Certified Coding Healthcare: Skills, Opportunities, and Career Path
Medical coding has become the backbone of modern healthcare systems. As healthcare evolves with advancements like telemedicine and AI integration, the need for accurate coding and compliant documentation is more critical than ever. This guide explores the updated landscape of medical coding in 2025, including essential skills, career paths, emerging trends, and job opportunities.
Why Medical Coding Matters More Than Ever
Medical coding translates complex healthcare services, diagnoses, and treatments into standardized alphanumeric codes. These codes ensure accurate billing, streamlined records, and compliance with healthcare regulations. With global healthcare expenditures surpassing trillions annually, efficient coding practices directly impact patient care, revenue management, and healthcare analytics. That is why medical coding is a great field to get into, you can make a great living after doing proper medical coding certifications.
Key Insights for Medical Coding in 2025
The medical coding profession is projected to grow by 10% by 2030, driven by increased healthcare demands and technological advancements.
Remote medical coding roles continue to rise, offering flexibility and access to a broader talent pool.
Certification and continuous learning remain crucial as coding standards evolve to accommodate new medical procedures and telehealth services.

Understanding Medical Coding: The Fundamentals
What Is Medical Coding?
Medical coding involves converting healthcare services into universally recognized codes. These codes facilitate communication between healthcare providers, insurance companies, and government agencies. Accurate coding ensures proper billing, supports healthcare analytics, and aids in population health management.
The process typically uses three primary code sets:
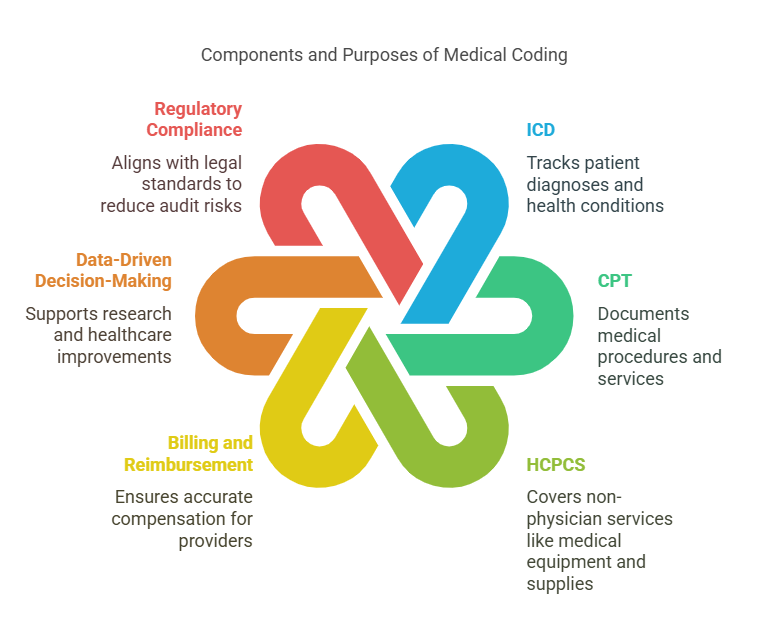
International Classification of Diseases (ICD): Tracks patient diagnoses and health conditions.
Current Procedural Terminology (CPT): Documents medical procedures and services.
Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System (HCPCS): Covers non-physician services like medical equipment and supplies.
The Purpose of Medical Coding
Medical coding serves multiple critical functions:
Billing and Reimbursement: Ensures healthcare providers receive accurate compensation.
Data-Driven Decision-Making: Supports research and healthcare improvements.
Regulatory Compliance: Aligns with legal and governmental standards, reducing risks of audits and penalties.
Patient Care Continuity: Provides clear, transferable records across healthcare institutions.
"Accurate medical coding is essential for efficient healthcare delivery and financial transparency." – Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) (cms.gov)
The Evolving Role of a Medical Coder in 2025
Medical coders have transitioned from traditional paperwork to dynamic roles requiring proficiency in digital tools, regulatory knowledge, and continuous education.
Core Responsibilities
Reviewing patient records for diagnoses, treatments, and services.
Assigning accurate ICD, CPT, and HCPCS codes.
Ensuring data accuracy for billing and insurance claims.
Collaborating with healthcare professionals to clarify documentation.
Key Competencies
Analytical Skills: Deciphering complex medical terms.
Attention to Detail: Minimizing errors that could impact patient care and revenue.
Technical Proficiency: Mastering Electronic Health Records (EHR) and coding software.
Regulatory Knowledge: Adapting to changes like ICD-11 implementation and telehealth coding requirements.
"Data integrity in healthcare starts with accurate medical coding." – American Health Information Management Association (AHIMA) (ahima.org)

Skills and Qualifications for Aspiring Medical Coders
The demand for skilled medical coders continues to rise, especially as telehealth and data analytics become healthcare mainstays. Success in this field requires a blend of technical knowledge, problem-solving abilities, and ongoing professional development.
Essential Skills
Medical Knowledge: Familiarity with medical terminology, anatomy, and physiology.
Coding Systems Proficiency: Expertise in ICD, CPT, and HCPCS standards.
Tech Savvy: Competence with EHR software and coding tools.
Critical Thinking: Ability to resolve discrepancies and validate documentation accuracy.
Communication: Collaborating with healthcare professionals to clarify codes.
Required Qualifications
High school diploma (minimum); associate's or bachelor's degree in health information management preferred.
Certification from recognized bodies like AAPC or AHIMA.
Practical experience through internships or entry-level roles.

Top Certifications for Medical Coders in 2025
Certified Professional Coder (CPC): Focuses on outpatient coding.
Certified Coding Specialist (CCS): Emphasizes inpatient coding.
Certified Inpatient Coder (CIC): Specialized in hospital coding.
"Certification boosts employability and credibility in the evolving medical coding landscape." – U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (bls.gov)
Emerging Trends Shaping Medical Coding in 2025
Medical coding is no longer confined to manual entries and static guidelines. Technological advancements and policy shifts have introduced new trends that are redefining the profession.
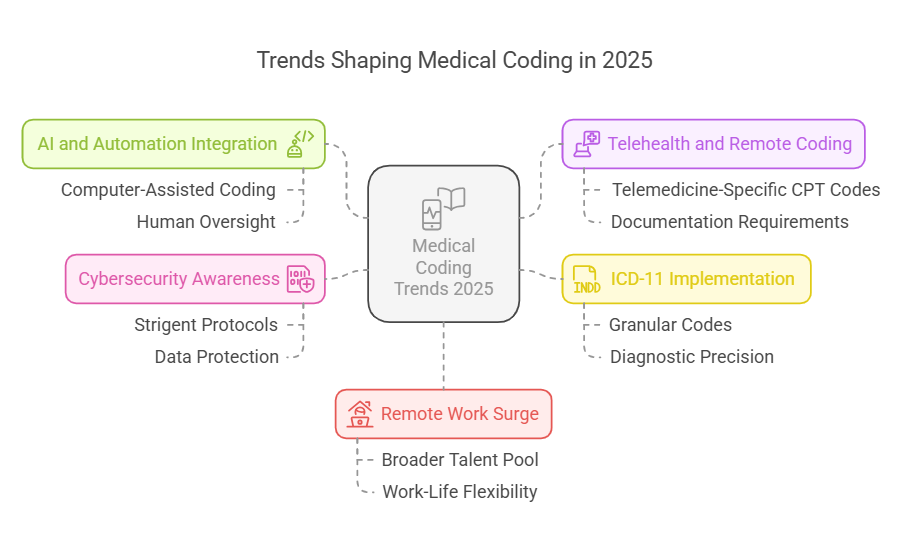
1. AI and Automation Integration
Artificial Intelligence (AI) applications like Computer-Assisted Coding (CAC) have streamlined code assignment processes, reducing human error and boosting productivity. While AI handles routine coding, human oversight remains essential to manage complex cases.
2. Telehealth and Remote Coding
Telehealth services, spurred by the pandemic, continue to expand. Coders must stay updated on telemedicine-specific CPT codes and documentation requirements.
3. ICD-11 Implementation
The transition from ICD-10 to ICD-11 introduces more granular codes, enhancing diagnostic precision. Medical coders must undergo retraining to adapt to these changes.
4. Cybersecurity Awareness
With patient data being a prime target for cyberattacks, coders must follow stringent protocols to protect sensitive information.
5. Remote Work Surge
The demand for remote coding professionals has surged, enabling healthcare providers to access a broader talent pool and allowing coders more work-life flexibility.
Career Opportunities in Medical Coding
Medical coding careers offer stability, growth potential, and diverse work settings. As healthcare services expand globally, certified coders are increasingly in demand.
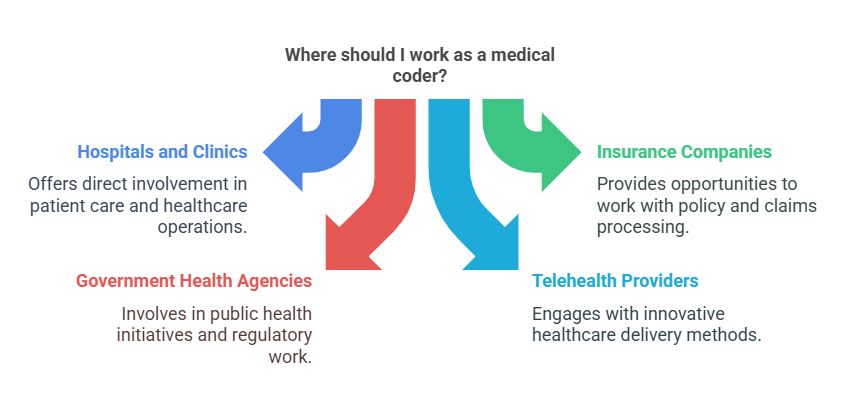
Where Do Medical Coders Work?
Hospitals and clinics
Insurance companies
Government health agencies
Telehealth providers
Medical billing firms
Salary Expectations in 2025
According to the AAPC, certified medical coders earn an average of $60,000 annually, with experienced professionals exceeding $80,000, especially in specialized areas like oncology and cardiology.
Growth Projections
The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics forecasts an 8-10% growth in health information jobs by 2030, outpacing the average for most professions.
"Healthcare information roles will continue to grow as data becomes central to patient care and administrative processes." – National Institutes of Health (NIH) (nih.gov)

Tools and Technologies Transforming Medical Coding
Modern medical coding relies heavily on technology to maintain accuracy, efficiency, and compliance.
Essential Coding Software
3M CodeFinder: Simplifies complex coding tasks.
Epic Systems: Integrates coding with EHR systems.
TruCode Encoder Essentials: Offers real-time coding assistance.
The Role of AI and Machine Learning
AI-driven tools predict code patterns, identify potential errors, and automate repetitive tasks, enabling coders to focus on cases requiring human judgment.

Best Practices for Medical Coders in 2025
To thrive in this evolving field, coders must adopt best practices that enhance productivity, ensure accuracy, and maintain compliance.
Continuous Education: Attend workshops, webinars, and industry conferences.
Regular Audits: Conduct self-audits to identify and rectify potential errors.
Collaboration: Communicate effectively with healthcare teams.
Stay Updated: Monitor regulatory changes, especially regarding ICD-11.
Use Reliable Resources: Refer to authoritative sources like CMS, AHIMA, and WHO.
How to Start a Career in Medical Coding
Step 1: Get Educated
Enroll in a reputable medical coding program that covers medical terminology, anatomy, and coding standards.
Step 2: Earn Certification
Pursue certifications like CPC or CCS to validate your skills.
Step 3: Gain Practical Experience
Participate in internships or entry-level roles to build real-world expertise.
Step 4: Apply for Jobs
Explore opportunities in hospitals, insurance companies, or remote coding platforms.
Step 5: Keep Learning
Engage in continuous education to stay ahead of industry trends.

Conclusion
Medical coding in 2025 remains a dynamic, essential field within healthcare. As technology, regulations, and healthcare demands evolve, skilled, certified coders will find abundant opportunities. By embracing continuous learning, adopting innovative tools, and adhering to best practices, medical coders can secure a rewarding, future-proof career.
