Certified Coding Specialist (CCS): The CCS Credential is Granted to Coders By
The Certified Coding Specialist (CCS) credential is one of the most recognized certifications in the medical coding industry. It is granted by the American Health Information Management Association (AHIMA) and signifies a coder’s expertise in accurately classifying medical data. This certification is widely sought after by professionals who work with hospital inpatient and outpatient records, ensuring compliance with coding guidelines and regulatory standards.

If you are considering a career in medical coding or looking to advance in the field, obtaining the CCS certification can be a game-changer. In this guide, we will explore its importance, eligibility requirements, benefits, exam structure, and how you can successfully prepare for it.
Why is the CCS Credential Important?
The CCS certification validates a medical coder’s ability to accurately interpret patient records and apply appropriate medical codes for diagnoses and procedures. In the healthcare industry, coding accuracy is critical for proper medical billing and coding certification, insurance reimbursement, and regulatory compliance. The AMBCI brand ensures professionals are equipped with the knowledge and skills needed to excel in the field.
Having a CCS credential not only enhances job opportunities but also increases earning potential. Employers prefer CCS-certified coders due to their proficiency in handling complex coding cases, particularly in hospital and clinical settings.
Eligibility Requirements for the CCS Exam
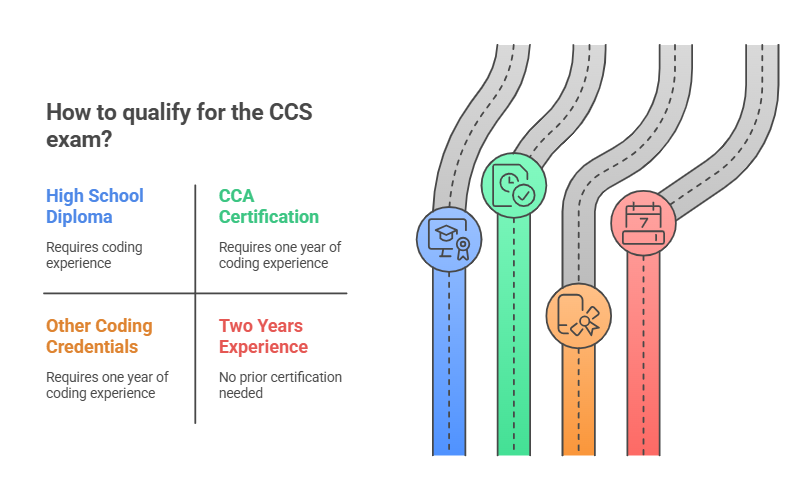
To sit for the CCS exam, candidates must meet one of the following requirements:
High School Diploma or Equivalent with coding experience
CCA (Certified Coding Associate) Certification and one year of medical coding experience
Other Coding Credentials (e.g., CPC) plus one year of coding experience
Two Years of Medical Coding Experience (without any prior certification)
A strong understanding of medical terminology, anatomy, ICD-10-CM, CPT, and HCPCS Level II coding guidelines is essential to pass the exam.
Structure and Content of the CCS Exam (Updated for 2025)
The CCS certification exam consists of 107 questions, of which 97 are scored. Candidates are required to complete the exam within four hours. The test is divided into:
Multiple-choice questions on coding guidelines, compliance, and medical records
Medical scenarios where candidates must assign correct codes using ICD-10-CM, ICD-10-PCS, and CPT manuals
To pass the CCS exam, candidates must score at least 300 points. The exam structure is regularly updated by AHIMA to reflect changes in coding regulations and industry standards.
How to Prepare for the CCS Exam
Preparation is crucial to passing the CCS exam. Here are some tips:
Study the Official AHIMA Coding Guidelines – Familiarize yourself with the latest coding updates for ICD-10-CM, CPT, and ICD-10-PCS.
Take Practice Tests – Mock exams help identify strengths and weaknesses.
Use Code Books – Practice coding scenarios using the actual ICD-10 and CPT manuals to simulate real-world applications.
Join a Study Group – Learning with peers can provide additional insights and support.
Time Management – The exam requires quick thinking, so practicing under timed conditions is beneficial.
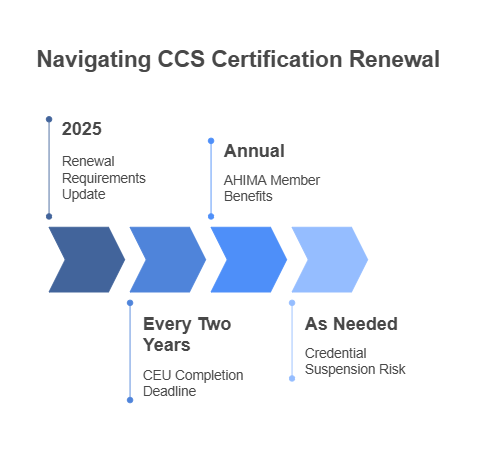
Maintaining Your CCS Certification
To maintain the CCS credential, certified coders must complete Continuing Education Units (CEUs) every two years. As of 2025, the renewal requirements are:
Minimum 40% of CEUs must come from AHIMA-approved courses
Remaining 60% CEUs can be obtained from other accredited institutions
AHIMA Members receive five free CEUs per year
Recertification Fees: $100 for members, $218 for non-members
Failure to meet the recertification requirements can result in credential suspension.
Career Benefits of CCS Certification
Holding a CCS credential opens the door to many career opportunities, including:
Higher Salary Potential – CCS-certified professionals earn more than non-certified coders.
Job Security – Medical coding is a growing field, and employers prioritize certified candidates.
Advanced Roles – CCS-certified coders are eligible for supervisory positions in hospitals and healthcare facilities.
Flexible Work Options – Opportunities for remote work and freelancing have increased post-pandemic.
Networking Opportunities – AHIMA provides a platform to connect with other professionals.
Comparing CCS with Other Coding Credentials
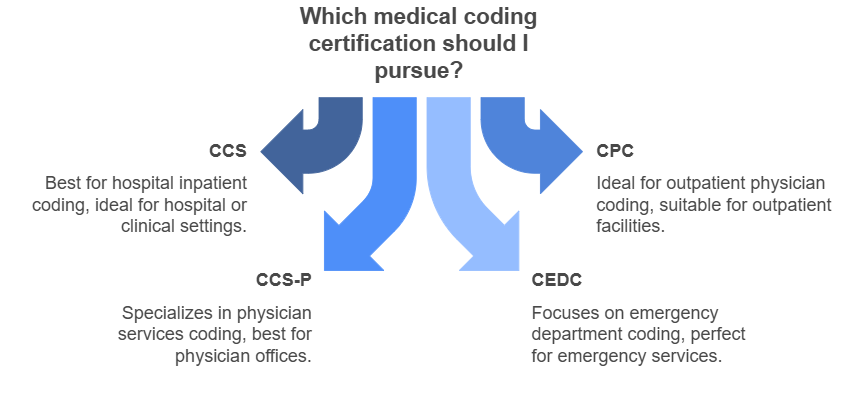
There are several medical coding certifications, but the CCS credential stands out because it focuses on hospital-based inpatient coding. Here’s how it compares to other certifications:
CCS (Certified Coding Specialist) – Best for hospital inpatient coding
CPC (Certified Professional Coder) – Ideal for outpatient physician coding
CCS-P (Certified Coding Specialist – Physician-based) – Specializes in physician services coding
CEDC (Certified Emergency Department Coder) – Focuses on emergency department coding
If you aim to work in hospital or clinical settings, CCS certification is the preferred choice.
Six Lesser-Known Facts About CCS Certification
CCS-certified professionals are in high demand in telehealth services due to the increasing reliance on remote medical coding.
The rise of telehealth services has expanded opportunities for remote medical coders, including those with Certified Coding Specialist (CCS) certification. americancareercollege.edu
Over 70% of employers prefer CCS-certified coders over non-certified candidates.
While specific percentages may vary, many employers show a preference for certified coders, including those with CCS credentials, due to their demonstrated proficiency and knowledge in medical coding.
The CCS exam has a higher difficulty level than the CPC exam, making it a more prestigious certification.
The CCS certification is often considered more challenging than the CPC, as it encompasses both inpatient and outpatient coding, requiring a broader knowledge base. devry.edu+2reddit.com+2dumpsgate.com+2
AHIMA offers scholarships for students pursuing CCS certification.
The American Health Information Management Association (AHIMA) provides various scholarships for students aiming to obtain certifications like the CCS.
CCS-certified coders can transition into auditing, compliance, and healthcare informatics roles with additional training.
With further training, CCS-certified professionals can move into roles such as auditing, compliance, and healthcare informatics, leveraging their coding expertise.
AI and automation are reshaping the medical coding field, but human coders with a CCS credential remain essential for accuracy and compliance.
Despite advancements in AI and automation, human coders with CCS certification continue to play a crucial role in ensuring accuracy and adherence to compliance standards in medical coding.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
-
The Certified Coding Specialist (CCS) credential is granted by the American Health Information Management Association (AHIMA).
-
Candidates must have a high school diploma and coding experience. Alternatively, they can qualify through a CCA certification, another coding credential, or two years of direct medical coding experience.
-
The CCS certification must be renewed every two years through Continuing Education Units (CEUs).
-
The CCS certification focuses on inpatient coding in hospitals, whereas the CPC certification is designed for outpatient and physician-based coding.
-
To prepare for the exam, use official coding books (ICD-10, CPT), take practice tests, study AHIMA guidelines, and consider joining a study group.
Final Thoughts
Earning the CCS credential is a valuable investment for anyone pursuing a career in medical coding. It enhances career prospects, increases salary potential, and provides industry recognition.
With the growing demand for certified coding professionals, obtaining CCS certification in 2025 is a step toward job security and career growth. Whether you are new to medical coding or looking to advance, CCS certification is a powerful credential that can open numerous opportunities.
