What is Advanced Medical Coding? A Comprehensive Introduction
Medical coding is a fundamental part of the healthcare industry. It involves translating medical diagnoses, procedures, and services into universal codes used by healthcare providers, insurers, and other entities. Medical coders are essential for accurate billing, ensuring that healthcare providers receive proper reimbursement for services rendered. But within the field of medical coding, there is a distinction between basic and advanced coding. Advanced medical coding requires a deep understanding of complex codes, medical terminology, anatomy, and regulatory requirements. In this blog post, we will explore what advanced medical coding is, its importance, and how it differs from basic coding.
Understanding Advanced Medical Coding
Advanced medical coding refers to the process of assigning specific codes to medical diagnoses and procedures based on comprehensive clinical documentation. These codes are used for billing purposes and help healthcare providers receive reimbursement from insurance companies. Advanced coders work with the most complex coding systems in the healthcare industry, including ICD-10, CPT, and HCPCS Level II codes. The work of an advanced medical coder ensures that medical records are accurately translated into standardized codes that can be used across the healthcare system. When evaluating this field, it’s important to consider the Medical Billing and Coding Pros and Cons. While advanced medical coding offers opportunities for specialization and high job demand, it also comes with challenges such as staying up-to-date with ever-changing regulations and managing the complexity of various coding systems.
The Role of an Advanced Medical Coder
In the intricate world of healthcare, where attention to detail is paramount, the role of an advanced medical coder cannot be overstated. These professionals serve as the linchpin in the claims management system, ensuring that every medical service, procedure, and diagnosis is properly documented and assigned the correct code. Their work is pivotal to the smooth functioning of healthcare systems, facilitating not only claims submissions and payment processing but also ensuring that medical practices stay compliant with complex regulations. Understanding the nuances of medical coding and the intricacies involved in this profession highlights its critical role in the modern healthcare landscape.
What is Advanced Medical Coding?
Medical coding is a fundamental part of the healthcare revenue cycle. It involves translating medical procedures, diagnoses, and services into universally accepted codes using specialized coding systems like ICD-10 (International Classification of Diseases), CPT (Current Procedural Terminology), and HCPCS (Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System). Advanced medical coders, who possess an extensive knowledge base and expertise, go beyond the basic functions of medical coding to deal with more complex cases and specialty areas.
While basic medical coders may focus on general coding tasks, advanced medical coders handle intricate medical conditions, complex procedures, and specialty services. Their responsibilities often extend to specific fields such as oncology, cardiology, and orthopedics, where in-depth knowledge of medical terminology and disease processes is essential. The codes they assign are used for various purposes, including billing insurance companies, tracking patient data, and ensuring proper reimbursement for healthcare providers.
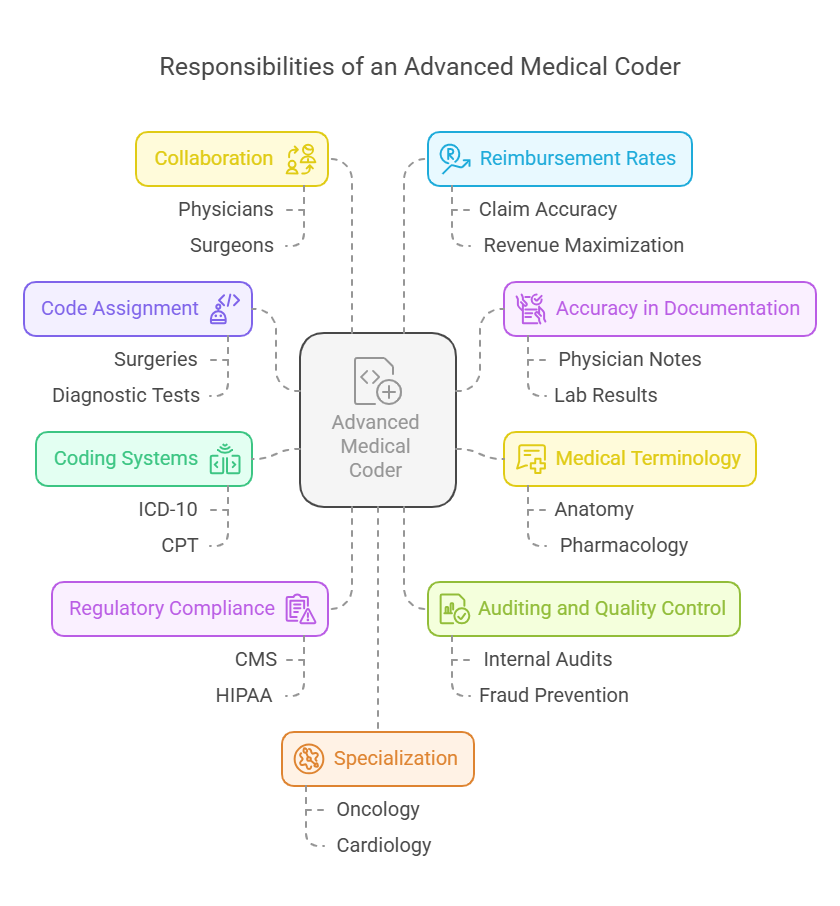
Responsibilities of an Advanced Medical Coder
An advanced medical coder's role goes far beyond simply assigning codes to medical records. Their responsibilities are multifaceted, requiring a combination of technical skills, medical knowledge, and attention to detail. The following are some of the core tasks that define the role of an advanced medical coder:
Code Assignment for Complex Cases
Advanced medical coders are entrusted with handling complex cases that require a deep understanding of medical conditions, treatments, and procedures. They assign codes for surgeries, diagnostic tests, treatments, and other healthcare services, ensuring that each code accurately reflects the patient's condition and the services provided. Their expertise ensures that even the most intricate procedures are accurately represented in the medical record.Ensuring Accuracy in Documentation
One of the most critical aspects of medical coding is ensuring accuracy in the assignment of codes. Inaccurate coding can result in claim denials, delayed payments, or legal issues related to fraud. Advanced coders meticulously review clinical documentation, including physician notes, lab results, and diagnostic imaging, to ensure the codes assigned are in full compliance with medical and insurance requirements.Understanding Complex Medical Terminology
To accurately assign codes, advanced medical coders must have an in-depth understanding of medical terminology. This includes knowledge of human anatomy, disease processes, pharmacology, and surgical techniques. Their ability to decipher complex medical language enables them to assign the correct codes that accurately reflect the services provided.Working with Various Coding Systems
Advanced coders are proficient in using multiple coding systems, such as ICD-10, CPT, and HCPCS. Each system serves a distinct purpose:ICD-10 Codes: These are used to describe diagnoses and conditions.
CPT Codes: These describe medical procedures and services.
HCPCS Codes: These are used for products, supplies, and services that are not included in the CPT system. Advanced coders must be well-versed in all these systems to ensure that all healthcare services are documented comprehensively.
Compliance with Regulatory Requirements
Healthcare providers must adhere to strict compliance standards, including those set by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS), the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), and other governing bodies. Advanced coders must stay current with changes in regulations and coding guidelines to ensure that coding practices remain compliant with these evolving requirements. They play a key role in reducing the risk of audits and penalties that may arise from coding errors or non-compliance.Auditing and Quality Control
Advanced coders are often involved in auditing medical records to ensure the accuracy of codes and their proper use. They perform internal audits, reviewing both their own work and that of other coders, to identify potential errors or discrepancies. This function is critical in preventing fraud, ensuring that claims are processed correctly, and maintaining the integrity of medical data.Collaboration with Healthcare Providers
Effective communication between coders and healthcare providers is essential to ensure the accuracy of medical coding. Advanced coders often collaborate with physicians, surgeons, and other healthcare professionals to clarify unclear documentation, discuss coding choices, and ensure that all services are adequately documented. Their ability to understand clinical practices and medical procedures allows them to bridge the gap between medical professionals and insurance companies.Improving Reimbursement Rates
Accurate coding directly influences a healthcare provider's reimbursement rate. By ensuring that codes are accurate and reflective of the services provided, advanced coders help improve reimbursement rates from insurance companies. They help healthcare organizations maximize revenue by ensuring that every service rendered is appropriately compensated, reducing the chance of rejected claims and lost revenue.Specialization in Certain Fields
Many advanced medical coders specialize in particular fields of medicine, such as oncology, cardiology, or orthopedics. Specializing in a particular area of healthcare allows coders to develop a more in-depth understanding of the procedures and treatments involved, making them invaluable to healthcare providers in those specialties. Specialized coders are also better equipped to handle the unique challenges that come with coding for complex or uncommon medical conditions.
Skills Required for Advanced Medical Coders
To succeed as an advanced medical coder, professionals must possess a combination of technical skills, medical knowledge, and soft skills. Here are some key abilities required for this role:
Attention to Detail: The accuracy of codes is essential, as errors can lead to claim denials and compliance issues. Advanced coders must be meticulous and detail-oriented in their work.
Knowledge of Medical Terminology: A strong understanding of medical terminology, human anatomy, and disease processes is crucial for accurately assigning codes.
Proficiency in Coding Systems: Advanced coders must be proficient in using ICD-10, CPT, and HCPCS coding systems, as well as any other relevant software or tools.
Problem-Solving Skills: When faced with ambiguous or incomplete documentation, advanced coders must be able to resolve discrepancies by researching and seeking clarification from healthcare providers.
Communication Skills: Effective communication with healthcare providers, insurance companies, and other coders is essential for resolving issues and ensuring accuracy.
Staying Current with Regulations: Medical coding is constantly evolving, with frequent updates to coding systems and regulations. Advanced coders must stay current with these changes to remain effective in their roles.
The Future of Medical Coding
The field of medical coding is continuously evolving, especially with the increasing use of electronic health records (EHRs) and the rise of artificial intelligence (AI) in healthcare. While AI is poised to automate some aspects of coding, advanced coders will continue to play a vital role in ensuring the accuracy and integrity of medical data. As coding systems become more complex and specialized, the demand for skilled and knowledgeable advanced medical coders will only continue to grow.
Moreover, with the increasing focus on value-based care and population health management, advanced coders will be required to adapt to new models of care that focus on outcomes rather than volume. This shift in healthcare delivery will necessitate changes in how codes are used to track patient outcomes, making the role of advanced medical coders even more critical in the years to come.
The Basics of Medical Coding
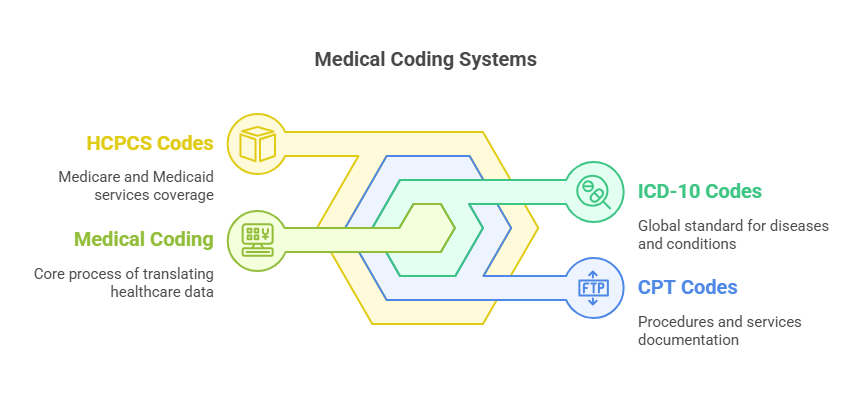
Before diving into the complexities of advanced medical coding, it’s important to understand the basics of medical coding. At its core, medical coding is the translation of healthcare services and diagnoses into numerical codes. These codes are essential for administrative tasks, including billing, insurance claims, and recordkeeping. There are three primary types of coding systems used in medical coding:
1. ICD-10 Codes (International Classification of Diseases)
The ICD-10 system is used to code diseases, conditions, and symptoms. It is a globally recognized system developed by the World Health Organization (WHO). The codes range from short, simple diagnoses to more complex medical conditions. For example, a simple diagnosis like the flu might be coded as J10, while a complex condition such as cancer would have its unique set of codes.
2. CPT Codes (Current Procedural Terminology)
CPT codes are used to document medical procedures and services provided by healthcare professionals. This system is maintained by the American Medical Association (AMA) and helps track a wide range of healthcare services, from routine visits to complex surgeries.
3. HCPCS Codes (Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System)
HCPCS codes are used for Medicare and Medicaid services and cover a range of healthcare services, including medical equipment, supplies, and certain drugs.
Differences Between Basic and Advanced Medical Coding
While basic medical coding covers essential codes for common diagnoses and procedures, advanced medical coding involves a deeper understanding and the ability to work with more complex medical cases. Let’s look at the key differences between basic and advanced medical coding:
1. Complexity of Codes
Basic Medical Coding: Involves standard diagnoses and procedures that are more straightforward and typically don't require in-depth understanding of complex medical scenarios.
Advanced Medical Coding: Deals with intricate medical conditions and sophisticated procedures that require extensive knowledge of human anatomy, disease processes, and medical terminology. Advanced coders must be familiar with coding systems like ICD-10, CPT, and HCPCS at an expert level.
2. Skill Level
Basic Medical Coding: Generally, anyone can learn basic coding through certification courses, which teach the fundamentals of coding and documentation.
Advanced Medical Coding: Requires years of experience and in-depth knowledge of clinical practices and regulatory guidelines. It also demands familiarity with coding tools, legal compliance, and quality control measures.
3. Type of Work
Basic Medical Coding: Focuses primarily on coding routine office visits, lab tests, and other common procedures.
Advanced Medical Coding: Involves more specialized coding for surgical procedures, rare diseases, and treatments that require a higher level of expertise and attention to detail.
Why is Advanced Medical Coding Important?
The importance of advanced medical coding cannot be overstated. Accurate medical coding ensures that healthcare providers are reimbursed correctly for their services, which is critical for the financial stability of healthcare institutions. Additionally, advanced medical coding plays a significant role in maintaining compliance with healthcare regulations, including those set by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) and other regulatory bodies.
1. Financial Implications
Incorrect coding can lead to delayed or denied claims, which can result in financial losses for healthcare providers. Accurate coding is essential for ensuring that healthcare services are reimbursed correctly, ensuring that healthcare organizations can continue to operate smoothly.
2. Legal Compliance
Medical coding also plays a critical role in compliance with healthcare laws and regulations. The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), for instance, governs how patient data should be handled and requires strict adherence to medical coding standards. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in legal consequences for healthcare providers.
3. Streamlined Healthcare Processes
By using standardized coding systems, medical coders help streamline the administrative aspects of healthcare. Advanced medical coders ensure that claims are processed efficiently and accurately, leading to faster payments and a reduction in claim rejections.
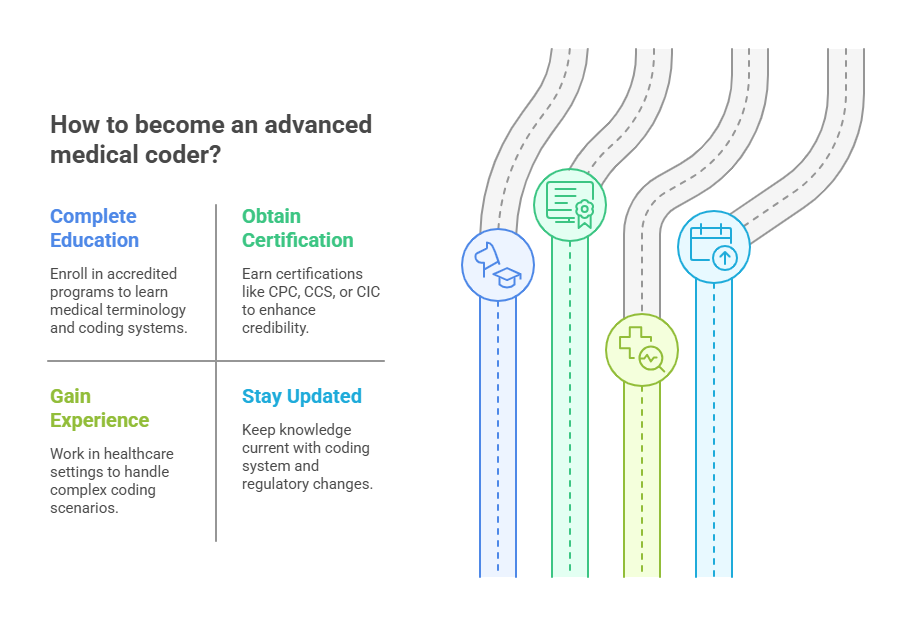
How to Become an Advanced Medical Coder
To pursue a career in advanced medical coding, one typically needs to follow several steps:
1. Complete Medical Coding Education
Many aspiring coders begin by enrolling in accredited medical coding programs. These programs typically cover the basics of medical terminology, anatomy, and the core coding systems (ICD, CPT, and HCPCS).
2. Obtain Certification
Earning certification is crucial for those looking to advance in the medical coding field. Popular certifications include:
Certified Professional Coder (CPC)
Certified Coding Specialist (CCS)
Certified Inpatient Coder (CIC)
3. Gain Practical Experience
Experience is key in advanced medical coding. Coders typically work in healthcare settings like hospitals, outpatient clinics, and physician offices. As they gain experience, they will work with more complex coding scenarios and develop the expertise needed for advanced coding.
4. Stay Updated
Advanced coders must stay informed about updates in coding systems and regulatory changes. The medical field is constantly evolving, and it’s important for coders to keep their knowledge up to date.
5 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
-
ICD-10 codes are used to classify diagnoses and diseases, while CPT codes are used to describe medical procedures and services.
-
It typically takes around 1-2 years to become an advanced medical coder, depending on education and certification requirements.
-
Yes, many medical coders work remotely for hospitals, insurance companies, and healthcare providers, especially with the rise of telemedicine and digital health services.
-
Skills needed include proficiency in medical terminology, knowledge of anatomy, familiarity with coding systems (ICD-10, CPT, HCPCS), attention to detail, and strong analytical abilities.
-
Certifications like the Certified Coding Specialist (CCS) or Certified Professional Coder (CPC) are highly valued in the industry.
5 Lesser-Known Facts About Advanced Medical Coding
Coding Can Prevent Fraud:
Healthcare Fraud Prevention – American Health Information Management Association (AHIMA)
The Role of Medical Coding in Healthcare Fraud Prevention – AAPC
Complex Codes Aren’t Just Numbers:
Medical Coders Can Specialize:
AI is Transforming Medical Coding:
It’s a High-Demand Field:
Conclusion: Why AMBCI?
At AMBCI, we understand the importance of advanced medical coding in today’s healthcare system. As a leading provider of medical coding and billing certifications, we are dedicated to providing our students with the knowledge and skills necessary to excel in this field. Our comprehensive courses and certification programs equip you with the expertise required to pursue a rewarding career in advanced medical coding.
We offer both medical coding and billing certification programs designed to meet industry standards. Whether you are just starting or looking to advance your skills, AMBCI is here to guide you every step of the way.