Understanding the Bureau of Labor Statistics Medical Coding Insights
The healthcare industry is evolving rapidly, and the field of medical coding and billing is no exception. As healthcare services expand, the demand for skilled medical coders has surged, making it a promising career path for those with strong analytical and organizational skills. The Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) offers valuable insights into the job outlook, employment trends, and educational requirements for this critical profession.
This guide delves into the current landscape of medical coding in 2025, exploring key trends, career paths, education, certifications, salary expectations, and technological advancements that shape this dynamic field.
1. The Growing Importance of Medical Coding and Billing Careers
Medical coding and billing professionals play a vital role in healthcare by translating patient care into universal codes for documentation, billing, and reimbursement. Every diagnosis, procedure, and medical service receives a unique code, ensuring accuracy in patient records and financial transactions.
According to the BLS, medical records specialists and health information technologists are essential for efficient healthcare delivery. Their work impacts everything from insurance claims to patient care quality.
Key Responsibilities of Medical Coders:
Assigning standardized codes to diagnoses and procedures using systems like ICD-11, CPT, and HCPCS.
Ensuring compliance with healthcare regulations and coding standards.
Collaborating with healthcare professionals to maintain accurate patient records.
Analyzing medical data for research, quality assurance, and financial planning.
BLS Source: U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics

2. Job Outlook and Employment Trends for 2025 and Beyond
The healthcare sector is one of the fastest-growing industries in the U.S., driven by an aging population and increased access to healthcare services. The BLS projects a 15% growth in employment for medical records specialists, including coders and billers, between 2024 and 2034 — significantly faster than the national average for all occupations.
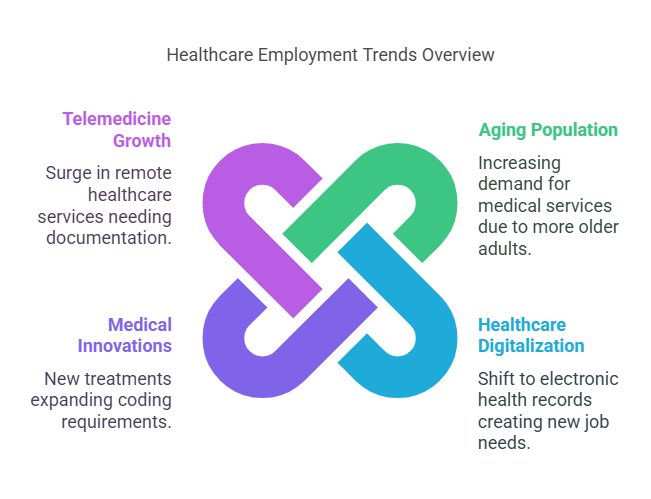
Factors Driving Demand:
Aging Population: An increasing number of older adults requires more medical services.
Healthcare Digitalization: The shift to electronic health records (EHRs) necessitates skilled coders.
Medical Innovations: New treatments and procedures continuously expand coding requirements.
Telemedicine Growth: Remote healthcare services have surged, requiring precise documentation.
Salary Insights: The median annual wage for medical coders was $52,400 in May 2024, with experienced professionals earning upwards of $90,000. Urban centers like New York, Los Angeles, and Chicago offer higher salaries due to increased demand.
BLS Source: Occupational Outlook Handbook
3. Career Paths and Specializations in Medical Coding
Medical coding isn't a one-size-fits-all profession. There are numerous specializations, each requiring unique skills and knowledge.
Popular Specializations:
Inpatient Coding: Coding for hospital stays and procedures.
Outpatient Coding: Focused on short-term patient interactions.
Risk Adjustment Coding: Evaluating patient risk profiles for insurance purposes.
Oncology Coding: Specializing in cancer treatments.
Career Progression:
Entry-Level: Medical Coding Specialist
Mid-Level: Certified Professional Coder (CPC)
Senior-Level: Health Information Manager
Leadership: Director of Health Information Services
With experience and certifications, medical coders can transition into roles like compliance officers or healthcare administrators.
Gov Source: Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services

4. Educational Pathways for Aspiring Medical Coders
Educational requirements for medical coders have evolved. While a postsecondary certificate remains the minimum, many employers now prefer candidates with an associate's or bachelor's degree.
Recommended Degrees:
Associate Degree: Health Information Technology
Bachelor's Degree: Health Administration or Public Health
Core Subjects:
Medical Terminology
Anatomy and Physiology
Health Data Standards
Healthcare Law and Ethics
Many institutions offer hybrid or fully online programs to accommodate working professionals.
Gov Source: National Center for Education Statistics

5. Certification and Licensing: Keys to Career Advancement
Certifications validate a coder's expertise and can significantly impact career growth. Employers often require credentials from recognized organizations like the AAPC or AHIMA.
Top Certifications for 2025:
Certified Professional Coder (CPC): Focuses on outpatient coding.
Certified Coding Specialist (CCS): Ideal for hospital coding.
Certified Inpatient Coder (CIC): Specialized for inpatient care.
Certified Risk Adjustment Coder (CRC): Essential for value-based care.
Certification Requirements:
Relevant educational background.
Passing a comprehensive exam.
Continuing education for recertification.
Gov Source: Health Resources and Services Administration

6. Salary and Compensation Trends in Medical Coding
The demand for skilled coders translates into competitive salaries and benefits. In 2025, the median annual wage for medical records specialists is expected to reach $55,000, with top professionals earning over $95,000.
Salary Influencers:
Experience Level: Entry-level coders start at approximately $40,000.
Location: Metropolitan areas offer higher wages.
Certification: Certified coders earn 20% more on average.
Additional Benefits:
Health insurance and retirement plans.
Flexible work options, including remote positions.
Continuing education stipends.

7. Work Environment and Conditions for Medical Coders
Medical coders work in diverse settings, from hospitals to insurance firms. The increasing adoption of telehealth has also opened doors to remote coding positions.
Common Workplaces:
Hospitals and Healthcare Systems
Private Medical Practices
Insurance Companies
Government Health Agencies
The job requires attention to detail, problem-solving skills, and the ability to adapt to evolving medical practices.

8. Technological Innovations Impacting Medical Coding
The integration of advanced technology has transformed medical coding into a more efficient and accurate process.
Key Innovations:
Artificial Intelligence (AI): Assists in code assignment and error detection.
Electronic Health Records (EHRs): Streamlines patient data access.
Blockchain Technology: Enhances data security.
Natural Language Processing (NLP): Interprets clinical documentation more effectively.
Staying updated with these technologies is essential for coders aiming for long-term career growth.

9. The Role of Medical Coding in Healthcare Compliance
Accurate coding is crucial for healthcare compliance. Coders must adhere to standards set by organizations like the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) and the World Health Organization (WHO).
Key Compliance Guidelines:
HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act)
ICD-11 (International Classification of Diseases)
CPT (Current Procedural Terminology)
Compliance ensures proper billing, minimizes fraud, and protects patient privacy.

10. Future Trends: What Lies Ahead for Medical Coders?
The field of medical coding will continue evolving alongside healthcare innovations.
Emerging Trends:
Increased Use of AI: Predictive analytics for better coding accuracy.
Telehealth Expansion: New codes for virtual care services.
Global Coding Standards: ICD-11 adoption worldwide.
Data Analytics Integration: Using coding data for healthcare improvements.
Medical coders who adapt to these changes will remain indispensable in the healthcare landscape.

Conclusion: A Promising Future for Medical Coders in 2025
Medical coding and billing professionals are the unsung heroes of healthcare documentation, ensuring accurate records, efficient billing, and seamless communication across medical systems. As the industry grows, the demand for skilled coders continues to rise, offering robust career opportunities.
Whether you're considering this field or already working within it, continuous learning, technological proficiency, and medical coding certification are essential for long-term success. The Bureau of Labor Statistics projects sustained growth, making medical coding a stable and rewarding career choice in the coming years.
Stay informed, stay certified, and contribute to the future of healthcare through this critical profession.
