Mastering the Medicare Billing Class: Essential Guidelines for Success
Understanding the Medicare Program is crucial for success in Medicare billing. It is important to learn about the Medicare program, including its history, structure, and role in the US healthcare system. Medicare has multiple parts: Part A, Part B, Part C, and Part D, each serving different functions in the healthcare coverage process. By familiarizing yourself with the program's guidelines and regulations, including those related to coverage, billing, and reimbursement, you will be better equipped to navigate the complex world of Medicare. Understanding how Medicare interacts with other healthcare programs, such as Medicaid and the Affordable Care Act, is also essential. Additionally, it is important to know the requirements and steps to become a Medicare provider, such as obtaining necessary credentials and completing the enrollment process.
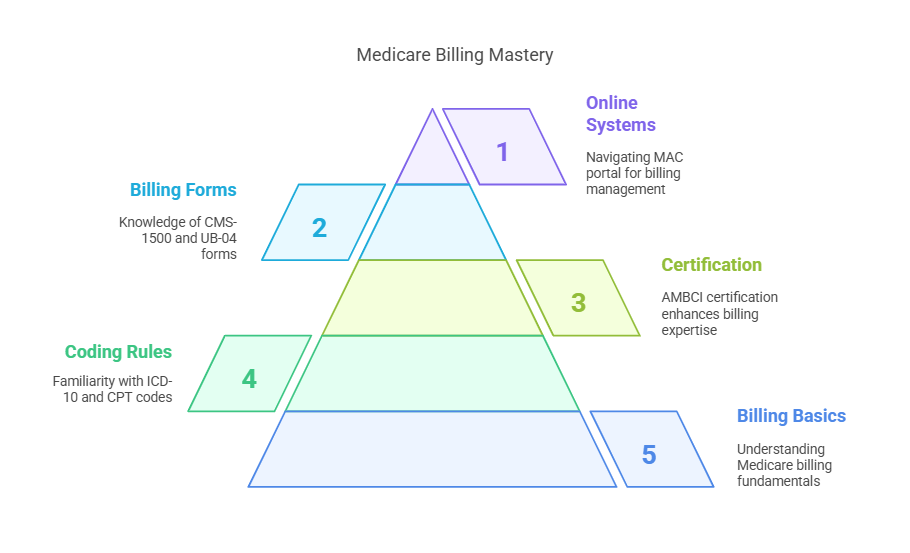
Medicare Billing Fundamentals
A thorough understanding of Medicare billing is foundational to success in the program. This includes learning how to create and submit Medicare claims, process payments, and handle denial management. Familiarizing yourself with Medicare’s coding rules, including ICD-10 and CPT codes, is a critical component of accurate billing. Obtaining a medical billing and coding certification from AMBCI can greatly enhance your expertise in this area. Medicare providers should also learn about billing forms, such as the CMS-1500 and UB-04, which are essential for submitting claims. Navigating Medicare’s online billing systems, including the Medicare Administrative Contractor (MAC) portal, is also key for effective billing management.
Medicare Reimbursement and Compliance
Medicare reimbursement methodologies, including fee-for-service and value-based care, are central to understanding how providers are compensated. Compliance with Medicare’s regulations is mandatory to ensure accurate reimbursement. This includes understanding medical necessity, documentation requirements, and coding accuracy. Familiarizing yourself with Medicare’s audit and enforcement processes, including the Recovery Audit Contractor (RAC) program, is essential for staying compliant and avoiding costly errors. Ensuring adherence to Medicare’s guidelines will protect you from audits and financial penalties.
Navigating the Medicare Appeals Process
Understanding the Medicare appeals process is essential for resolving disputes and ensuring appropriate reimbursement. There are different levels of appeal, including redetermination, reconsideration, and hearings, each requiring specific documentation. Providers must also familiarize themselves with the appeals timeline, which includes strict deadlines and timeframes. By learning how to effectively navigate this process, providers can address denied claims and ensure appropriate compensation for services rendered.
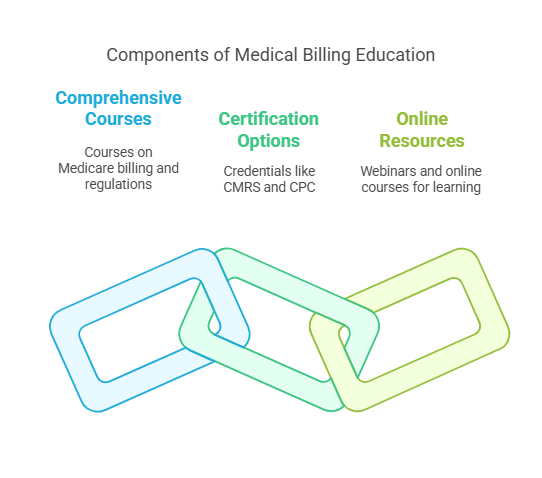
Medical Billing Education and Training
Medical billing education and training are vital for healthcare professionals who work with Medicare claims. Comprehensive courses on Medicare billing and regulations provide the knowledge needed to navigate the system. Certification options, such as the Certified Medical Reimbursement Specialist (CMRS) and Certified Professional Coder (CPC), help professionals demonstrate their expertise. Online resources and training tools, including webinars and online courses, offer immediate access to materials and lifetime resources for continued learning.
Leveraging Technology for Efficient Medicare Billing
Technology plays a critical role in streamlining Medicare billing processes. Electronic Health Records (EHRs) and Practice Management Systems (PMS) allow providers to automate billing tasks, increasing efficiency and reducing errors. Familiarity with Medicare’s Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) system is essential for successful electronic billing. Embracing technology ensures that billing processes are both accurate and timely, improving overall practice management.
Best Practices for Medical Practices
Implementing best practices for billing, coding, and compliance is essential for any medical practice working with Medicare. Accurate and timely billing is critical for maintaining cash flow and ensuring proper reimbursement. Providers must adhere to Medicare’s guidelines for medical practices, particularly regarding documentation and medical necessity. Effective billing and coding processes help minimize errors and improve the efficiency of medical practices.
Fraud Prevention and Detection in Medicare Billing
Fraud prevention is a key aspect of Medicare billing. Practices must be vigilant against fraud and abuse, including upcoding, unbundling, and billing for services not rendered. The American Medical Association (AMA) and the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) provide resources to help prevent and detect fraud. Staying informed about Local Coverage Determinations (LCDs) and National Coverage Determinations (NCDs) helps avoid billing errors and fraudulent activities. Accurate coding and tools such as prior authorization and the Advance Beneficiary Notice (ABN) help prevent fraudulent claims. Regular audits of Medicare claims are effective in identifying and addressing fraud.
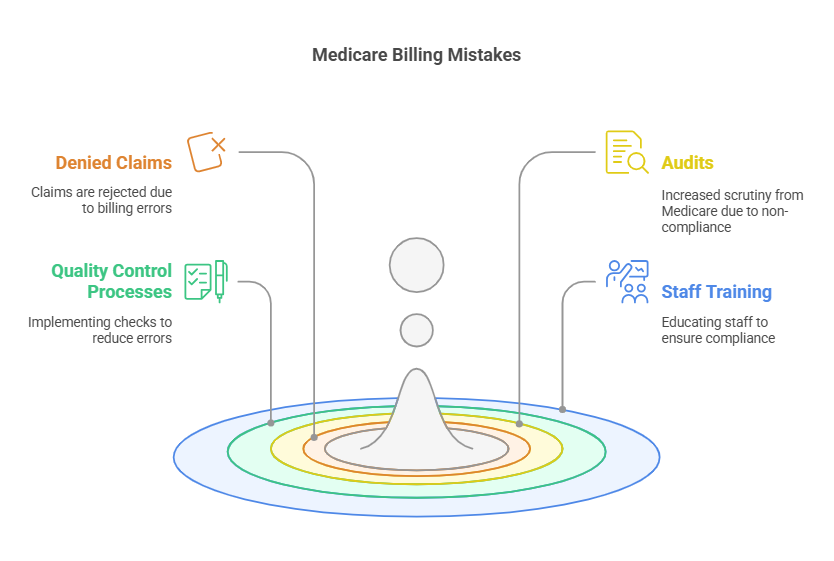
Common Medicare Billing Mistakes to Avoid
Common Medicare billing mistakes, such as errors in coding, billing, and documentation, can lead to denied claims and audits. Providers must familiarize themselves with Medicare’s guidelines for avoiding these mistakes. Implementing quality control processes, such as regular audits and staff training, helps reduce errors and ensures compliance.
Conclusion: Key Takeaways for Mastering Medicare Billing Success
To master Medicare billing, ongoing education and training are essential. Understanding Medicare’s billing processes, coding rules, and reimbursement methodologies provides the foundation for success. Providers must remain compliant with Medicare’s guidelines to avoid costly errors and fraud. Utilizing available resources, including online courses and webinars, ensures continued learning and up-to-date knowledge on Medicare billing.
Six Lesser-Known Facts About Medicare Billing:
Medicare Advantage Plans have unique billing rules: Unlike traditional Medicare, Medicare Advantage plans have their own set of billing rules that providers must adhere to. Understanding these rules is key for accurate billing.
Medicare’s Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) system: The EDI system is an integral part of Medicare's electronic billing process. It allows for efficient claim submission and reimbursement processing.
The Recovery Audit Contractor (RAC) program: RAC auditors are tasked with identifying improper payments and ensuring Medicare compliance. Providers should regularly review claims to prevent mistakes that might trigger audits.
Learn more about the RAC program.Local Coverage Determinations (LCDs): LCDs help define Medicare coverage and reimbursement for specific services, making it essential for providers to stay informed about any changes.
Learn more about LCDs.Medicare’s compliance audit process: Medicare’s audits are an ongoing part of the billing system. Being proactive in staying compliant and conducting internal audits can help prevent issues before they arise.
Learn more about Medicare's audit process.Medical necessity documentation is critical: Accurate documentation that supports the medical necessity of services provided is essential to avoid claim denials.
Learn more about medical necessity documentation
FAQs
-
Medicare has four parts: Part A (hospital insurance), Part B (medical insurance), Part C (Medicare Advantage), and Part D (prescription drug coverage). Each part covers different aspects of healthcare services.
-
To become a Medicare provider, you must meet specific requirements, such as obtaining the necessary credentials, completing the enrollment process, and ensuring compliance with Medicare regulations.
-
The Medicare appeals process allows providers and beneficiaries to challenge denied claims. It includes multiple levels of appeal: redetermination, reconsideration, and hearings, each with specific documentation requirements.
-
The Medicare EDI system facilitates the electronic submission of claims, making the billing process more efficient and reducing errors.
-
Common mistakes can be avoided by staying informed about Medicare’s billing guidelines, using accurate coding, ensuring proper documentation, and conducting regular internal audits.