How Can I Get EMT Certified
How Can I Get EMT Certified: A Step-by-Step Guide to Success
Introduction to Emergency Medical Services
Emergency Medical Technicians (EMTs) provide out-of-hospital emergency medical care and transportation for critical and emergent patients. Emergency medical technicians function within a broader emergency medical services (EMS) system, emphasizing their role in providing care and transportation for patients in critical situations.
EMTs function as part of a comprehensive EMS response system, under medical oversight, highlighting their critical role in connecting emergency scenes with the broader healthcare system.
EMTs perform interventions with basic equipment typically found on an ambulance, requiring basic knowledge of essential skills and understanding to handle various emergency situations effectively.
Emergency Medical Services (EMS) professionals must meet their state’s standards of certification.
The National EMS Education Standards are comprised of four components: Competencies, Knowledge, Clinical behaviors and judgments, and Educational infrastructure.
Prerequisites and Eligibility Requirements
To become an EMT, you must meet certain prerequisites and eligibility requirements. These requirements may vary depending on the state and local EMS agencies, but here are some general guidelines:
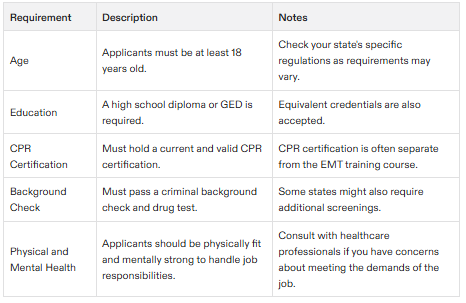
Age: You must be at least 18 years old to apply for EMT certification.
Education: A high school diploma or equivalent, such as a GED, is required.
CPR Certification: A current CPR certification is necessary, which is usually separate from the EMT training course.
Background Check: Passing a criminal background check and drug test is mandatory.
Physical and Mental Health: The job of an EMT can be demanding and traumatic, so you must be physically and mentally strong.
It’s essential to check with your state’s EMS agency and local training programs for specific requirements, as they may vary. This ensures you meet all the necessary criteria to successfully complete your EMT training and certification process.
Becoming an EMT
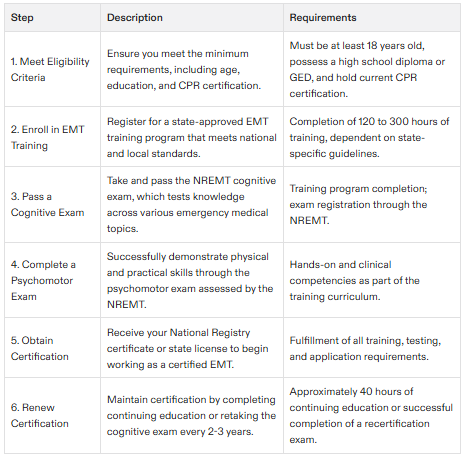
To become an EMT, you need to be 18 years old or older and have either a high school diploma or a GED.
You will also need certification in CPR and take a state-approved EMT course that meets the standards of the National Registry of Emergency Medical Technicians (NREMT).
You can apply for EMT certification after completing the training course and passing the cognitive and psychomotor skill exam provided by the NREMT. Obtaining the EMT National Registry certificate is a crucial step in the certification process.
EMTs must complete a high school program or get a GED, CPR certification, and an education program approved by their state to receive certification.
EMT students taking the National Registry Emergency Medical Technician cognitive exam must achieve a “standard level of competency” according to the National Registry of Emergency Medical Technicians.
EMT Training and Coursework
EMT courses are usually around 150 hours long over a period of months and can be taken in person or online.
Hands-on training is the best way to become an experienced EMT.
An EMT course must meet both local and national requirements.
EMTs handle a range of services, from critical care to routine medical transports, highlighting their role in both emergent and non-emergency situations.
EMTs must complete 120 to 300 hours of classroom training, depending on their state’s requirements.
EMTs operate under the national EMS scope, which defines their roles and responsibilities within the broader EMS system, ensuring they provide emergency medical care and transportation guided by national standards.
AEMTs must complete an additional 100 to 300 hours of classroom training after receiving their EMT certification.
Financial Aid and Scholarships for EMT Training
Pursuing a career as an EMT can be costly, but there are financial aid options and scholarships available to help. Here are some ways to fund your EMT training:
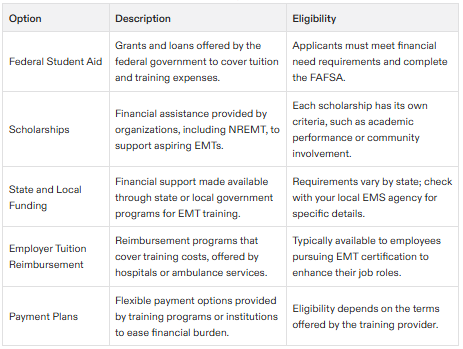
Federal Student Aid: You can apply for federal student aid, such as grants and loans, to help cover the cost of your EMT training.
Scholarships: Many organizations, including the National Registry of Emergency Medical Technicians (NREMT), offer scholarships to aspiring EMTs.
State and Local Funding: Some states and local governments provide funding for EMT training programs.
Employer Tuition Reimbursement: Certain employers, such as hospitals and ambulance services, offer tuition reimbursement programs for employees pursuing EMT certification.
It’s crucial to research and explore these financial aid options to help fund your EMT training. This can significantly reduce the financial burden and make it easier to achieve your goal of becoming an emergency medical technician.
EMT Certification Process
To become a certified EMT, you need to complete the EMT training requirements, which typically take about 154 hours. Various types of EMT certifications are recognized by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), including EMR, EMT, AEMT, and Paramedic.
You will need to renew your certification, which is usually valid for 2 years, and can be renewed by taking a cognitive exam or approximately 40 hours of continuing education. Maintaining and renewing these certifications according to state-specific regulations is crucial.
You can apply for an EMT certification program as soon as you finish high school or receive your GED, and must be at least 18 years of age to get your EMT certification.
EMTs can seek out additional education to receive one or more of the following EMT specialty certifications: Wilderness EMT, Tactical EMT, Flight Paramedic, and Wilderness Paramedic.
State-Specific Certification Requirements
EMT certification requirements vary from state to state, so it’s essential to check with your state’s EMS agency for specific requirements. Here are some general guidelines:
Certification Levels: Most states offer different levels of EMT certification, such as EMT-Basic, EMT-Intermediate, and EMT-Paramedic.
Training Programs: You must complete a state-approved EMT training program to be eligible for certification.
National Registry Certificate: Many states require EMTs to obtain a National Registry certificate, which is issued by the NREMT.
Recertification: EMTs must recertify periodically, usually every 2-3 years, to maintain their certification.
It’s vital to check with your state’s EMS agency for specific certification requirements, as they may vary. Understanding these requirements will help you navigate the certification process more effectively and ensure you meet all necessary criteria to become a certified EMT.
Career Opportunities for EMTs
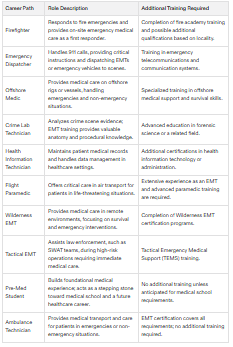
EMTs may be employed as firefighters, emergency dispatchers, contract medics, or offshore medics.
With additional training, an EMT could also transition into a job as a crime lab technician, biological technician, or health information technician.
Many people undergo EMT training for a wide variety of careers, including emergency medical services, first responders, ambulance technicians, police, S.W.A.T, firefighters, and coast guard.
EMTs have the necessary knowledge and skills to stabilize and safely transport patients ranging from those in non-emergency situations to critical, life-threatening cases, illustrating the breadth of care within the emergency medical services framework.
An EMT certification is also valuable to many people who want a medical career, as it provides valuable experience and looks good on a pre-med student’s resume.
Frequently Asked Questions
The EMT Basic course is generally about 16 weeks in length, and the required clinical work may take longer to complete.
You will need to pass a criminal background check and drug test, and may have to provide medical and immunization records when registering.
Becoming an EMT is not for everyone, as it can be traumatic and require working with gruesome injuries, victims in excruciating pain, and death.
Emergency medical technicians provide crucial out-of-hospital emergency medical care and transportation for patients in critical situations. This includes both routine medical transports and immediate responses to life-threatening emergencies, highlighting the EMTs' role as essential links in the emergency medical services system, operating under medical oversight with specific equipment.
Next Steps and Resources
The best way to find a course is to visit your local EMS or Fire Department and ask how to get your EMT certification.
You can earn your CPR certification in person or online, and it can help to be CPR certified before taking an EMT training course.
Local EMS agencies can provide information on state-approved EMT courses and certification requirements.
Conclusion
Becoming an EMT offers a rewarding opportunity as a healthcare provider, providing emergency medical care and transportation to the ill and injured.
EMTs must stay calm in a crisis and be physically and mentally strong, working as part of a team dedicated to providing care to people in need.
A career as an EMT or other EMS professionals can be dynamic and challenging, offering a sense of service to others.