Essential Billing and Coding Regulations for Healthcare Professionals
Medical coding involves the use of standardized codes to describe diagnoses, procedures, and medical services, while medical billing focuses on submitting claims to insurance companies. Medical billing and coding certification ensures that professionals are well-equipped to manage these tasks accurately. Accuracy in coding and billing is critical, as errors can lead to claim denials, financial losses, and legal issues. Given the complexities of the billing process, healthcare organizations must prioritize thorough documentation and strict adherence to evolving regulations. AMBCI provides trusted certification and training for professionals in this field, helping them stay updated with industry standards.
Key Regulations in Medical Billing Compliance
The medical billing landscape is governed by several federal laws that protect patient data, prevent fraud, and ensure ethical billing practices.
HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) ensures that protected health information (PHI) is handled securely.
The False Claims Act prohibits the submission of fraudulent claims to Medicare or Medicaid. Violations can lead to severe penalties, including hefty fines and exclusion from federal healthcare programs.
The Anti-Kickback Statute (AKS) forbids healthcare providers from offering or receiving incentives for patient referrals.
The Affordable Care Act (ACA) mandates that healthcare providers implement compliance programs to qualify for reimbursement under federal programs.
The No Surprises Act (NSA) protects patients from unexpected out-of-network medical bills, ensuring transparency in pricing.
Adhering to these laws is crucial for avoiding legal repercussions and maintaining trust in the healthcare system.
Challenges in Medical Billing Compliance
Medical billing compliance is essential to prevent claim denials, financial penalties, and reputational damage. Healthcare providers face numerous challenges, including:
Frequent Regulatory Changes: Government policies, billing standards, and procedure codes are constantly updated, requiring healthcare organizations to stay informed.
Complexity in Reimbursement Processes: Reimbursement rates differ across various healthcare settings, making billing more challenging.
Risk of Fraud and Errors: Billing errors, whether intentional or accidental, can result in severe penalties and legal consequences.
Data Security Risks: With the increasing reliance on electronic health records (EHRs), protecting patient data from breaches is a growing concern.
To mitigate these challenges, healthcare organizations must conduct regular audits, implement compliance training, and adopt advanced billing software to ensure accuracy.
Medical Coding and Billing in Different Healthcare Settings
Medical billing and coding practices vary across different healthcare environments:
Hospitals: Medical coders and billers manage complex claims across multiple departments, such as emergency care, radiology, and surgery.
Clinics and Private Practices: While operating on a smaller scale, billing specialists in clinics must ensure accurate coding to maximize reimbursements.
Long-Term Care Facilities: These settings require specialized billing knowledge due to differences in insurance coverage and patient care requirements.
Understanding these distinctions is key to ensuring proper billing procedures across diverse healthcare settings.
Best Practices for Medical Billing and Coding
To maintain compliance and efficiency in medical billing, healthcare providers should follow these best practices:
Ensure Coding Accuracy: Use the correct ICD-10, CPT, and HCPCS codes to avoid claim denials.
Stay Updated on Regulatory Changes: Regular training and workshops help professionals stay current with evolving regulations.
Implement Automated Billing Systems: Advanced billing software can minimize errors and streamline claims processing.
Conduct Regular Audits: Identifying discrepancies early can prevent financial losses and legal repercussions.
Prioritize Patient Data Security: Adhering to HIPAA guidelines ensures the confidentiality and integrity of patient records.
By following these best practices, healthcare organizations can improve financial performance and reduce compliance risks.
Patient Privacy and Data Security in Billing and Coding
With the increasing digitization of healthcare records, protecting patient data has become more important than ever. HIPAA mandates strict protocols to safeguard sensitive health information. To enhance data security, healthcare providers should:
Use Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): This adds an extra layer of security to prevent unauthorized access.
Encrypt Electronic Health Records (EHRs): Data encryption protects PHI from cyber threats.
Implement Role-Based Access Controls: Restricting access to sensitive data minimizes risks.
Perform Regular Security Audits: Identifying vulnerabilities ensures proactive protection.
Educate Staff on Cybersecurity Best Practices: Employees should be trained to recognize phishing scams and other cyber threats.
Maintaining patient privacy and data security is essential for compliance and trust within the healthcare industry.
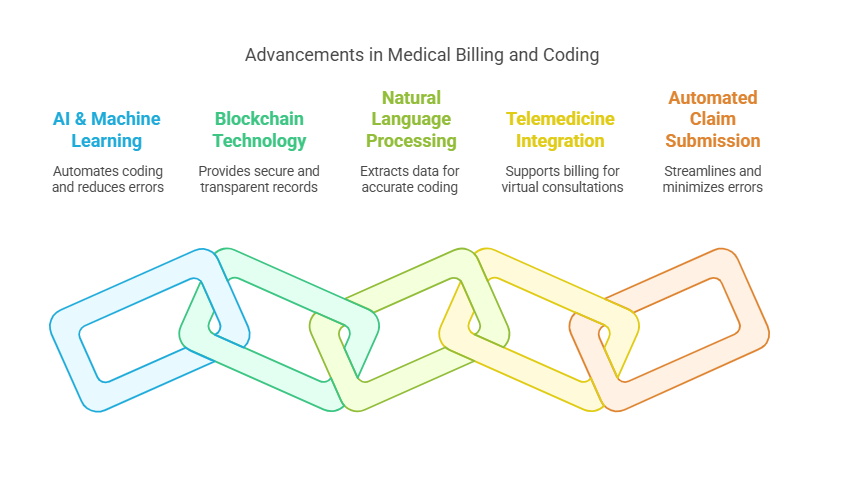
Technological Advancements in Medical Billing and Coding
Technology is revolutionizing medical billing and coding, improving accuracy and efficiency. Key advancements include:
Artificial Intelligence (AI) & Machine Learning (ML): AI-powered billing systems can automate coding, reducing human errors and speeding up claims processing.
Blockchain Technology: Enhances security by providing transparent and tamper-proof billing records.
Natural Language Processing (NLP): Helps extract meaningful data from medical records to improve coding accuracy.
Telemedicine Integration: Billing platforms now accommodate virtual consultations and remote patient monitoring.
Automated Claim Submission: AI-driven systems minimize errors and streamline reimbursement processes.
By leveraging these innovations, healthcare organizations can enhance billing accuracy, improve compliance, and optimize revenue cycle management.
Six Less-Known Facts About Medical Billing and Coding
Medical coding dates back to the 17th century, when the London Bills of Mortality were used to track diseases.
The ICD-10 coding system has over 70,000 codes, covering everything from common illnesses to unusual injuries like "struck by a duck" (W61.62XD).
Billing fraud accounts for nearly 10% of total healthcare expenditures, leading to billions of dollars in losses each year.
Some insurance companies use AI to detect fraudulent claims, flagging patterns that indicate potential abuse.
Medical coders can specialize in fields like oncology, cardiology, or emergency medicine, requiring additional certifications.
Outsourcing medical billing can reduce overhead costs by up to 30%, making it a cost-effective option for healthcare providers.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
-
Medical bills can have errors due to incorrect coding, duplicate charges, or misinterpretation of patient records. Regular audits and automated billing systems help minimize these mistakes.
-
The No Surprises Act protects patients from unexpected out-of-network medical bills, ensuring greater transparency and fairness in healthcare pricing.
-
Certifications like the Certified Professional Coder (CPC) from AAPC and the Certified Coding Specialist (CCS) from AHIMA are widely recognized in the industry.
-
AI automates coding, detects billing errors, and streamlines claim submissions, reducing human workload and improving accuracy.
-
Non-compliance can lead to claim denials, hefty fines, legal action, and potential exclusion from federal healthcare programs.