Everything You Need to Know About the Exam for Medical Billing and Coding
If you’re planning to take a medical billing and coding certification exam, you may be wondering what to expect. This guide provides an overview of the exam process, including what to study, the prerequisites, and how to register. By preparing adequately, you’ll be able to ace your exam and kick-start a career in this essential field within the healthcare industry.

What Is Medical Billing and Coding?
Medical billing and coding are essential functions in the healthcare industry that ensure accurate reimbursement for services rendered. Medical billing involves submitting claims to insurance companies and government programs, while medical coding translates diagnoses and procedures into standardized codes. These codes are essential for accurate billing, and their proper use ensures that healthcare providers are paid for the services they offer. Obtaining a medical billing and coding certification from a reputable organization like AMBCI can enhance one's expertise and career opportunities in this crucial field.
Medical coding professionals use coding systems such as ICD-10-CM and CPT to assign codes to medical procedures and diagnoses. This process helps maintain organized patient records and ensures the financial health of healthcare providers. As the healthcare industry becomes increasingly complex, professionals who are skilled in medical billing and coding play a crucial role in ensuring services are billed correctly and efficiently.

Medical Billing and Coding Exams: Types and Prerequisites
To become certified in medical billing and coding, you must pass an exam. Some of the most widely recognized certifications include the Certified Professional Coder (CPC) from the American Academy of Professional Coders (AAPC) and the Certified Billing and Coding Specialist (CBCS) certification. The CPC exam focuses on outpatient coding, while the CBCS certification is often required for those working in insurance companies.
The prerequisites for taking these exams include having a high school diploma or GED, completing an accredited medical billing and coding program, and gaining some practical knowledge through coursework. Although prior experience in healthcare is not mandatory, completing a formal education program greatly enhances your chances of passing the exam.
Preparing for the Exam
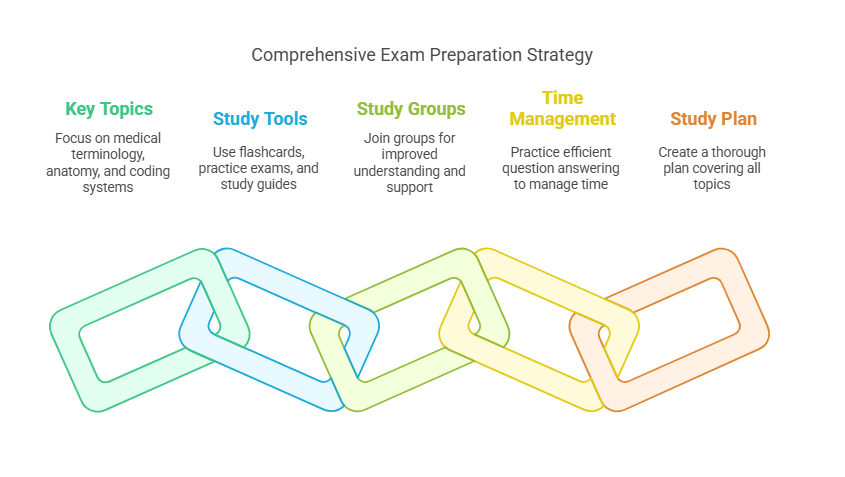
Preparing for the certification exam involves studying key topics such as medical terminology, anatomy, and various coding systems. You will likely encounter multiple-choice questions on coding systems like ICD-10-CM, CPT, and HCPCS, as well as case studies that assess your ability to apply coding principles to real-world scenarios. Time management is crucial on exam day—practice answering questions efficiently to ensure you complete the exam within the allotted time.
It’s helpful to use study tools like flashcards, practice exams, and study guides. Joining a study group or taking a preparatory course can also improve your understanding of the material and provide additional support. It’s essential to create a study plan that covers all exam topics thoroughly so that you feel confident going into the test.
What to Expect on Exam Day
On the day of your exam, you’ll need to bring your coding manuals (ICD, CPT, and HCPCS), which may include marginal notes but cannot have any exam-specific information written in them. Prepare for a comprehensive exam that will test your knowledge of medical terminology, coding systems, billing processes, and compliance regulations. To manage the exam effectively, break down your time into smaller segments and avoid spending too much time on any one question. Stay calm, and focus on selecting the most accurate answer based on your knowledge.
Maintaining Certification
After passing your certification exam, it’s important to maintain your certification by completing continuing education units (CEUs). You will need to complete 36 CEUs every two years to retain your certification. If you hold multiple certifications, the CEU requirement will increase. Keeping up with your education ensures you remain current with the latest industry trends and standards.
Career Benefits of Certification
Obtaining a medical billing and coding certification opens up various career opportunities. Certified professionals are highly sought after by employers and often enjoy higher salaries, with certified individuals earning an average salary of $58,055 annually. Those with additional certifications, such as the CPC, can earn upwards of $80,000 per year. Furthermore, certification can lead to career advancement and greater job security, as it demonstrates expertise and a commitment to maintaining high professional standards.

Six Lesser-Known Facts About Medical Billing and Coding
Medical Coding Systems Are Constantly Updated: New codes are introduced regularly, and outdated codes are retired. Staying up to date with the latest revisions is essential for accurate billing.
Medical Billers Work with More Than Just Doctors: Billers often interact with insurance companies, government programs, and even patients to ensure claims are processed correctly.
Remote Work Opportunities: Many medical billers and coders can work remotely, which has become more common due to advancements in technology and the increasing demand for flexible job opportunities.
CPC Certification Is Recognized Globally: While the CPC is widely recognized in the United States, it’s also respected internationally, opening up global career opportunities.
AAPC - Certified Professional Coder (CPC)®Medical Coding Requires Attention to Detail: The accuracy of codes directly impacts reimbursements and patient care. Even a small mistake in coding can lead to claim denials or delayed payments.
HealthIT.gov - Accurate CodingMedical Billing and Coding Can Be a Stepping Stone: Many professionals use their certification as a launchpad to pursue other roles within healthcare, such as medical auditing, health information management, or administrative positions.
AHIMA - Career Map
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
-
To take the certification exam, you need a high school diploma or GED and have completed an accredited medical billing and coding program. Previous healthcare experience is not required.
-
You can bring coding manuals (ICD, CPT, and HCPCS) with notes in the margins but ensure they do not contain any specific test-related information.
-
To maintain your certification, you must complete 36 CEUs every two years. If you hold multiple certifications, the requirement may increase.
-
The average annual salary is around $58,055, but certified professionals can earn more, especially if they hold additional certifications or have significant experience.
-
Registration is completed online. After submitting your application and paying the necessary fees, you will have up to 120 days to take the exam. Ensure your identification matches the name you used during registration.
