Essential Facts About Medical Billing and Coding You Need to Know
Medical billing and coding are essential processes in healthcare facilities, including hospitals, clinics, and private practices. These functions ensure accurate documentation of patient diagnoses, treatments, and insurance claims.
Medical coding involves assigning standardized codes, such as Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) and Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System (HCPCS), to medical conditions, treatments, and procedures. On the other hand, medical billing focuses on submitting and managing claims with insurance providers and patients. Together, they form the backbone of healthcare reimbursement, ensuring that medical professionals receive payment for their services. Obtaining a medical billing and coding certification from AMBCI enhances the expertise required to efficiently navigate these processes, ensuring accuracy and compliance in healthcare documentation.
Education and Certification
To enter the medical billing and coding field, individuals need at least a high school diploma or GED. However, completing a training program from an accredited institution significantly improves job prospects.
Certification is highly recommended, with options such as Certified Billing and Coding Specialist (CBCS), Certified Professional Biller (CPB), and Certified Coding Associate (CCA). Additional credentials, including Certified Medical Reimbursement Specialist (CMRS) and Certified Professional Coder (CPC), can further enhance career opportunities. These certifications demonstrate proficiency and make candidates more attractive to potential employers.
Career Outlook and Salary Expectations
The medical billing and coding industry is projected to grow by 8% from 2022 to 2032, according to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS). This increase is driven by the expanding healthcare sector and the need for professionals who understand insurance claims and medical coding standards.
The median annual salary for medical coders and billers is approximately $48,000 in 2025, with experienced professionals earning over $60,000. Factors such as specialization, certification, and geographic location can impact salary potential.
Skills and Qualities for Success
Success in medical billing and coding requires a combination of technical skills and personal attributes, including:
Attention to detail: Ensuring accurate coding and billing to avoid claim denials.
Knowledge of medical terminology: Understanding diagnoses and procedures for accurate coding.
Proficiency in billing software: Familiarity with Electronic Health Records (EHRs) and specialized coding tools.
Analytical and problem-solving skills: Identifying errors and resolving claim disputes.
Strong communication: Coordinating with healthcare providers, insurance companies, and patients.
Medical Coding Specializations
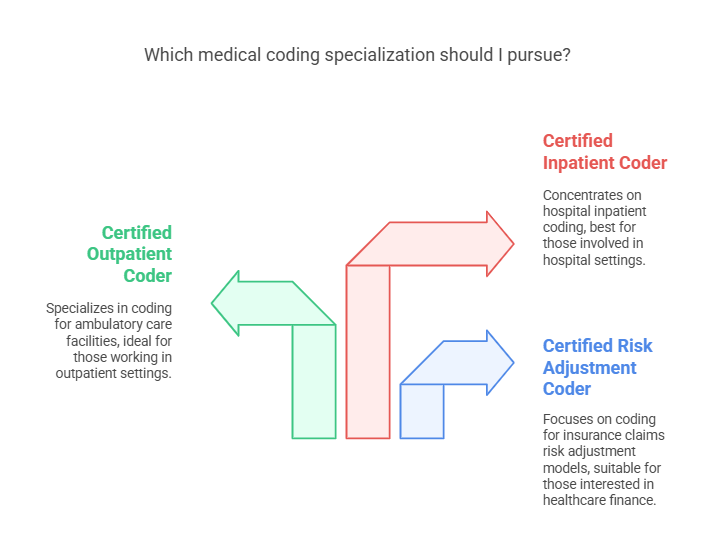
Medical coders can pursue specialty certifications to enhance their expertise in specific healthcare areas. Some of the most sought-after specializations include:
Certified Risk Adjustment Coder (CRC): Focuses on coding for risk adjustment models in insurance claims.
Certified Outpatient Coder (COC): Specializes in coding for ambulatory care facilities.
Certified Inpatient Coder (CIC): Concentrates on hospital inpatient coding.
These specializations can lead to higher salaries and increased job opportunities in niche medical fields.
Importance of Medical Billing in Healthcare
Accurate medical billing ensures that healthcare providers receive timely reimbursement, helping maintain smooth operations in medical facilities. Additionally, efficient billing reduces errors, minimizes claim rejections, and enhances patient satisfaction by preventing unexpected medical expenses.
The adoption of cloud-based billing software and AI-driven coding systems has streamlined processes, reducing paperwork and improving claim accuracy. As the healthcare industry embraces digital transformation, professionals with strong technological skills will be in high demand.
Regulatory Compliance and Technological Advancements
Medical billing and coding professionals must adhere to Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) regulations, ensuring patient data confidentiality and compliance with federal laws. They must also stay updated on evolving guidelines from organizations like AAPC and AHIMA.
Technological advancements, such as AI-assisted coding, robotic process automation (RPA), and blockchain for medical records, are revolutionizing the industry. These innovations improve efficiency, accuracy, and security in medical billing and coding processes.
Ethical Considerations in Medical Billing and Coding
Maintaining ethical practices is crucial in medical billing and coding. Professionals must avoid fraudulent billing, upcoding, or unbundling—practices that can lead to legal consequences and financial penalties. Ethical training and continuous education help coders and billers maintain integrity and ensure fair billing practices.
Impact on Patient Care
Errors in medical billing and coding can lead to denied insurance claims, causing delays in patient treatment. Accurate coding ensures that healthcare providers are properly reimbursed, allowing them to focus on delivering quality care. Additionally, transparent billing practices help patients understand their medical expenses, reducing financial stress and confusion.
6 Lesser-Known Facts About Medical Billing and Coding
Medical coders don’t diagnose patients. They translate physician diagnoses into standardized codes but do not make medical decisions.
Medical coders play an essential role in the billing process by translating healthcare diagnoses, treatments, procedures, and services into standardized codes from patient records. Career Step+1AAPC+1
Coding errors can cost millions. Mistakes in coding and billing contribute to billions of dollars in lost revenue annually for healthcare providers.
Errors in medical coding and billing can lead to significant financial losses for healthcare providers, with mistakes contributing to billions of dollars in lost revenue annually.
There are over 70,000 medical codes. The ICD-10 system includes an extensive list of codes covering a vast range of medical conditions and procedures.
The ICD-10 system includes an extensive list of codes covering a vast range of medical conditions and procedures, with the U.S. version containing approximately 70,000 codes. Medwave Billing & Credentialing
Telehealth has changed billing. Virtual healthcare services require new coding and billing methods to align with evolving insurance policies.
Coding for telehealth services has evolved, with new codes introduced to accurately represent virtual healthcare encounters and align with changing insurance policies. AAFP
Medical coding is global. Many countries use the ICD system, but coding standards and billing regulations vary by region.
While many countries use the ICD system for coding diagnoses, coding standards and billing regulations can vary by region, affecting how medical coding is implemented globally.
AI is revolutionizing coding. Artificial Intelligence and automation are streamlining repetitive tasks, reducing human error, and increasing efficiency in medical billing.
Artificial Intelligence and automation are transforming medical coding by streamlining repetitive tasks, reducing human error, and enhancing efficiency in billing processes.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
-
Most certification programs take 4 to 12 months, depending on the institution and level of training.
-
Yes! Many professionals work from home, especially with the rise of cloud-based billing systems and telehealth services.
-
While it requires attention to detail and adherence to strict regulations, many professionals find it rewarding due to job stability and remote work opportunities.
-
Inpatient coding applies to hospital stays and requires ICD-10-PCS codes.
Outpatient coding is used for non-hospital treatments, using CPT codes.
-
No, but completing a certificate or diploma program and obtaining certification significantly improves job prospects.
Medical billing and coding remain vital components of the healthcare industry, with expanding opportunities in AI-driven automation, telehealth, and remote work. As technology continues to reshape the field, professionals who stay updated with trends and certifications will have a competitive edge in the industry.