Top Tips: How Can I Become a Medical Coder
If you’re wondering how can I become a medical coder, you’re in the right place. This article will guide you through the essential steps, including meeting educational requirements, completing training programs, obtaining certification, and gaining practical experience. By the end, you’ll have a clear roadmap to launch your career in medical coding.
Key Takeaways
Medical coding is essential for accurate billing and maintaining patient records, acting as a bridge between healthcare providers and insurance companies.
To become a medical coder, individuals should meet prerequisites, complete training programs, and obtain relevant medical coding certifications to enhance job prospects.
Practical experience through internships and entry-level positions, along with ongoing education, networking, and exploring medical coding jobs through job searching strategies, is crucial for career advancement in medical coding.
Understanding Medical Coding
Medical coding serves as the crucial infrastructure within the healthcare sector, converting intricate medical data into uniform codes that are essential for both billing purposes and research, notably in relation to medical procedures. These standardized codes are vital for ensuring precise reimbursement of healthcare providers and the thorough upkeep of patient health records.
In your capacity as a medical coder, you will be instrumental in this system, acting as an intermediary between healthcare professionals and insurance carriers. Medical coding certifications play a significant role in different healthcare settings, including medical practices, outpatient and inpatient facilities, and insurance companies, highlighting the value of certification in advancing a career in medical coding.
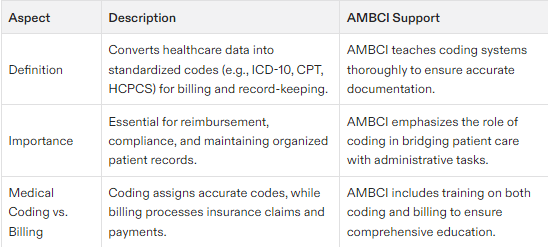
What is Medical Coding?
Medical coding entails the process of transforming healthcare information from a patient’s visit into standardized alphanumeric codes. These medical codes, such as those for ICD-10, CPT, and HCPCS classifications, are utilized by healthcare providers and insurers for purposes including billing and keeping records. It is the role of medical coders to meticulously go through patient documentation to identify fitting codes so that services rendered are precisely billed and recorded. Medical coding jobs are highly relevant in this field, and obtaining certifications is crucial for securing these positions.
It is vital to recognize the differences between medical coding and medical billing. While the former pertains to encoding health care details into standardized codes, the latter deals with handling financial operations and insurance claims submission. Medical coders are responsible for figuring out these necessary codes. On the other hand, it falls upon a medical biller to dispatch these determined codes in order to secure reimbursements from payers like insurance companies—this combined effort ensures payment delivery for services offered by healthcare providers.
For a well-functioning billing cycle free from disarray or errors—and crucially—to safeguard adherence within legal standards of practice compliance. Accuracy in determining applicable medical codes is indispensable. The significance carried by this precision underpins not only correct payments issued toward healthcare establishments, but also controls overpayments, underscoring its vitality both financially & operationally across multiple institutional scopes within medicine’s economic ecosystem.
Medical Coding vs. Medical Billing
Medical coding and medical billing are two distinct yet interconnected processes within the healthcare industry. Medical coding involves translating patient data into standardized codes, such as ICD-10-CM, CPT, and HCPCS, to facilitate accurate billing and reimbursement. This process ensures that every diagnosis, procedure, and service provided during a patient visit is accurately documented and coded.
On the other hand, medical billing involves creating and submitting claims to insurance companies based on the codes provided by medical coders. Medical billers use these codes to prepare claims that include patient demographics, insurance information, and billing details. Their primary goal is to ensure that healthcare providers receive timely and accurate reimbursement for the services rendered.
While medical coders focus on assigning the correct codes to diagnoses, procedures, and services, medical billers concentrate on preparing and submitting claims to insurance companies. In many healthcare settings, medical coders and medical billers work closely together as a team. The medical coder assigns the necessary codes, and the medical biller uses these codes to create and submit the claim. However, it’s not uncommon for professionals to perform both coding and billing tasks, especially in smaller practices.
Understanding the distinct roles of medical coders and medical billers is crucial for anyone looking to enter the healthcare industry. Both positions are essential for the smooth operation of healthcare facilities and the accurate processing of patient information and insurance claims.
Importance of Medical Coders
In the healthcare sector, medical coders serve a critical role. They convert patient information into uniform codes to guarantee that medical records adhere strictly to regulatory standards. Their precision is crucial in handling patient data effectively, coding illnesses correctly, and securing prompt reimbursement from insurance entities. The financial security of healthcare providers would be jeopardized without the contributions of medical coders. Obtaining relevant qualifications and certifications is significant for coders who wish to work in physician practices, which are integral parts of the overall healthcare ecosystem.
Proficient communication skills are essential for medical coders as they often liaise with healthcare professionals to rectify documentation or resolve any billing inconsistencies. This position calls for rigorous attention to detail along with an extensive grasp of both medical terminology and coding protocols to assure the legitimacy and exactitude of every assigned code.
Steps to Become a Medical Coder
Venturing into the profession of a medical coder requires a series of crucial steps, ranging from fulfilling fundamental educational requirements to achieving certification. These steps are structured to provide you with the essential expertise and abilities required for proficiency in this domain.
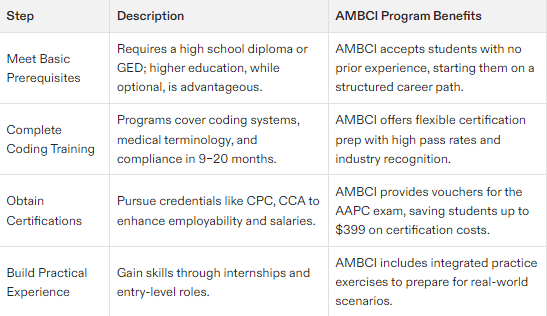
Meet Basic Prerequisites
Embarking on a career in medical coding necessitates fulfilling some fundamental requirements. Possessing a high school diploma or GED is essential for entry into this profession. Although not mandatory, acquiring specialized knowledge through an associate degree program or certificate is often expected to secure entry-level roles in the field. Community colleges offer accredited programs that serve as suitable academic pathways.
Entering a course dedicated to medical coding comes with no prior conditions, opening doors for numerous aspirants desiring to venture into this vocation. These instructional sessions impart the essential understanding needed to interpret and utilize medical codes effectively.
Complete Medical Coding Training
The expertise to proficiently convert medical records into specific codes is developed through medical coding training. This training can be acquired via a range of avenues including associate degree programs, certificates from recognized institutions, and practical experience obtained directly in the field. Earning an associate degree typically requires up to three years, whereas certification courses may take between nine and twenty months.
These educational courses are designed to equip learners with qualifications such as the combined CPC + CPB certifications and provide comprehensive instruction on various coding systems such as HCPCS, CPT Category II, and ICD-10. These programs often offer assurances like full refunds if not satisfied within 14 days or a 100% money-back guarantee along with commitments for job placement within six months after completion, fostering confidence among graduates about their career prospects.
Those who successfully complete this type of vocational education have potential access to jobs that yield annual salaries exceeding $80,000 – validating the financial investment made in their skills development. Completing robust medical coding training positions you advantageously for entering into employment as an efficient and self-assured medical coder.
Obtain Medical Coding Certification
Securing a medical coding certification can markedly improve your career trajectory in the domain of medical coding. Possessing such certifications validates your expertise and is frequently mandated by potential employers. There are several types of credentials you could pursue, for instance, Certified Professional Coder (CPC), Certified Coding Associate (CCA), or Certified Billing and Coding Specialist (CBCS). Gaining these certifications as a certified medical coder opens doors to better employment opportunities.
For those aspiring to become certified professional coders, fulfilling an associate degree requirement in medical coding or gaining comparable experience is necessary. For novices aiming at entering the field, acquiring the CPC credential would be beneficial whereas more seasoned professionals may opt for the CCS certification considering their existing proficiency.
Prominent bodies like AHIMA and AAPC offer esteemed certifications that bolster both one’s legitimacy within this arena as well as prospective job advancement. Courses tailored towards educating future specialists in medical billing and coding commonly include vouchers covering fees associated with undertaking relevant certification exams—providing yet another cost-effective benefit on this path. Ultimately, securing such a qualification signifies a crucial leap toward achieving success as an adept coder specializing in healthcare documentation.
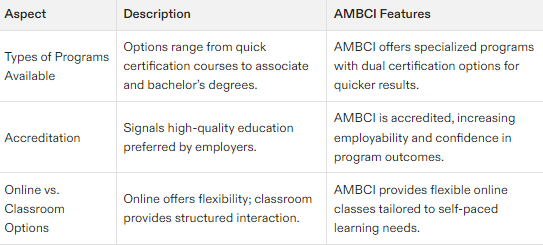
Choosing the Right Medical Coding Program
Choosing an appropriate medical coding program is a pivotal choice that has the potential to shape your professional path. Various educational routes are tailored to meet different career objectives. It’s imperative to opt for a program that matches both your ambitions and availability.
Types of Programs Available
A spectrum of educational programs is available in medical coding, from brief certification courses to extensive degree pathways. The abbreviated certification courses equip learners with essential skills for entry-level positions and can be accomplished relatively quickly. Conversely, associate degree programs provide a broader education that encompasses multiple facets of medical coding as well as healthcare administration.
Individuals aiming for more profound understanding and upper-tier roles might consider bachelor’s degree programs, which probe into the intricacies of medical coding alongside pertinent healthcare subjects. The choice of an appropriate program should align with one’s professional aspirations and the depth of knowledge they desire to acquire.
Accreditation and Quality
Opting for an accredited medical coding program is crucial to guarantee the caliber of your educational experience and to enhance job prospects. Such programs, which are usually favored by employers, enable eligibility for financial assistance and transferability of credits. They pave the way for improved career progression opportunities.
Selecting a program that’s recognized can give you an advantage in the workforce by boosting both your employability and potential earnings. Take into account elements like overall expense, duration of the program, and its effectiveness in preparing you for certification exams when making your choice. This deliberate evaluation will assist in finding a medical coding program that aligns with your personal requirements.
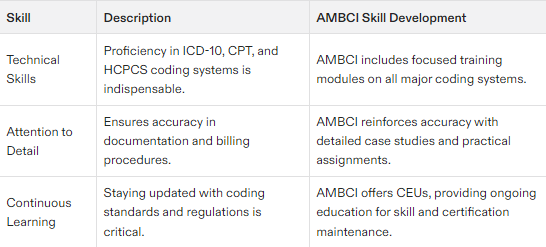
Essential Skills for Medical Coders
To thrive in the role of a medical coder, possessing both technical expertise and interpersonal abilities is crucial. These competencies are vital for accurately converting medical records into standardized codes while also maintaining clear communication with healthcare providers.
Technical Skills
A strong grasp of technical skills is essential for a thriving career in medical coding. Proficient knowledge of key coding systems such as ICD-10, HCPCS, and CPT is imperative for medical coders to perform their duties with precision. These code sets form the backbone of the industry’s standard practices, making their comprehension fundamental to proficient coding.
Exemplary time management abilities are crucial for medical coders to excel in their field. The ability to prioritize tasks effectively and adhere strictly to deadlines plays a significant role in ensuring that billing and coding workflows are executed smoothly. Committing to continuous professional development can aid in minimizing mistakes and bolstering overall efficiency within operational procedures related to medical coding.
Soft Skills
Medical coders must possess not only technical capabilities but also robust soft skills. Proficient communication is essential for dealing with billing complications and engaging with healthcare providers. The ability to analyze deeply aids in spotting inaccuracies within medical records and insurance submissions, thereby guaranteeing precise execution during the coding cycle. A coding specialist’s meticulous work in medical billing is instrumental in maintaining this precision.
Harmonizing communication prowess with analytical aptitude bolsters a medical coder’s proficiency within their profession. These soft abilities are imperative for triumphing in the realm of medical coding, potentially influencing career progression opportunities significantly.
Preparing for Certification Exams
Preparing for medical coding certification exams requires a combination of education, training, and practice. Here are some steps to help you prepare:
Meet the Eligibility Requirements: Before you can take a certification exam, you need to meet the eligibility requirements set by the certification organization. For example, the Certified Professional Coder (CPC) exam by AAPC requires candidates to have completed a medical coding training program or have relevant work experience.
Complete a Medical Coding Training Program: Enroll in a medical coding training program that covers the coding systems and guidelines relevant to the exam you plan to take. These programs provide comprehensive instruction on ICD-10-CM, CPT, and HCPCS coding systems, as well as medical terminology and healthcare regulations.
Study the Exam Content: Review the exam content outline and study materials provided by the certification organization. Focus on understanding the coding guidelines, conventions, and principles that will be tested. Make use of textbooks, online resources, and study guides to reinforce your knowledge.
Practice with Sample Questions: Practice with sample questions and case studies to help you apply your knowledge and develop your coding skills. Many certification organizations offer practice exams that simulate the actual test environment, allowing you to assess your readiness and identify areas for improvement.
Join a Study Group or Online Community: Join a study group or online community to connect with other medical coders who are also preparing for certification exams. These groups provide support, share study tips, and offer valuable insights into the exam preparation process.
By following these steps, you can build a strong foundation of knowledge and skills, increasing your chances of passing your medical coding certification exam.
Study Tools for Certification Exams
There are several study tools available to help you prepare for medical coding certification exams. Here are a few:
Certification Study Guides: Certification study guides, such as the CPC Study Guide, provide a comprehensive review of the exam content. These guides include practice questions, case studies, and detailed explanations of coding guidelines and principles, helping you to thoroughly prepare for the exam.
Online Practice Exams: Online practice exams, such as the CPC Practice Exam, offer a simulated exam experience. These practice tests help you assess your knowledge and skills, identify areas for improvement, and become familiar with the exam format and time constraints.
Coding Manuals and Resources: Coding manuals and resources, such as the ICD-10-CM and CPT coding manuals, provide detailed information on coding guidelines and conventions. These manuals are essential tools for understanding the coding systems and accurately assigning codes.
Online Courses and Webinars: Online courses and webinars, such as those offered by the AAPC and AHIMA, provide instruction and guidance on specific topics and coding systems. These courses often include interactive elements, such as quizzes and discussions, to enhance your learning experience.
Utilizing these study tools can significantly enhance your preparation for medical coding certification exams, helping you to build confidence and achieve success.
Tips for Passing Certification Exams
Here are some tips to help you pass your medical coding certification exam:
Read the Questions Carefully: Take your time to read each question carefully and make sure you understand what is being asked. Pay attention to keywords and details that can help you determine the correct answer.
Manage Your Time Effectively: Manage your time effectively during the exam. Allocate a specific amount of time for each question and stick to it. If you encounter a difficult question, move on and come back to it later if you have time.
Use the Process of Elimination: Use the process of elimination to narrow down your answer choices. Eliminate any options that are clearly incorrect, and then focus on the remaining choices to increase your chances of selecting the correct answer.
Stay Calm and Focused: Stay calm and focused throughout the exam. Practice stress management techniques, such as deep breathing and positive visualization, to help you stay composed and confident.
By following these tips, you can improve your performance on the exam and increase your chances of passing.
What to Expect on Exam Day
Here’s what you can expect on exam day:
Arrive Early: Arrive early at the testing center to allow yourself plenty of time to check in and get settled. Make sure you have all the required materials, such as your ID and certification documents.
Check-In and Registration: Check in and register for the exam. The testing center staff will verify your identity and provide instructions on the exam rules and procedures.
The Exam Format: The exam format will vary depending on the certification organization and the exam you are taking. Most exams consist of multiple-choice questions and case studies that test your knowledge and application of coding principles.
The Exam Duration: The exam duration will vary depending on the certification organization and the exam you are taking. Most exams last between 2-4 hours, so be prepared to manage your time effectively.
Results and Certification: After completing the exam, you will receive your results and certification documents if you pass. Some certification organizations provide immediate results, while others may take a few weeks to process and deliver your certification.
By understanding what to expect on exam day, you can reduce anxiety and focus on performing your best.
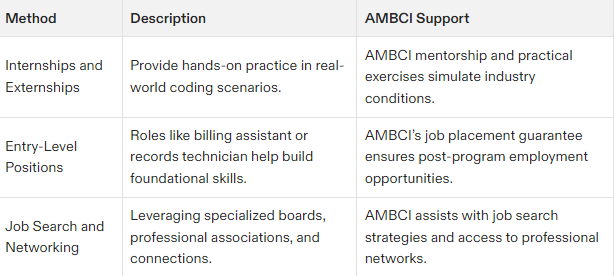
Gaining Experience in Medical Coding
In medical coding, it is crucial to apply theoretical knowledge in practical settings. Internships and entry-level positions provide an excellent opportunity for hands-on learning, greatly improving your abilities.
Internships and Externships
Gaining hands-on experience in medical coding through internships and externships can be immensely beneficial. Numerous hospitals and clinics are on the lookout for interns to assist with their coding duties, providing practical training across different coding specialties.
Engaging in these programs can significantly enhance your grasp of medical coding procedures and boost your chances of getting a job.
Entry-Level Positions
Beginning careers in roles like billing assistant or medical records technician may act as stepping stones for those aiming to become medical coders. These entry-level positions offer valuable hands-on experience and lay a strong groundwork in the field of medical coding.
Prior professional involvement in the healthcare sector can prove advantageous when seeking employment as a medical coder.
Navigating the Job Market
Exploring the employment landscape for medical coders requires employing successful job hunting techniques and seizing networking prospects. The occupational growth projection for medical coders is optimistic, expected to surpass the average rate of job expansion across other fields.
Job Search Strategies
Explore dedicated platforms such as FlexJobs to discover genuine opportunities in medical coding jobs. You might find superior job prospects by tapping into niche job boards that cater exclusively to the medical or telecommuting sectors. When searching for medical coding jobs, consider obtaining relevant certifications, exploring remote work opportunities, and leveraging professional networks to secure stable positions within this growing field. Personalize your resume and cover letter uniquely for each distinct role.
Emphasize your expertise, academic background, credentials, and quantifiable accomplishments to differentiate yourself from other candidates.
Networking and Professional Associations
For medical coders seeking to improve their career prospects and professional development, networking is essential. Participation in organizations such as the AAPC offers significant opportunities for networking and access to employment resources.
To take advantage of these benefits for advancing one’s career, it is advisable to become a member of a professional association.
Continuous Learning and Career Advancement
Ongoing education in continuous learning is essential to keep abreast of updates in coding guidelines and industry standards, thereby maintaining your relevance and improving your career opportunities.
Advanced Certifications
Securing advanced credentials such as CPC, CCS, and CRC can notably improve your employment opportunities and facilitate access to more senior roles in the realm of medical coding. Holding these certifications is a testament to your expertise and dedication to the profession, thereby making you an increasingly appealing prospect for potential employers.
Continuing Education
It is crucial for medical coders to maintain up-to-date knowledge of the evolving coding protocols and industry norms. To ensure compliance with certification renewal mandates and to remain well-informed, they must engage in ongoing education efforts by acquiring continuing education units (CEUs).
Participating in healthcare conferences offers significant benefits such as expanding professional connections and gaining critical perspectives on the sector.
Summary
Summarize the key points discussed in the guide and motivate readers to take the necessary steps to become successful medical coders. Emphasize the importance of continuous learning and certification in advancing their careers.
Frequently Asked Questions
What educational prerequisites are needed to start a career in medical coding?
To begin a career in medical coding, you need at least a high school diploma or GED. While a specific degree isn’t required, completing a certificate or associate degree program can enhance your employability.
What are the different certification options available for medical coders?
There are several certification options for medical coders, including the Certified Professional Coder (CPC), Certified Coding Associate (CCA), and Certified Billing and Coding Specialist (CBCS), offered by organizations such as AHIMA and AAPC.
Selecting the right certification can enhance your credibility and career opportunities in the field.
How long does it take to complete medical coding training?
Typically, medical coding training can be completed in nine to twenty months through certification programs, whereas an associate degree may take up to three years.
Consider your career goals when choosing the right path for you.
Why is accreditation important when choosing a medical coding program?
When choosing a medical coding program, accreditation is essential as it ensures the standard of education and boosts opportunities for employment. Graduates from accredited programs are often preferred by employers, and these programs frequently provide advantages such as easier transfers of credits and access to financial aid.
What is the job growth outlook for medical coders?
The job growth outlook for medical coders is promising, with an expected increase of 8%, which is faster than the average for other occupations.
This trend indicates strong demand and stability in the field.