Medical Billing and Coding Certification in Nebraska: Complete Guide for 2025–2026
Nebraska’s healthcare systems — from Omaha’s academic hospitals to Lincoln’s fast-expanding outpatient networks — are experiencing a surge in digital transformation. Revenue-cycle management (RCM) teams are prioritizing efficiency, compliance, and claim accuracy like never before. This shift has made certified billing and coding professionals indispensable across hospitals, physician groups, and telehealth firms.
If you’re ready to join one of the most stable and remote-friendly healthcare careers, the AMBCI Medical Billing and Coding Certification offers the most efficient path. This guide dives deep into salary data, certification pathways, software proficiencies, and employer trends, drawing comparisons with Kansas, South Dakota, Missouri, and Iowa.
1) Nebraska’s Healthcare Outlook & Why Certification Matters
Nebraska’s healthcare employment growth is outpacing national averages. The Bureau of Labor Statistics projects a +10.5% rise in medical coding and billing jobs from 2025 to 2030. This growth stems from payer audits, telehealth reimbursements, and AI-supported coding tools now common across health systems.
Major employers like Nebraska Medicine, CHI Health, and Bryan Health have modernized billing workflows around software like Epic and Cerner. Yet, human accuracy remains the critical differentiator. Certified coders ensure compliance with ICD-10-CM, CPT®, and HCPCS Level II standards — areas tested heavily within the AMBCI certification exam.
For comparison, check how Kentucky and Louisiana have leveraged AMBCI-trained professionals to cut denials by 22–28% statewide.
Nebraska’s employers follow a similar trend — prioritizing coders with proven audit-defense metrics and high first-pass claim rates.
Nebraska Medical Billing & Coding — 2025–2026 Salary, Skills & Job Outlook
2) Certification Pathways, Course Content & Training Options
To enroll, candidates need a high school diploma or GED and basic computer literacy. Nebraska’s AMBCI-aligned programs combine real billing case studies, ICD-10-CM coding exercises, and payer denial analysis — all focused on day-one job readiness.
Core modules include:
Medical Terminology & Anatomy
CPT®/HCPCS Level II coding with practical application
EHR navigation (Epic, Cerner, eCW)
Denial management (CO-16, CO-97, PR-204)
Payer audits & appeals documentation
Telehealth policy updates (Medicare and Medicaid)
Students typically finish training within 4–6 months. If you’re balancing work and study, compare flexible schedules in Virginia and remote modules in Utah for better pacing inspiration.
AMBCI’s exam emphasizes application, not memorization. You’ll decode E/M levels, modifier usage, and claim edits under timed simulations — precisely what Nebraska employers demand.
3) Salary Benchmarks, Remote Work, and Job Market Insights
The average salary for certified coders in Nebraska is $52,600, climbing past $70K with experience and multi-specialty expertise. The highest wages come from Omaha’s hospital systems and telehealth RCM vendors.
Remote work is booming due to payer digitization — especially within AI-assisted claim processing and virtual care billing. Coders trained in Epic, Meditech, and AdvancedMD stand out.
Compare similar pay ladders in Oregon and Rhode Island — both showcase rapid growth in telehealth billing roles.
Tip: Employers look for quantifiable metrics. List achievements like:
“Processed 1,500+ claims monthly with a 98% first-pass rate.”
“Reduced CO-97 denials by 20% within 45 days.”
These are the performance outcomes AMBCI graduates consistently achieve.
Quick Poll: What’s Your Biggest Challenge in Medical Billing?
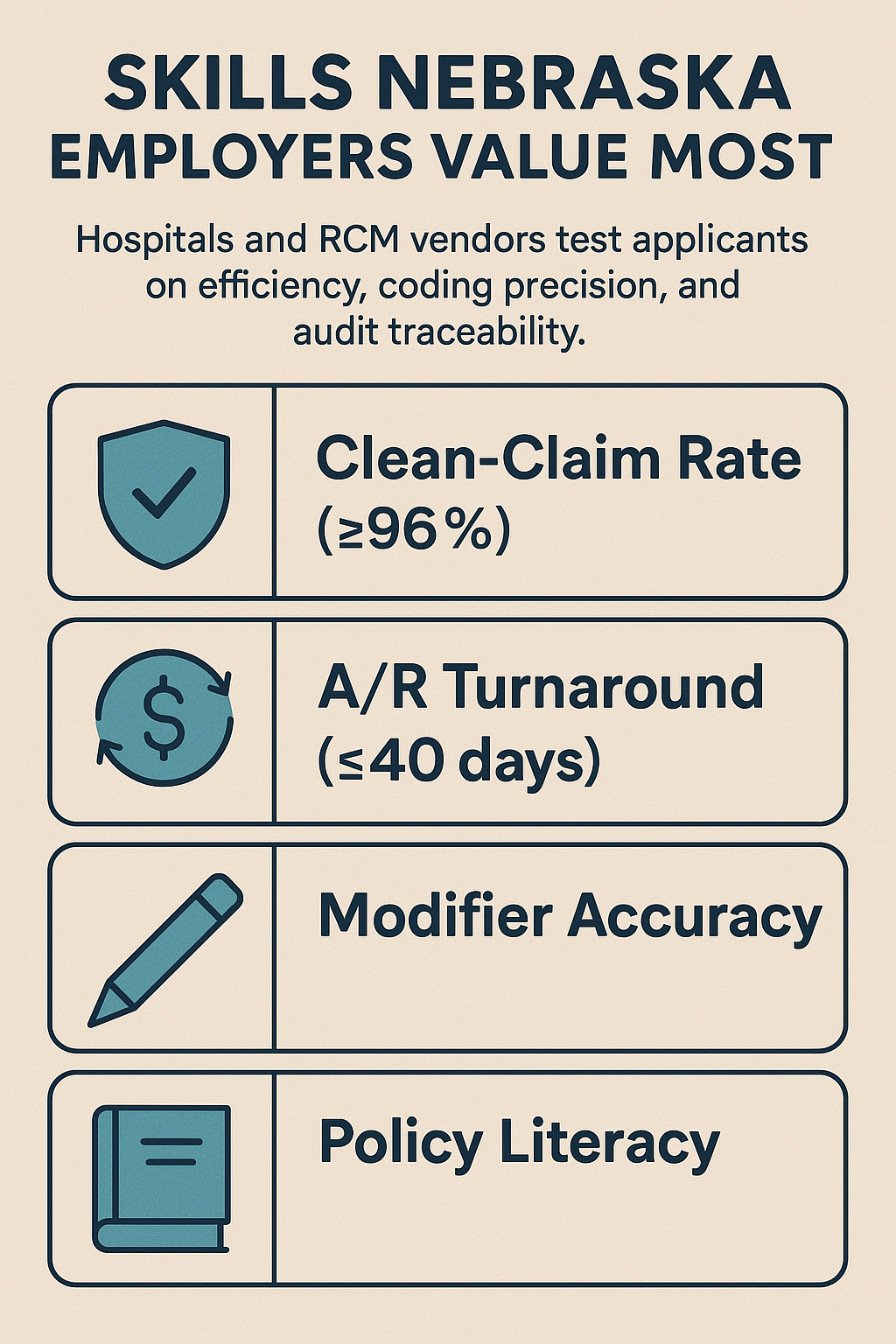
4) Skills Nebraska Employers Value Most
Hospitals and RCM vendors test applicants on efficiency, coding precision, and audit traceability. Here’s what Nebraska recruiters actually evaluate:
Clean-Claim Rate (≥96%) — how often you get claims right the first time
A/R Turnaround (≤40 days) — how quickly you resolve outstanding payments
Modifier Accuracy — especially 25, 59, and 95 for telehealth
Policy Literacy — understanding Nebraska Medicaid and private payer edits
Top performers master cross-state payer logic, referencing insights from Maryland and Massachusetts, where compliance and edit audits shape similar workflows.
Action Tip: Track your personal “error log” and “fix-paths.” This practice — adopted widely in South Carolina — improves your interview performance dramatically.
5) AMBCI Exam Strategy & Six-Week Study Blueprint
AMBCI’s six-week prep model is proven to boost pass rates by 20%+ for first-time test takers. Here’s the breakdown:
Weeks 1–2: ICD-10-CM and Nebraska Medicaid policy. Decode musculoskeletal and cardiovascular chapters.
Week 3: CPT®/HCPCS code applications and modifier optimization.
Week 4: Denial analytics — study CO-16 and PR-204 audit cases.
Week 5: Two timed AMBCI mock exams; log and fix common coding errors.
Week 6: Create your professional portfolio — include 3 redacted claims, denial taxonomy, and KPI sheet.
Model your prep using best practices documented in Wisconsin’s AMBCI guide and Pennsylvania’s coding curriculum.
6) FAQs — Nebraska Medical Billing & Coding Certification (2025–2026)
-
Most learners complete the AMBCI program in 4–6 months, including live coding labs and two timed practice exams. Accelerated 12-week bootcamps are available in Omaha and Lincoln.
-
While CPC, CBCS, and CCA remain common, AMBCI’s case-based format aligns best with payer audits and CMS transparency standards, similar to Rhode Island’s AMBCI framework.
-
Entry-level coders earn $36K–$42K, while multi-specialty or senior coders cross $70K+. Pay increases correlate with KPIs like clean-claim rates and audit performance.
-
Yes — remote and hybrid roles are expanding rapidly. Telehealth billing and multi-state payer expertise make AMBCI graduates highly desirable to national RCM vendors.
-
Start with Epic and eClinicalWorks, then add Meditech or AdvancedMD for versatility. AMBCI’s labs simulate all major EHR environments.
-
Yes — AMBCI maintains partnerships with hospitals, billing companies, and payer networks across the Midwest, helping graduates secure positions within 60–90 days.
-
Study payer-specific edit codes (CO-16, CO-97, PR-204) and maintain a documentation crosswalk. Maryland’s audit strategies provide an excellent template..
-
Cardiology, orthopedic surgery, and behavioral health — particularly within ambulatory surgery centers (ASCs) — offer the fastest advancement opportunities