Comprehensive Guide to MACRA & Quality Payment Programs:
The Medicare Access and CHIP Reauthorization Act (MACRA), enacted in 2015, transformed healthcare reimbursement by shifting focus from volume-based payments to value-based care. This legislation introduced the Quality Payment Program (QPP), which ties reimbursement to quality performance rather than the number of services provided. For healthcare providers, understanding and navigating MACRA’s structure is crucial to ensuring compliance and maximizing reimbursement.
As the healthcare industry continues to evolve, MACRA and QPP are central to reshaping the future of patient care. Billing specialists, physicians, and healthcare administrators must stay informed about the program’s requirements, performance categories, and scoring mechanisms to thrive in this value-driven environment. This guide will explore the key components of MACRA and QPP, and provide actionable insights for professionals looking to succeed in value-based reimbursement systems.
What is MACRA?
History and Background of MACRA
The Medicare Access and CHIP Reauthorization Act (MACRA) was signed into law in 2015 to address longstanding issues with the Medicare reimbursement system. Prior to MACRA, the Sustainable Growth Rate (SGR) formula dictated Medicare payment rates for healthcare providers, but it was widely criticized for being unsustainable and for frequently requiring temporary fixes by Congress. These fixes created payment instability, making it difficult for providers to plan and invest in long-term healthcare improvements.
MACRA was introduced as a solution to provide financial predictability and encourage better patient outcomes. By repealing the SGR and replacing it with more value-driven reimbursement models, MACRA aimed to improve the quality of care while reducing overall healthcare costs. The law also established the Quality Payment Program (QPP), which incentivizes healthcare providers to deliver higher-quality care in a more efficient, patient-centered manner.
MACRA’s Key Goals and Objectives
The primary goals of MACRA are to improve patient care, increase healthcare efficiency, and reduce overall healthcare costs. To achieve this, the law focuses on shifting from a fee-for-service model to a value-based system where providers are reimbursed based on the quality of care they deliver. MACRA also aims to streamline reporting processes for providers, making it easier for them to track performance and make improvements.
One of MACRA’s key objectives is to provide financial incentives for providers who participate in the Quality Payment Program (QPP), which includes two pathways: MIPS (Merit-based Incentive Payment System) and APMs (Alternative Payment Models). Providers who excel in performance categories such as quality, cost, clinical improvement, and use of technology are rewarded with positive payment adjustments. The law also incentivizes healthcare innovation, encourages patient engagement, and promotes population health management to ensure that healthcare systems are more sustainable and effective over the long term.
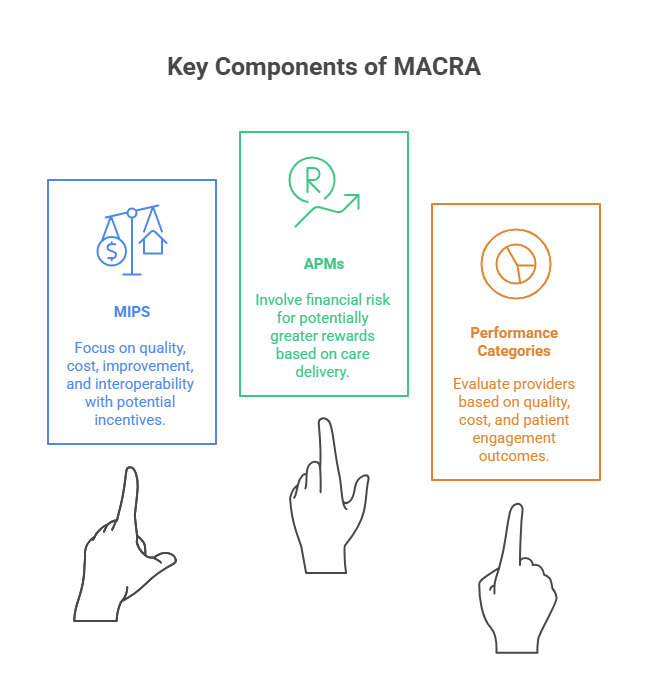
Key Components of MACRA
MIPS: Performance Categories and Scoring
The Merit-based Incentive Payment System (MIPS) is one of the two tracks under MACRA's Quality Payment Program (QPP). MIPS evaluates healthcare providers based on four key performance categories: Quality, Cost, Improvement Activities, and Promoting Interoperability. These categories determine how much a provider will be reimbursed under Medicare, with a higher performance score leading to positive payment adjustments.
Quality: This category measures how well providers perform in areas like patient outcomes, care coordination, and preventive services. Providers are assessed based on metrics like patient satisfaction, clinical outcomes, and the effectiveness of their treatments.
Cost: This category assesses the cost efficiency of the care provided, focusing on resource utilization, including hospitalization rates, medication adherence, and overall healthcare spending.
Improvement Activities: Providers must demonstrate their efforts to improve care quality through activities like patient education, care coordination, and access to healthcare.
Promoting Interoperability: This category evaluates how effectively providers use technology, particularly Electronic Health Records (EHR), to improve patient care, data sharing, and collaboration across the healthcare system.
APMs: How They Differ from MIPS
While MIPS focuses on performance-based reimbursement for individual healthcare providers, Alternative Payment Models (APMs) offer a different approach to value-based care. APMs allow healthcare organizations to take on more risk in exchange for the potential for higher rewards. APMs include Accountable Care Organizations (ACOs), patient-centered medical homes, and bundled payment arrangements, where providers are rewarded for coordinating care and improving patient outcomes across a whole patient population rather than on an individual basis.
In APMs, providers are incentivized to keep costs down and improve quality by coordinating care within a defined population. Unlike MIPS, where individual providers are scored based on their performance in the four categories, APM participants take on more financial responsibility for the health of their patient populations. If they meet performance targets, they receive a higher reimbursement, but they also bear the risk of financial penalties if their performance falls short.
While both MIPS and APMs aim to move the healthcare system toward value-based care, APMs typically offer more flexibility and the potential for greater financial rewards, while MIPS provides a more standardized, performance-based approach for healthcare providers at all levels.
Quality Payment Programs (QPP): Overview
How QPP Affects Reimbursement Rates
The Quality Payment Program (QPP) is designed to transition healthcare providers from a traditional fee-for-service model to a more value-based payment system. Under QPP, providers are reimbursed based on the quality of care they deliver rather than the volume of services provided. The performance categories under MIPS and APMs help determine reimbursement rates.
Providers who demonstrate high-quality care through patient outcomes, cost efficiency, and care coordination are eligible for positive payment adjustments. Conversely, those with lower performance scores may face payment penalties. QPP’s impact on reimbursement encourages healthcare providers to focus on delivering better care, improving patient outcomes, and controlling healthcare costs.
One significant change under QPP is the penalty structure for poor performance. If a provider fails to meet the required benchmarks, they risk reduced reimbursements for Medicare services. This system creates a clear incentive for providers to invest in quality improvements and integrate advanced healthcare technologies to enhance patient care while reducing costs.
Performance Categories in QPP
QPP evaluates provider performance across four key categories:
Quality: This category focuses on the outcomes of care delivered to patients. Providers are measured based on metrics like hospital readmission rates, preventive care compliance, and patient satisfaction. High-quality care in these areas directly contributes to higher reimbursement rates.
Cost: Cost performance is assessed by looking at how well healthcare providers manage the cost of care for their patient populations. This includes evaluating resource utilization and the ability to provide cost-effective treatments without sacrificing quality.
Improvement Activities: Providers are rewarded for participating in activities that promote continuous quality improvement. These may include care coordination, patient engagement, and implementing innovative care practices. It’s essential for providers to show progress in improving their healthcare processes and outcomes.
Promoting Interoperability: This category measures how effectively providers use technology to enhance patient care and data sharing. Providers who adopt EHR systems, ensure data accuracy, and facilitate information exchange across care teams receive higher scores in this category, leading to positive payment adjustments.
QPP not only emphasizes quality but also rewards providers who adopt health IT systems, collaborate with care teams, and focus on improving the patient experience. These categories collectively drive a more patient-centered approach to healthcare while ensuring providers are compensated fairly for delivering high-value care.
How to Succeed in the Quality Payment Program
Importance of Reporting
Accurate reporting is critical for success in the Quality Payment Program (QPP). Providers must document and report their performance in key areas such as quality care, cost efficiency, and patient engagement to ensure they meet QPP’s performance standards. These reports are used to calculate performance scores, which directly affect reimbursement rates. Failure to report accurately or on time can lead to penalties and missed opportunities for positive payment adjustments.
Timely and complete reporting ensures that providers meet the necessary benchmarks for each category under MIPS, including quality measures, cost reporting, and improvement activities. By submitting data on quality outcomes, EHR utilization, and care coordination, providers improve their performance scores and avoid penalties. The more detailed and accurate the performance data, the better the reimbursement rate providers can secure.
Tips for Maximizing Your Performance Score
Stay Up-to-Date with QPP Requirements: As regulations and performance measures evolve, it’s crucial for providers to stay informed about the latest updates to the QPP. Regularly reviewing the CMS updates and performance measures ensures that your practice remains compliant and maximizes its score potential.
Leverage Technology: Providers should adopt advanced EHR systems and billing software that streamline reporting and help ensure data accuracy. Promoting interoperability through integrated platforms enables seamless data collection and reduces the risk of errors in cost reporting.
Focus on Patient Engagement: High performance in patient satisfaction and engagement leads to improved scores in quality measures. Invest in patient education programs, use tools for feedback collection, and foster an environment of continuous communication to enhance patient outcomes.
Collaborate and Improve Continuously: Engage in quality improvement activities such as care coordination, clinical process optimization, and preventive care initiatives. These activities directly impact performance scores and provide opportunities for improved patient care, leading to higher reimbursement rates.
Track and Analyze Performance: Regularly review your practice’s performance in each of the MIPS categories to identify areas of improvement. Data analytics tools can help assess clinical outcomes, track cost utilization, and provide insights into areas where improvements can boost performance and payment adjustments.
By focusing on these tips, healthcare providers can maximize their performance score in the Quality Payment Program and ultimately boost their reimbursement rates while enhancing overall patient care.
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Accurate Reporting | Submitting accurate and timely data for MIPS and APMs is essential for improving performance scores and avoiding penalties. |
| Patient Engagement | Enhance patient satisfaction, improve care coordination, and engage patients to improve quality scores and reimbursements. |
| Adopt Technology | Utilize EHR systems and health IT to streamline care delivery, increase interoperability, and improve data sharing. |
MACRA and Quality Payment Programs: The Future of Healthcare
As value-based care continues to evolve, MACRA and the Quality Payment Program (QPP) will play an even more central role in shaping the future of the U.S. healthcare system. The transition from fee-for-service to value-based reimbursement marks a critical shift toward improving patient outcomes while controlling costs. As more healthcare providers embrace MIPS and APMs, we can expect increased collaboration among care teams, better care coordination, and a focus on prevention rather than reactive care.
Looking ahead, technology will continue to be a significant driver of healthcare transformation. The use of EHR systems, telemedicine, and AI-driven analytics will make it easier for providers to track and report performance, improving efficiency and accuracy in cost reporting and quality measures. Additionally, patient-centered care models will become more prominent, leading to more personalized treatment plans that focus on patient needs and goals. With these innovations, patient satisfaction will become an even more critical component of value-based reimbursements, directly impacting healthcare organizations' financial outcomes.
In the coming years, MACRA will likely expand to cover more healthcare professionals, offering more flexibility for providers who participate in Alternative Payment Models (APMs). As providers shift toward population health management, they’ll be incentivized to manage the overall health of communities rather than just individual patients. This will require providers to work closely with public health organizations, community outreach programs, and mental health initiatives to improve care and reduce health disparities.
As data collection and performance analytics become even more refined, we expect more transparent pricing models and quality assessments that empower patients to make informed decisions about their care. Ultimately, the future of healthcare will be characterized by cost-effective, high-quality care, driven by continuous improvement and collaborative efforts among providers, payers, and patients.
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Value-Based Care | MACRA promotes a shift towards value-based care, prioritizing quality outcomes over volume of services provided. |
| Technological Integration | Health IT advancements like EHR systems and data analytics will play a key role in improving care quality and patient outcomes. |
| Patient-Centered Models | The future will focus on personalized care, with more emphasis on patient engagement, prevention, and holistic care models. |
How the Medical Billing and Coding Certification by AMBCI Prepares You for MACRA Compliance
The Medical Billing and Coding Certification by AMBCI offers healthcare professionals the skills needed to succeed in value-based reimbursement models like MACRA. With the Quality Payment Program (QPP) under MACRA, healthcare providers are required to meet specific performance standards in areas such as quality of care, cost efficiency, and patient engagement. The Medical Billing and Coding Certification by AMBCI equips professionals with the necessary knowledge to navigate these performance categories effectively, ensuring compliance with MACRA guidelines.
Through the certification program, students learn the essentials of Medicare, Medicaid, and private payer regulations, with a strong focus on cost reporting, coding systems, and reimbursement processes. By understanding how to accurately report data and track performance, billing and coding specialists play a critical role in a practice’s ability to succeed under MACRA and the Quality Payment Program.
In addition, the Medical Billing and Coding Certification by AMBCI provides real-world case studies that simulate the reporting requirements for MIPS and APMs. This hands-on training prepares students to handle Medicare cost reports, performance measures, and clinical data, ensuring they are ready to optimize their practice’s reimbursement rates under MACRA.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
MACRA (Medicare Access and CHIP Reauthorization Act) significantly changed healthcare reimbursement by replacing the Sustainable Growth Rate (SGR) formula with the Quality Payment Program (QPP). This value-based model incentivizes healthcare providers to improve patient care while controlling costs. Providers are evaluated on their performance in areas such as quality, cost, improvement activities, and interoperability. Depending on their performance, providers may receive positive or negative payment adjustments, making it critical for them to meet MACRA's requirements to maintain financial stability and maximize reimbursements.
-
The Medical Billing and Coding Certification by AMBCI provides healthcare professionals with the necessary skills to navigate MACRA and the Quality Payment Program (QPP). The certification covers Medicare, Medicaid, and private payer regulations, teaching students how to accurately report cost data and track performance measures. By mastering coding systems and cost reporting, professionals are equipped to meet MACRA’s guidelines and help providers maximize reimbursements under MIPS or APMs.
-
MIPS (Merit-based Incentive Payment System) and APMs (Alternative Payment Models) are the two pathways under MACRA’s Quality Payment Program. MIPS evaluates healthcare providers based on quality, cost, improvement activities, and promoting interoperability. Providers are scored in these categories and rewarded with payment adjustments. APMs, on the other hand, involve providers taking on more financial risk in exchange for potential higher rewards. APM participants are incentivized to improve patient care and reduce overall healthcare costs across patient populations.
-
Both MIPS and APMs have a direct impact on reimbursement rates for healthcare providers under MACRA. In MIPS, providers are scored across four performance categories, with higher scores leading to positive payment adjustments. Providers with lower scores may face payment penalties. APMs, which focus on population-based care, offer providers shared savings for improving care and reducing costs but also carry the risk of financial penalties if performance metrics are not met. Both models encourage quality care and cost efficiency.
-
MIPS evaluates providers across four performance categories:
Quality: Measures clinical outcomes, patient satisfaction, and treatment effectiveness.
Cost: Assesses the cost-efficiency of care delivered, including resource utilization.
Improvement Activities: Evaluates efforts to improve care quality and patient engagement.
Promoting Interoperability: Measures the use of health IT systems, especially EHRs, for patient care and data sharing.
These categories determine a provider’s performance score, directly influencing their payment adjustment.
-
The Medical Billing and Coding Certification by AMBCI teaches students the essentials of cost reporting, coding systems, and QPP performance measures. Through real-world case studies, students gain hands-on experience in preparing quality reports, tracking performance metrics, and understanding how to meet MACRA requirements. The certification also emphasizes the importance of using EHR systems and billing software to ensure accurate and timely reporting for MIPS and APMs, which is essential for successful participation in the Quality Payment Program.
-
QPP regulations are updated annually, with changes to performance measures, reporting requirements, and reimbursement structures. It is essential for billing specialists to stay informed about these updates to ensure compliance and maximize reimbursement rates. To stay current, specialists should attend CMS webinars, subscribe to industry newsletters, and participate in professional development courses related to healthcare regulations. The Medical Billing and Coding Certification by AMBCI also provides ongoing education and resources to help specialists stay up-to-date.
Conclusion: Navigating MACRA for Success
Navigating MACRA and the Quality Payment Program (QPP) is essential for healthcare providers aiming to thrive in the value-based care environment. By understanding MIPS, APMs, and the core principles behind quality reporting, providers can not only ensure compliance but also optimize reimbursement rates and improve overall patient care. The Medical Billing and Coding Certification by AMBCI equips professionals with the necessary skills to excel under MACRA’s framework, enabling them to manage cost reporting, performance categories, and data submission accurately.
As healthcare continues to shift toward value-based reimbursement, MACRA and QPP will remain central to the way healthcare providers are reimbursed. Staying up-to-date with the latest regulations, embracing electronic health records (EHR), and focusing on patient-centered care are key strategies for succeeding in this evolving landscape. With the right tools and knowledge, healthcare professionals can navigate MACRA with confidence, ensuring they remain competitive, compliant, and prepared for long-term success in the ever-changing healthcare industry.
Poll: What do you think is the biggest challenge of complying with MACRA?