What Is a Medical Biller
Medical billing is essential to the healthcare revenue cycle, ensuring providers receive timely and accurate payments. Without medical billers, healthcare facilities would face financial instability, and patients would struggle with billing issues. But what exactly does a medical biller do, and how is it different from medical coding? This guide explores their evolving role, responsibilities, career prospects, and essential skills needed to succeed in 2025, including the importance of medical billing certification, which demonstrates expertise in handling the complexities of healthcare billing processes and increases job opportunities in this growing field.

Understanding the Role of a Medical Biller in 2025
Medical billers serve as financial navigators in healthcare, ensuring providers are compensated for the services they offer to patients. Their primary responsibilities involve translating healthcare services into billing claims, submitting these claims to insurance companies, and following up to secure payments. However, their role extends far beyond claim submission.
In 2025, medical billers are expected to handle more complex tasks as technology and regulatory policies continue to evolve. With the rise of artificial intelligence (AI) and automation, billers must adapt to new digital tools while maintaining a human touch in resolving billing disputes. Understanding medical policies, payer regulations, and coding accuracy is more critical than ever, as errors in medical billing can lead to claim denials, financial losses, and compliance issues. To stay competitive, it’s essential to explore the best medical billing classes for your business, ensuring you and your team are well-equipped to navigate these changes and meet industry standards.
Medical billers must also stay ahead of frequent changes in healthcare laws, insurance requirements, and reimbursement models. For example, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) frequently updates billing codes and guidelines, requiring billers to be agile in their approach to submitting and managing claims.

The Difference Between Medical Billing and Coding
Medical billing and medical coding are often mentioned together, but they serve distinct functions within the healthcare revenue cycle. Medical coding is the process of translating a patient’s medical records into standardized codes, such as ICD-10 (diagnoses) and CPT (procedures). These codes are then used by medical billers to submit claims to insurance companies.
While medical coders focus on accuracy in translating patient encounters into codes, medical billers ensure that these codes are applied correctly for insurance claims. A medical biller bridges the gap between healthcare providers, insurance companies, and patients to make sure the financial aspect of healthcare operates smoothly.
The success of a medical biller heavily relies on collaboration with medical coders. Coding inaccuracies can lead to claim denials, which in turn result in delayed payments. In some cases, medical billers may need to have coding knowledge to identify errors and work closely with coders to correct them before claims are submitted.
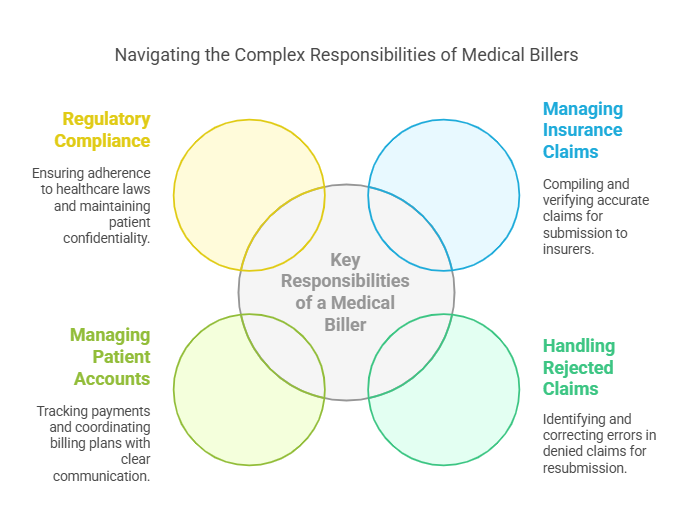
Key Responsibilities of a Medical Biller
Medical billers handle multiple responsibilities that go beyond submitting insurance claims. They play a vital role in managing the financial health of healthcare practices. Their responsibilities include processing claims, handling patient billing inquiries, reviewing denied claims, reconciling accounts, and ensuring all transactions are accurately documented.
One of the most critical functions of a medical biller is managing insurance claims. This process starts when a healthcare provider renders services to a patient. The medical biller then compiles all necessary details, including diagnostic codes, procedure codes, and patient demographic information, to create a claim. Before submitting the claim, they must verify its accuracy to prevent denials.
A crucial aspect of medical billing is handling rejected claims. Insurance companies may deny claims for various reasons, including missing information, coding errors, or lack of prior authorization. When a claim is denied, the medical biller must identify the reason, correct any mistakes, and resubmit the claim to ensure payment is received.
Beyond insurance claims, medical billers also manage patient accounts. They track payments, send out billing statements, and coordinate payment plans for patients who may be unable to pay their medical bills in full. Clear communication with patients is essential, as they often have questions about insurance coverage, out-of-pocket expenses, and payment options.
Medical billers must also stay updated with regulatory compliance. Healthcare laws, such as HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act), require strict confidentiality when handling patient financial records. Ensuring compliance with these regulations is a core responsibility of medical billers.
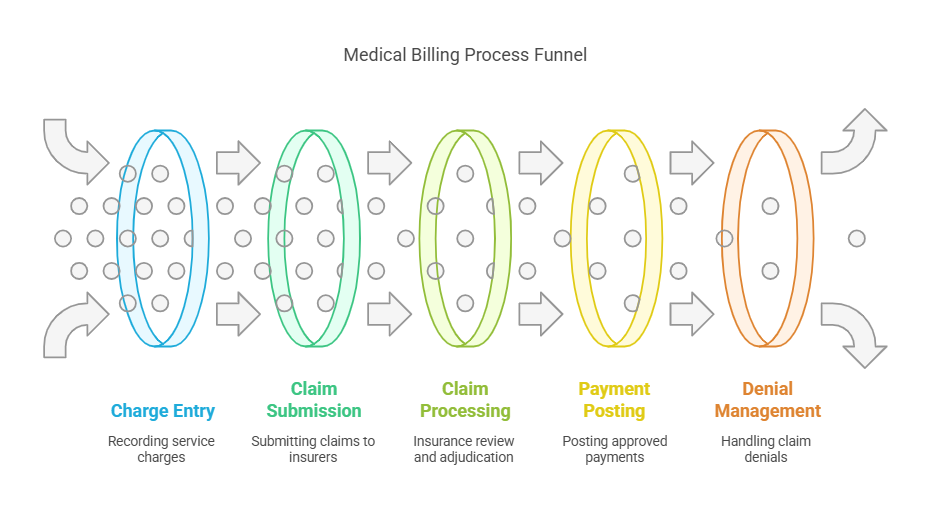
The Medical Billing Process: From Patient Visit to Payment
The medical billing process is a multi-step cycle that ensures healthcare providers receive payment for services rendered. The process begins with patient registration and ends when the provider receives full payment.
Patient Registration: The patient's demographic and insurance details are collected. Accuracy at this stage is critical to avoid claim denials.
Charge Entry: After a medical service is provided, charges are recorded using standard medical codes.
Claim Generation and Submission: Medical billers compile all relevant information and submit the claim to insurance companies.
Claim Processing and Adjudication: The insurance company reviews the claim, approves or denies it, and determines the payment amount.
Payment Posting: Approved claims result in payments from insurers. Any remaining balance is billed to the patient.
Accounts Follow-Up and Denial Management: If a claim is denied, the biller must identify the reason, make necessary corrections, and resubmit it.
Errors at any stage of this process can lead to delayed payments or financial losses for healthcare providers, making the role of a medical biller indispensable.
The Future of Medical Billing: AI, Automation, and Industry Trends
As technology advances, medical billing is evolving. Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are being integrated into billing software to automate tasks such as claim scrubbing, fraud detection, and insurance verification. These advancements reduce human errors and speed up payment processing.
However, automation does not replace medical billers; rather, it enhances their efficiency. Billers must now adapt to working with AI-driven tools while maintaining critical thinking and problem-solving skills to handle complex cases that automation cannot address.
The increasing shift toward value-based care is also influencing medical billing. Traditional fee-for-service models are being replaced with outcome-based reimbursement models, requiring billers to navigate new billing structures and ensure compliance with emerging healthcare policies.

Medical Billing Salary Expectations and Career Growth
Medical billing offers competitive salaries, with variations based on experience, education, certification, and location. The demand for medical billers is expected to continue growing due to the increasing need for healthcare services.

Medical billers who earn certifications, such as Certified Professional Biller (CPB) or Certified Medical Reimbursement Specialist (CMRS), can command higher salaries and better job opportunities.
FAQs on Medical Billing
What is the golden rule in medical billing?
The golden rule in medical billing is accuracy. Ensuring claims are error-free before submission prevents delays, denials, and revenue loss.
What does a medical biller need to know?
A medical biller must understand medical terminology, insurance policies, coding systems, compliance regulations, and billing software.
What is the most common rejection in medical billing?
The most common rejection is incorrect patient or insurance details. Errors in demographic information or missing authorization can lead to claim denials.
Which medical biller makes the most money?
Medical billers working in specialized fields, such as hospital revenue cycle management or coding-billing hybrid roles, tend to earn the highest salaries.
Can medical billers work remotely?
Yes, many medical billers work from home, especially with the rise of electronic health records (EHR) and cloud-based billing systems.
What is the hardest part of medical billing?
Handling claim denials and navigating complex insurance policies can be challenging, requiring strong analytical and problem-solving skills.
Is certification necessary to become a medical biller?
While not mandatory, certification enhances job prospects and earning potential.
What software do medical billers use?
Medical billers use practice management software, electronic health records (EHR), and AI-driven claim scrubbing tools.
Final Thoughts on Medical Billing in 2025
Medical billing is a dynamic and ever-evolving field that requires precision, adaptability, and a keen understanding of the healthcare revenue cycle. As technology reshapes the industry, the demand for skilled medical billers will continue to grow, making it a lucrative and stable career choice for those willing to master the complexities of healthcare finance. For official guidelines and industry regulations, professionals can refer to the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS)
