The Future of Advanced Medical Coding: Trends, Challenges, and Opportunities
Medical coding is an essential aspect of the healthcare industry. As the industry evolves, so does the role of medical coders, especially those involved in advanced medical coding. The transition to electronic health records (EHR), the adoption of advanced coding systems, and the growing focus on data security are all reshaping the future of medical coding.
In this blog, we will explore the current trends in advanced medical coding, the challenges coders face, and the opportunities available in this ever-changing field. Additionally, we will look at the impact of emerging technologies and how coders can stay ahead of the curve.
The Shift Towards Value-Based Care and Its Impact on Medical Coding
The healthcare system is undergoing a significant transformation, moving away from the traditional fee-for-service model towards value-based care. In a value-based system, healthcare providers are reimbursed based on patient outcomes, rather than the number of services provided. This shift has important implications for medical coders, as it requires them to be more skilled in coding not only for services rendered but also for patient conditions, treatments, and long-term health outcomes. To stay ahead in this changing environment, it's crucial for medical coders to sharpen their skills. One way to do this is by practicing with the top billing and coding practice tests to ace your exam. These tests help coders familiarize themselves with the latest coding practices, ensuring they are well-prepared for the challenges presented by value-based care systems.
How This Affects Coders:
Coders must understand risk adjustment models that help healthcare providers receive appropriate reimbursement for taking on high-risk patients.
There will be a greater emphasis on coding for prevention and management of chronic conditions, not just treatment for acute care.
Coders will need to collaborate closely with clinical staff to ensure accurate chronic care management (CCM) and care coordination coding.
Pro Tip:
Familiarize yourself with the Hierarchical Condition Categories (HCC) coding system. As risk-based models become more prevalent, this system will be key in ensuring correct reimbursement.
The Role of Technology in Advanced Medical Coding
As we look ahead to 2025, the demand for skilled professionals in the healthcare industry continues to rise, particularly for those pursuing the Best Medical Billing and Coding Certification Programs. Technology is playing a significant role in advancing the field of medical coding. From artificial intelligence (AI) to machine learning (ML), new tools are being developed to automate the coding process, reduce errors, and improve efficiency. However, these technologies are not meant to replace coders; rather, they serve as tools to assist coders in their work. This means that individuals who earn certification in medical billing and coding will have the opportunity to work alongside these technologies, further enhancing their ability to deliver accurate, timely, and compliant coding in a healthcare setting.
Key Technological Trends:
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning: AI can help identify patterns in medical records, suggest potential codes, and improve the accuracy of diagnoses and procedure coding.
Natural Language Processing (NLP): This technology allows coders to process large amounts of unstructured text from clinical notes and other documents, making it easier to extract the necessary data for accurate coding.
Coding Automation: Several coding software tools are being developed to automate repetitive tasks, such as assigning ICD codes for common diagnoses, which allows coders to focus on more complex cases.
The Future of AI in Medical Coding:
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are transforming industries around the globe, and the healthcare sector is no exception. Medical coding, a critical component of healthcare administration, is set to undergo profound changes as AI and ML technologies continue to evolve. Medical coding is a highly specialized field where professionals assign standardized codes to diagnoses, treatments, and procedures. This process is essential for billing, reimbursement, data analysis, and healthcare management. However, the sheer volume of data, complex coding systems like ICD-10, and the increasing pressure for accuracy and compliance have made it increasingly challenging for human coders to keep up.
As AI and ML technologies advance, they will undoubtedly have a significant impact on the future of medical coding. Let's explore how these technologies will shape the profession, enhance accuracy, improve efficiency, and offer new opportunities for coders.
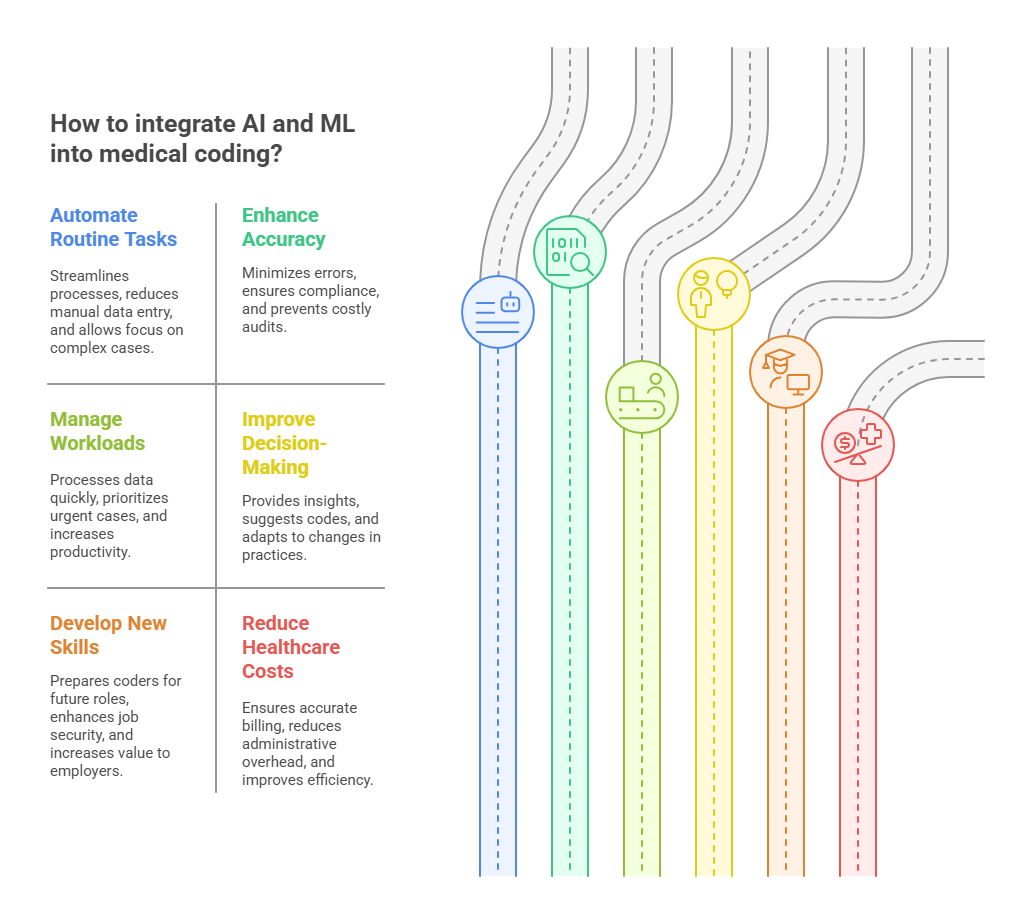
1. The Role of AI and ML in Automating Routine Tasks
One of the most obvious advantages of AI and ML in medical coding is their ability to automate routine and repetitive tasks. Traditionally, medical coders have to sift through patient records, transcribe diagnoses, and manually assign the appropriate codes. This process is time-consuming, error-prone, and requires high attention to detail.
AI-powered systems can streamline this process by automatically extracting relevant information from medical records, analyzing it in real time, and assigning the correct code based on pre-programmed guidelines. Natural Language Processing (NLP), a subfield of AI, can help decipher unstructured data such as physician notes, which often contain valuable information but are difficult for traditional coding systems to interpret.
By automating routine tasks, AI can significantly reduce the amount of time spent on manual data entry. This will allow medical coders to focus more on higher-level decision-making, such as reviewing complex cases, ensuring compliance, and resolving discrepancies.
2. Increased Accuracy and Compliance
Accuracy in medical coding is crucial for proper billing, reimbursement, and compliance with healthcare regulations. Coding errors can lead to claim denials, audits, and even legal penalties for healthcare providers. Unfortunately, even experienced coders are prone to mistakes due to the sheer complexity of coding guidelines and the ever-changing nature of healthcare policies.
AI and ML can enhance accuracy by continuously learning from vast datasets and identifying patterns that might be missed by human coders. These technologies can flag inconsistencies, suggest more accurate codes, and help prevent common errors like upcoding or undercoding. Furthermore, AI-driven tools can stay up-to-date with the latest changes in coding systems (such as ICD-10 updates) and automatically adjust coding recommendations to reflect these changes.
AI's ability to maintain compliance with the latest coding standards will also help reduce the risk of errors, thus minimizing the potential for costly audits or legal issues. Coders who embrace AI will have more confidence in the quality of their work and be able to ensure better compliance with industry standards.
3. Handling Larger Workloads Efficiently
As the demand for healthcare services continues to rise, the volume of medical data that needs to be processed is growing exponentially. This puts pressure on coders to handle larger workloads in a timely manner while maintaining high levels of accuracy. However, human coders have limitations in terms of speed and capacity.
AI has the potential to process vast amounts of data quickly and efficiently, which can help medical coders manage larger workloads. With AI-assisted tools, coders can process more cases in less time, thus increasing productivity and throughput. AI systems can help prioritize the most urgent or complex cases, enabling coders to focus their attention on the most critical issues, while the AI handles routine tasks.
This ability to handle larger workloads will be especially beneficial in settings like hospitals, clinics, and insurance companies, where the volume of claims and patient records can be overwhelming. Coders who integrate AI into their workflow will be able to process more claims and diagnoses in a shorter period, allowing healthcare organizations to stay competitive and meet growing demands.
4. Enhanced Decision-Making and Case Review
While AI and ML can automate many aspects of medical coding, human coders will still play a crucial role in decision-making, especially when it comes to complex or ambiguous cases. AI can assist coders by providing suggestions and insights, but the final decision often requires human expertise to ensure that the coding is appropriate for the clinical context.
AI can also enhance the case review process by identifying potential discrepancies or flags in the data that may require further investigation. For instance, if a coder is unsure about the correct code for a specific procedure, AI-powered tools can offer recommendations based on past cases or best practices. Coders can then review these suggestions, make adjustments as needed, and ensure that the codes are accurate and appropriate.
Additionally, AI tools can improve the decision-making process by providing coders with access to real-time data and trends. By analyzing historical coding patterns, AI can help identify emerging trends, allowing coders to adapt quickly to changes in medical practices or insurance regulations.
5. Training and Skill Development for Coders
As AI becomes a larger part of the medical coding process, coders will need to develop new skills and adapt to working alongside advanced technologies. Coders who embrace AI will find themselves in a more strategic position, as they will be able to focus on higher-level tasks like case review, compliance, and quality assurance, rather than getting bogged down with routine coding.
Training programs for medical coders will likely evolve to include an understanding of AI and ML technologies, with a focus on how these tools can be leveraged to improve efficiency and accuracy. Coders will need to learn how to interact with AI-driven systems, troubleshoot issues, and interpret data that is processed by these tools.
In the long term, coders who can successfully integrate AI into their workflow will have a competitive advantage in the job market. The ability to work effectively with AI tools will make coders more valuable to employers, and those who stay ahead of the curve will be more likely to secure high-paying, advanced positions.
6. AI’s Role in Reducing Healthcare Costs
Medical coding plays a vital role in ensuring that healthcare providers are reimbursed for the services they provide. However, the process of billing and coding is complex, and errors in coding can lead to delayed or denied payments, which in turn results in lost revenue for healthcare organizations.
AI-powered coding tools can help reduce the number of coding errors, leading to faster and more accurate reimbursement. By automating much of the coding process, AI can also reduce administrative overhead costs, as fewer resources will be required for manual data entry and error correction.
In the long term, the use of AI in medical coding could help reduce overall healthcare costs by improving efficiency, ensuring more accurate billing, and streamlining administrative tasks. Healthcare organizations that invest in AI-driven coding systems may see cost savings in the form of reduced overhead, fewer coding errors, and better utilization of their coding staff.
7. AI and the Future of Medical Coding Careers
While AI will undoubtedly change the way medical coding is performed, it does not signal the end of the profession. Instead, it opens new opportunities for coders to focus on higher-level tasks and engage in strategic decision-making. Coders who embrace AI will be able to handle more complex cases, work more efficiently, and provide greater value to their employers.
The future of medical coding will likely involve a combination of AI-assisted coding systems and human expertise. Coders will still be needed to review complex cases, ensure compliance, and make high-level decisions that require clinical judgment. Those who are able to adapt to these changes and develop new skills in AI technology will be well-positioned to succeed in the evolving healthcare landscape.
Coding for New and Emerging Procedures
With the development of new treatments, therapies, and medical technologies, medical coders are increasingly tasked with coding procedures and services that didn’t exist a few years ago. For example, the introduction of telemedicine, genetic testing, and minimally invasive surgeries all require specialized coding.
Telemedicine Coding:
As telemedicine grows, coders will need to stay up-to-date with changes in CPT and HCPCS codes that reflect remote patient consultations and monitoring. Telehealth services are reimbursed differently than in-person visits, requiring careful documentation of the medium used (video call, phone call, etc.) and the specifics of the consultation.
Pro Tip: Stay informed about state-specific regulations regarding telemedicine coding and billing, as they may vary.
Genetic Testing and Personalized Medicine:
The rise of genomic medicine has led to an increase in genetic testing and personalized treatment plans. Coders must understand the nuances of coding for these tests, which may involve complex ICD-10 and CPT codes.
Coders must also stay aware of reimbursement policies surrounding these high-cost, high-tech tests.
Addressing the Challenges in Advanced Medical Coding
While the future of medical coding is full of opportunities, it also brings challenges. As the healthcare landscape becomes more complex, coders face increasing pressure to stay current with evolving regulations, coding systems, and healthcare policies.
Common Challenges:
Regulatory Changes: Healthcare regulations are constantly changing, and coders must keep up with updates to coding guidelines, payer rules, and insurance policies.
Denials and Audits: Incorrect coding leads to denied claims, delayed reimbursements, and audits. Coders must work closely with healthcare providers and billing departments to ensure accuracy.
Data Security: With the increase in digital health records, the importance of securing patient data is paramount. Coders must be aware of HIPAA compliance and data protection regulations.
How to Overcome These Challenges:
Regularly attend continuing education and training programs to stay up-to-date with the latest coding guidelines and technologies.
Collaborate with healthcare providers to ensure clear documentation that reduces errors and minimizes denials.
Implement data protection measures to comply with HIPAA and safeguard patient information.
The Increasing Need for Certified Medical Coders
As medical coding becomes more specialized and integral to the healthcare system, the demand for highly skilled, certified coders is expected to rise. Certified coders are more likely to be trusted with complex cases and higher-level positions, such as coding auditors, trainers, or compliance officers.
How Certification Helps:
Certification enhances credibility: Professional credentials, like the Certified Professional Coder (CPC) or Certified Coding Specialist (CCS), show employers that you have the knowledge and expertise needed for high-level coding.
Higher earning potential: Coders with certifications often earn higher salaries due to their specialized knowledge and expertise.
Career growth: Certifications often open doors to more advanced positions, such as coding managers or healthcare compliance auditors.
5 Lesser-Known Facts About the Future of Medical Coding
Increased automation will not replace coders: While automation tools are helpful, human coders will still be necessary for complex cases, troubleshooting, and ensuring compliance with regulations.
SourceRisk adjustment coding will become more important: As the healthcare industry shifts to value-based care, risk adjustment models will be a major factor in reimbursement, requiring coders to be highly skilled in coding for chronic conditions.
SourceTelemedicine codes will continue to evolve: As telehealth becomes more widespread, new codes will be developed to reflect the growing range of virtual services offered by healthcare providers.
SourceICD-11 will replace ICD-10: The World Health Organization (WHO) plans to implement ICD-11, which will require coders to learn a new coding system.
SourceMedical coding will be crucial for public health data: Accurate coding will be essential for tracking public health outcomes, such as the spread of diseases and treatment effectiveness, particularly in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Source
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
-
Join professional organizations like AHIMA or AAPC to access continuous education, certifications, and updates on coding changes.
-
Specialties such as cardiology, oncology, and orthopedics are highly sought after due to the complexity of the procedures and the volume of patients requiring specialized care.
-
No, while automation tools assist with basic coding tasks, human coders will always be needed to handle complex cases and ensure compliance.
-
Telemedicine introduces new challenges for coding, as virtual visits are billed differently than in-person visits. Coders must stay informed about the latest telehealth coding guidelines.
-
To become a certified medical coder, you can take courses through organizations like AAPC or AHIMA and pass the certification exams for credentials like the CPC or CCS.
Conclusion
The future of advanced medical coding offers numerous opportunities for coders who embrace emerging trends and technologies. With the transition to value-based care, the rise of telemedicine, and the increasing demand for specialized expertise, coders are positioned to play a pivotal role in the healthcare system. As the industry grows and changes, those who stay ahead of the curve with continuous education and certification will remain in high demand.
At AMBCI, we provide medical coding and billing certification programs designed to prepare you for the future of the healthcare industry. Stay ahead of the trends and secure your place in this exciting, dynamic field.