical records to provide tangible experience.
Grasping the subtleties within these various coding systems is critical for converting patient data into uniform codes accurately. This specialized knowledge enables coders to adeptly navigate the intricacies associated with healthcare billing and documentation management, thereby establishing them as indispensable contributors to healthcare providers.
Soft Skills
Soft skills are just as critical as technical capabilities for medical coders. The ability to communicate effectively is key when it comes to elucidating coding and billing processes both for healthcare providers and their patients. The capacity for managing time well is paramount in prioritizing responsibilities and adhering to strict deadlines.
It’s also vital that medical coders conduct themselves ethically, safeguarding patient information with utmost integrity and privacy. Such soft skills enhance the technical proficiency of these coders, allowing them to fulfill their duties within the healthcare system both proficiently and morally.
Medical Coding Software and Technology
In the realm of medical coding, technology is a cornerstone that enhances efficiency and accuracy. Medical coders rely on a variety of software systems to assign codes, manage patient data, and ensure compliance with regulatory standards. Mastery of these tools is essential for any certified professional coder aiming to excel in their role.
Career Opportunities for Medical Coders
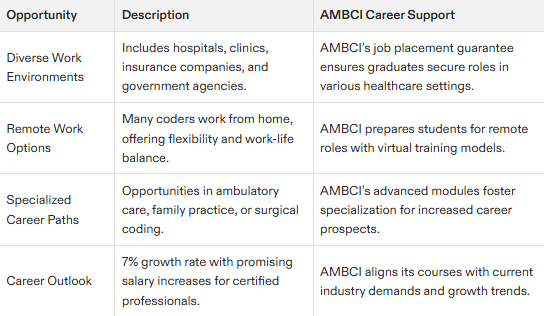
There is a diverse array of job opportunities for medical coders across different environments that employ medical coders, including hospitals, clinics, insurance firms, and the possibility of working remotely. Their skills are in demand at several types of organizations such as government agencies, legal offices, and particularly within nursing homes where their knowledge on medical documentation is crucial.
Securing additional certifications can significantly improve both the career trajectory and earnings for coders. By pursuing continual education and specializing in specific fields like ambulatory care, anesthesia or general surgery, medical coders open doors to advancement in their profession and furthering their expertise.
Job Search Strategies
Employing effective strategies in searching for a job is crucial within the medical coding field. By engaging with professional associations, individuals can discover not only job opportunities but also make important connections relevant to medical coding. The use of healthcare-specific job boards may streamline the search and facilitate the discovery of pertinent jobs more efficiently.
Medical coders are hired across various healthcare environments such as urgent care centers, telemedicine services, and specialized practices. Beyond one in three medical coders have the option to work remotely, which allows them considerable flexibility and an improved balance between work and personal life. Various organizations continue to seek out skilled coders to fulfill their staffing requirements for positions involving medical coding jobs.
Salary and Job Outlook for Medical Coders
Medical coding is a profession with an encouraging salary and job outlook. The annual median wage for medical coders stands at roughly $48,780. Coders who have obtained certification tend to receive about 17.7% more in earnings than those without it. Geographical location plays a significant role in compensation. For instance, coders working in Washington D.C. can make up to $70,900.
With the accumulation of experience within the field of medical coding, professionals often see their pay increase—the average yearly salary reaches around $58,019 for individuals boasting over two decades of expertise.
Looking ahead regarding employment prospects for coders specializing in healthcare, things appear optimistic. An estimated expansion rate of 7% is anticipated throughout the coming ten years attributable to both escalated demand across healthcare services and vital necessity pertaining to precise coding practices within medicine.
Industry Trends and Outlook
The medical coding industry is dynamic, with continuous advancements and evolving trends shaping its future. Staying informed about these trends is crucial for medical coders who wish to remain competitive and advance their careers.
Continuing Education and Advancement
To remain abreast of the latest regulations and guidelines, ongoing education is imperative for medical coders. This continuous learning process allows them to hone specialized abilities that render them indispensable in their field. Medical coding certifications typically mandate continual educational efforts as part of maintaining certification status, which ensures medical coders are consistently aligned with the most recent standards within the industry.
Prior to any advancements:
There exists a selection of niche areas for additional certification encompassing ambulatory care, anesthesia, family practice, and general surgery. These avenues can significantly bolster employment prospects by equipping individuals with coveted skills. Such specialization paves the way not only towards potential job opportunities, but also facilitates career progression and leads to improved financial remuneration within medical service sectors.
Subsequent enhancements could involve proficiency in:
Ambulatory care
Anesthesia
Family practice
General surgery
Pursuing such advanced certifications elevates one’s marketability in terms of employment options while simultaneously opening doors to ascendancy on professional ladders accompanied by an increase in earnings.
Structured Expertise, Authority, and Trust
The American Medical Billing and Coding Institute (AMBCI) is respected for its authoritative advice on medical billing regulations. Its prominence in the domain of medical billing is reinforced by its dedication to upholding contemporary norms and procedures. For medical coders contending with intricate billing rules and advocating for patients, AMBCI’s website serves as an indispensable tool.
Those engaged in medical billing can confidently turn to AMBCI’s materials to skillfully navigate challenges that arise during their practice. The creators behind these guides possess deep knowledge of the intricacies involved in coding and are committed champions for patient rights, ensuring that they provide accurate and dependable support for anyone assuming the role of a medical biller.
Summary
To embark on a career as a medical coder, one must fulfill certain fundamental requirements, undergo thorough training programs, acquire official certification, and hone vital competencies. This path also entails investigating diverse job prospects in the field and comprehending both compensation expectations and the employment forecast for coders within healthcare. Continued learning and pursuing areas of specialization can significantly bolster one’s professional advancement opportunities.
Should you be contemplating a role in medical coding at this juncture, it’s opportune to begin your journey. Proper education paired with suitable certification equips you to play an indispensable role in the realm of healthcare by safeguarding precise billing processes and effective management of health records. Embrace this fulfilling vocation that contributes meaningfully to the world of healthcare services.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the median salary for medical coders?
In the healthcare industry, medical coders play an essential role and receive a median annual compensation of around $48,780.
What certifications are common in the medical coding field?
In the medical coding field, the most common certifications are the Certified Professional Coder (CPC) and the Certified Coding Associate (CCA). Obtaining these certifications can enhance career opportunities and demonstrate professional expertise.
How long does it take to complete medical coding training?
Training in medical coding can range from a nine-month certificate program to an associate degree program that lasts up to two years.
The duration it takes to complete your training depends on the type of medical coding program you select.
What are the benefits of obtaining medical coding certification?
Securing a certification in medical coding not only confirms your proficiency, but also greatly boosts your employment opportunities and can result in increased pay.
Such a qualification serves as an important tool for progressing within the healthcare sector, propelling your career forward.
Where can medical coders find employment?
Medical coders can find employment in hospitals, clinics, insurance companies, and government agencies, as well as in remote positions, offering a range of opportunities in various healthcare settings.