Medical Billing and Coding: How Long Does It Take?
If you're considering a career in medical billing and coding, you might be wondering how long it takes to become proficient in this field. The duration of training programs can vary depending on the type of education you pursue, such as a certificate program or an associate degree. In this article, we'll explore the different training options, how long they typically take, and other factors that can influence the length of your education.
Key Takeaways for a Successful Career in Medical Billing and Coding
Training Duration: Medical billing and coding programs typically range from 4 months to 3 years, depending on the program and prior experience.
Certifications: Certifications such as CPC, CCA, and CBCS enhance job prospects but require extensive preparation time.
Practical Experience: Internships or on-the-job training are critical for bridging theoretical knowledge with real-world applications.
Overview of Medical Billing and Coding Careers
In the healthcare sector, medical coders and billers play a critical yet often overlooked role. These professionals are responsible for ensuring accurate and efficient compensation for health service providers. They handle patient data, categorize diagnoses, and initiate payment requests to insurance companies. Their role is essential in converting patient encounter information into standardized CPT codes that inform the insurance claims process. Earning a medical billing and coding certification through a trusted organization like AMBCI equips individuals with the skills and credibility needed to excel in this vital field.
Specialized training is vital for anyone entering this field. This training covers medical terminology, pharmacology, and compliance with regulations such as HIPAA. It also involves mastering coding standards to ensure accuracy and efficiency in medical billing and coding tasks. The demand for trained professionals in medical billing and coding remains strong, offering opportunities in a variety of settings, including hospitals, insurance companies, and consulting agencies.
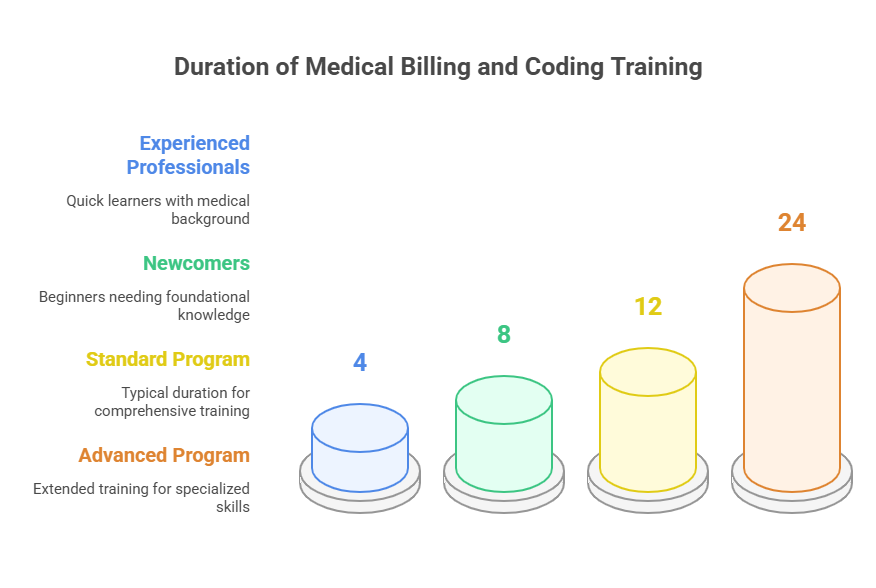
Duration of Medical Billing and Coding Training Programs
Many aspiring medical billers and coders ask how long it will take to complete their training. The duration of medical billing and coding programs depends on several factors, including the educational route chosen. Training can last anywhere from 1 to 3 years. Those with previous experience in the medical field might complete their training in as little as 4 months, while newcomers may require about 8 months to grasp the essential concepts.
Training Duration for Medical Billing and Coding
Certificate Programs: Quick Path to Entry-Level Jobs
Certificate programs are an accelerated route to entering the field of medical billing and coding. These programs typically take between 6 months to 1 year to complete, making them ideal for individuals eager to start working quickly. The curriculum is designed to equip students with the necessary skills and knowledge to enter the job market as certified medical coders and billers.
Associate Degree Programs: Comprehensive Education
Associate degree programs in medical billing and coding usually take around two years to complete. These programs provide a more in-depth education, covering a broad range of topics within the field. Obtaining an associate degree can increase job opportunities and provide a deeper understanding of both billing and coding.
Certification Exams for Medical Billing and Coding
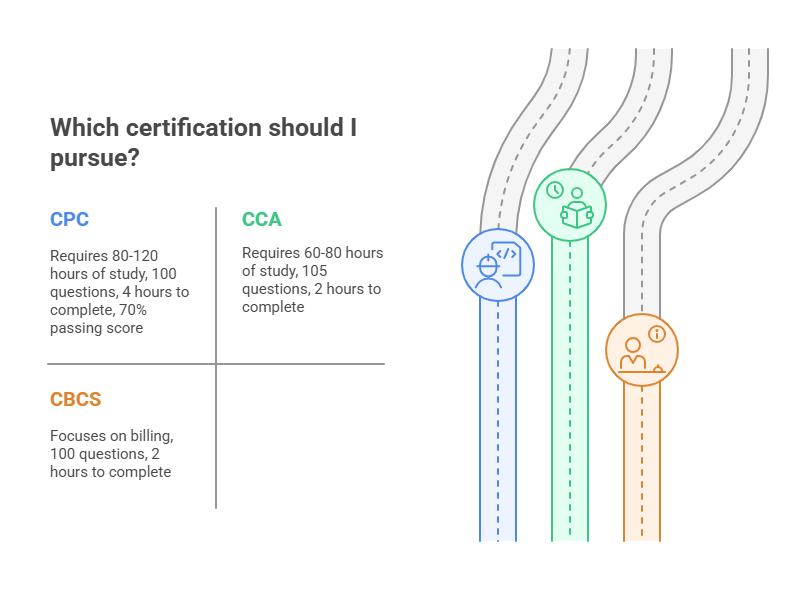
Earning certification is a key step in advancing your career in medical billing and coding. The three primary certifications available are:
Certified Professional Coder (CPC): The CPC exam consists of 100 multiple-choice questions and must be completed within 4 hours. A passing score of 70% is required. Preparing for this exam takes between 80 to 120 hours of study.
Certified Coding Associate (CCA): The CCA exam consists of 105 questions and must be completed in 2 hours. Preparation for this exam typically takes 60 to 80 hours.
Certified Billing and Coding Specialist (CBCS): The CBCS exam is specifically for medical billing professionals and contains 100 questions. It is typically completed in 2 hours, and preparation involves studying insurance claims processing, coding protocols, and billing processes.
Factors Influencing Training Duration
The length of time required to complete medical billing and coding training can vary depending on several factors, including:
Program Type: Certificate programs are shorter, while associate degree programs take longer.
Study Pace: The speed at which you complete your coursework also affects the duration. Full-time students tend to complete their studies faster than part-time students.
Previous Experience: Having prior healthcare experience can significantly reduce the time needed to finish training. If you already have experience in medical settings, you'll be able to grasp medical billing and coding concepts more quickly.
Full-Time vs. Part-Time Study
The choice between full-time and part-time study can significantly impact how long it takes to complete your training. Full-time study generally allows students to finish their programs more quickly, while part-time study offers more flexibility for those with other commitments. Depending on your circumstances, you can choose the option that works best for you.
Online vs. In-Person Courses
Medical billing and coding programs are available both online and in-person. Online programs offer greater flexibility and can typically be completed in 4 to 12 months, depending on the student's pace. In-person programs may take longer but provide a more structured learning environment.
Real-World Application and Hands-On Experience
Hands-on experience is crucial for success in the medical billing and coding field. Internships, externships, and on-the-job training are invaluable for gaining practical experience and preparing for real-world challenges. Many programs include internships as part of the curriculum to help students gain this practical experience before entering the workforce.
Career Advancement and Continuing Education
Continuing education is essential for staying up to date with the latest industry trends and maintaining your certification. Medical coders and billers are required to complete continuing education units (CEUs) to keep their credentials active. Pursuing additional certifications and specializations can also open doors to new career opportunities and higher salaries.
6 Lesser-Known Facts About Medical Billing and Coding
CPT Codes: The American Medical Association (AMA) released the CPT 2024 code set, which includes 11,163 codes describing medical procedures and services. American Medical Association
Global Impact: Medical billing and coding are essential internationally, as many countries adopt similar coding systems. Wikipedia
Growth Potential: The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics projects that employment of medical records specialists will grow 9% from 2023 to 2033, much faster than the average for all occupations. Bureau of Labor Statistics+3Bureau of Labor Statistics+3Elite education for all.+3
Remote Work Opportunities: Many medical billing and coding professionals work remotely, offering flexibility in their careers.
HIPAA Compliance: Medical billers and coders must understand HIPAA regulations to ensure patient privacy is maintained.
Multiple Specializations: Medical coders can specialize in areas like outpatient or inpatient coding, enhancing career advancement opportunities.
FAQs About Medical Billing and Coding
-
The length of time varies, but it typically takes between 4 months to 3 years, depending on the type of program you choose.
-
The primary certification exams are the CPC, CCA, and CBCS, each designed for specific areas within medical billing and coding.
-
Yes, online programs are available and typically take between 4 to 12 months to complete, offering flexibility to learn at your own pace.
-
If you have previous healthcare experience, such as working as a medical assistant, you may be able to complete your training more quickly due to your familiarity with medical terminology and procedures.
-
You must complete 36 continuing education units (CEUs) every two years to maintain your certification. Holding multiple certifications requires additional CEUs.
Conclusion
In conclusion, becoming a medical biller and coder involves a commitment to education and continuous learning. With various training options and certification exams, you can choose a path that suits your career goals and timeline. Staying current with continuing education and obtaining advanced certifications will ensure your career in medical billing and coding remains rewarding and full of opportunities.