What a Medical Coder Does: Roles, Skills, and Career Insights
A medical coder is the silent force behind healthcare administration, ensuring every diagnosis, treatment, and procedure is translated into a standardized coding system. Without medical coders, healthcare providers would struggle with reimbursement, insurance claims would face constant denials, and patient records would be incomplete. If you’re considering a career in medical coding or pursuing medical coding certification to refine your expertise in this ever-evolving field, understanding the depth of this profession is crucial.
Medical coding has evolved significantly over the years. With advancements in AI-powered healthcare systems, regulatory updates, and an increasing demand for accurate healthcare documentation, medical coders are more essential than ever. This article delves into what a medical coder does, the critical skills required, career growth potential, and why this profession remains one of the most stable and rewarding paths in healthcare administration.

The Core of Medical Coding: Why It’s Essential in Healthcare
Medical coding is more than just assigning numbers to diagnoses and procedures. It is a critical function that ensures patient information is recorded accurately, insurance claims are processed seamlessly, and healthcare providers are reimbursed efficiently. Medical coders convert complex healthcare procedures into universally recognized codes such as ICD (International Classification of Diseases), CPT (Current Procedural Terminology), and HCPCS (Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System). To excel in this field, enrolling in the best medical coding classes for your career can equip you with the knowledge and skills needed to succeed.
By standardizing medical records, coders play a pivotal role in enhancing communication between healthcare providers, insurance companies, and government agencies. Accuracy in medical coding can prevent claim rejections, legal disputes, and potential compliance issues, making coders indispensable in the healthcare industry.

Key Responsibilities of a Medical Coder
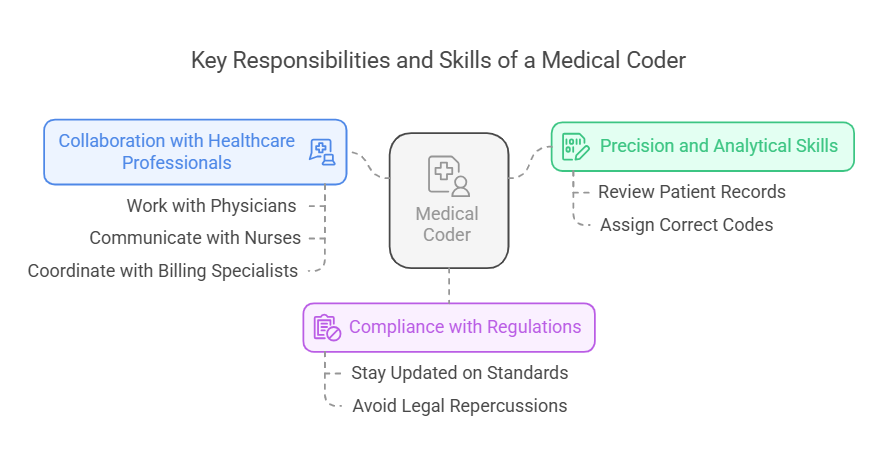
A medical coder’s day-to-day tasks require precision, analytical skills, and in-depth knowledge of medical terminology. Every entry in a patient’s record must be reviewed and assigned the correct code to ensure seamless healthcare operations. For those pursuing this career, financial aid for medical coders is often available to help ease the burden of education costs. Medical coders carefully analyze physician notes, lab reports, and treatment plans to extract essential details for coding. They ensure that the codes reflect the exact medical service provided, preventing any discrepancies that could lead to rejected claims. Their work is not just about assigning numbers; it’s about translating a patient’s medical journey into a structured, universally understood format.
Coders are also responsible for maintaining compliance with government regulations and insurance policies. Healthcare laws are continuously changing, and it is their job to stay updated on new coding standards to avoid errors that could lead to financial or legal repercussions. A single incorrect code could result in denied claims, revenue loss for healthcare providers, or even legal scrutiny, highlighting the need for their meticulous approach.
Collaboration is another crucial aspect of a coder’s role. They often work closely with physicians, nurses, and billing specialists to clarify medical procedures and ensure documentation accuracy. Effective communication skills are essential, as they must discuss discrepancies, resolve conflicts, and ensure proper coding to maintain high standards in patient care and financial transactions.
The Technology Behind Medical Coding: How AI and Software Are Changing the Field
In 2025, medical coding is not just about memorizing codes; it’s about understanding how technology integrates into healthcare documentation. With the rise of Electronic Health Records (EHRs), coding software, and Artificial Intelligence (AI)-powered automation, medical coders now use advanced tools to enhance accuracy and efficiency.
Automated coding systems assist coders by suggesting the most relevant codes based on patient records. However, human coders remain essential as AI tools still require oversight to prevent misinterpretation of complex cases. The demand for coders who understand both technology and medical coding standards continues to grow, making this a highly sought-after profession.
To work efficiently, medical coders must be proficient in:
EHR platforms that store and manage patient records
Coding software that simplifies the assignment of medical codes
AI-assisted tools that enhance accuracy and reduce manual workload
Understanding these systems allows medical coders to work more efficiently while maintaining high standards of accuracy and compliance.

Salary, Job Growth, and Career Opportunities in Medical Coding
The medical coding industry is thriving, with job opportunities expanding year after year. The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics projects an 8% job growth for medical coders from 2022 to 2032, outpacing many other professions. With an aging population and increasing healthcare demands, the need for skilled medical coders continues to rise.
Salaries for medical coders vary based on experience, certification, and location. The median annual salary is approximately $48,780, but those with advanced certifications and specializations can earn well over $80,000 per year. Certified Professional Coders (CPCs) typically have higher earning potential than non-certified coders, highlighting the importance of obtaining recognized credentials.
The career path in medical coding is also diverse, offering opportunities to specialize in areas such as:
Inpatient Coding – Focuses on hospital stays and extensive treatments
Outpatient Coding – Deals with procedures performed in clinics and ambulatory settings
Surgical Coding – Requires an in-depth understanding of surgical procedures
Risk Adjustment Coding – Ensures accurate reimbursement for healthcare providers based on patient conditions
Compliance Coding – Ensures all codes adhere to regulatory and legal guidelines

Table: Average Medical Coder Salary by Certification Level (2025 Data)

FAQs
What is the role of a medical coder?
A medical coder translates patient diagnoses, treatments, and medical procedures into standardized codes. These codes are used for insurance claims, reimbursement, and accurate medical record-keeping.
Which skill is most crucial for a medical coder?
Attention to detail is the most critical skill. Even a small error in coding can result in claim denials, financial losses, or compliance issues. Understanding medical terminology and coding systems is equally important.
What computer skills do you need for medical coding?
Medical coders should be proficient in EHR platforms, coding software, and AI-assisted coding tools. Strong typing skills, familiarity with spreadsheets, and an understanding of healthcare compliance software are also beneficial.
What is a professional summary for a medical coder?
A professional summary for a medical coder should highlight expertise in ICD, CPT, and HCPCS coding systems, knowledge of insurance claim processing, and experience with healthcare compliance. It should also emphasize accuracy, attention to detail, and proficiency in medical coding software.
What are the biggest challenges medical coders face?
Medical coders deal with constant updates in coding regulations, insurance claim rejections, and evolving AI-assisted technology. Staying updated with certifications and training is essential to overcome these challenges.
Is medical coding a good career choice in 2025?
Yes, medical coding remains one of the most stable and well-paying careers in healthcare. With the rise of remote medical coding jobs and increased demand for accurate healthcare documentation, it is an excellent career option.
How can I become a medical coder without experience?
Enroll in an accredited medical coding course, obtain a certification like CPC or CCS, and gain practical experience through internships or entry-level roles. Continuous learning and networking can help secure a stable position.
Can medical coders work from home?
Yes, remote medical coding jobs are increasingly available, providing flexibility and work-life balance. Many healthcare organizations hire certified coders for remote positions, making it a viable option for those seeking flexible work arrangements.
Conclusion
Medical coding is a dynamic and rewarding profession that continues to grow in importance. As healthcare systems evolve and technology integrates further into medical documentation, the demand for skilled coders and clinical trial managers remains strong. Whether you're entering the field or advancing your career, staying informed, obtaining certifications, and embracing new technologies will set you up for long-term success in medical coding.
