The Ultimate Guide For Medical Billing and Coding
The Ultimate Guide for Medical Billers and Coders
Introduction
Medical billing and coding are critical components of the healthcare industry, ensuring that healthcare providers are reimbursed for their services. This guide covers essential topics, like the roles and responsibilities of billers and coders, key coding systems, and tips for success in the field.
1. Understanding Medical Billing and Coding
Definition and Importance: Medical billing involves submitting and following up on claims with health insurance companies, while coding involves translating healthcare services into standardized codes.
Roles and Responsibilities: Billers handle the financial transactions, while coders ensure accurate documentation of patient diagnoses and procedures.
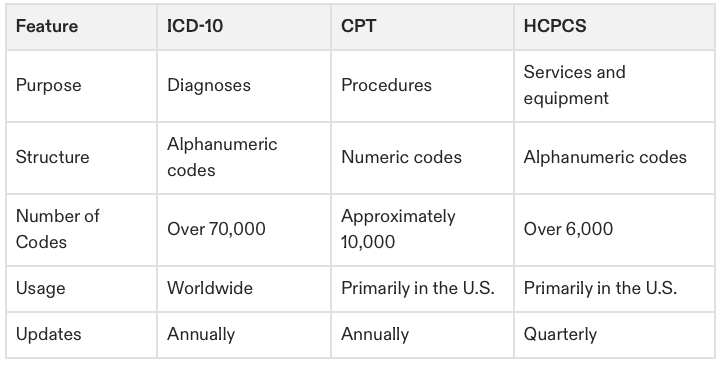
2. Key Coding Systems
ICD-10: International Classification of Diseases, used for diagnoses.
CPT: Current Procedural Terminology, used for procedures.
HCPCS: Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System, used for services and equipment.
3. The Billing Process
Patient Registration: Collecting patient information and insurance details.
Insurance Verification: Confirming coverage and benefits.
Claim Submission: Preparing and submitting claims to insurance companies.
Payment Posting: Recording payments received from insurers and patients.
Denial Management: Addressing and resolving denied claims.
4. Compliance and Regulations
HIPAA: Ensuring patient privacy and data security.
Coding Guidelines: Adhering to coding standards to avoid errors and fraud.
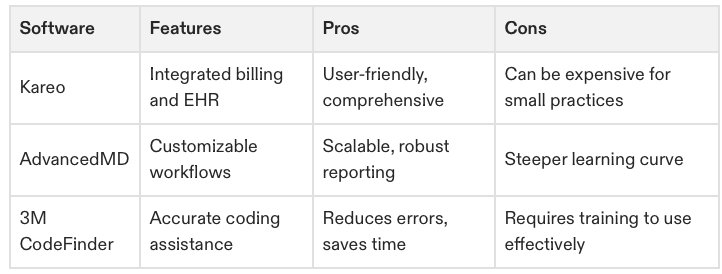
5. Tools and Software
Billing Software: Streamlining the billing process with tools like Kareo or AdvancedMD.
Coding Software: Using tools like 3M CodeFinder for accurate coding.
6. Career Development
Certification: Obtaining credentials like CPC (Certified Professional Coder) or CPB (Certified Professional Biller).
Continuing Education: Staying updated with changes in coding systems and regulations.
Networking: Joining professional organizations like AAPC or AHIMA.
7. Challenges and Solutions
Common Challenges: Keeping up with coding changes, managing denials, and ensuring compliance.
Solutions: Regular training, using updated software, and maintaining open communication with insurers.
Keep Scrolling to Read the Most Commonly Asked Questions About Billing and Coding!
1. How to do medical billing and coding?
To perform medical billing and coding effectively:
Understand key coding systems like ICD-10, CPT, and HCPCS to accurately translate healthcare services into standardized codes.
Use billing software to process insurance claims and generate invoices.
Communicate with insurance providers to verify coverage and resolve claim disputes.
Maintain compliance with healthcare regulations and coding guidelines.
Stay updated through continuous education on changes in coding systems and billing practices.
2. What is medical billing and coding?
Medical billing and coding are administrative processes in healthcare. Medical coding assigns standardized codes to diagnoses, treatments, and procedures using classification systems like ICD-10 and CPT. Medical billing ensures these codes are used to create insurance claims and patient invoices, facilitating reimbursement for medical services.
3. What is the salary for medical billing and coding professionals?
The average annual salary for medical billing and coding professionals ranges between $35,000 and $55,000, with variations based on experience, certification, and location. Entry-level roles often start around $30,000 to $40,000, while experienced coders can earn $60,000 or more with advanced certifications.
4. What does medical billing and coding consist of?
Medical billing and coding involve:
Analyzing patient records for accurate service documentation.
Assigning codes for diagnoses, treatments, and procedures using systems like ICD-10 or CPT.
Preparing and submitting insurance claims.
Resolving claim rejections and coordinating with insurers.
Maintaining comprehensive billing summaries for patient accounts.
5. What is billing and coding?
Billing and coding are essential administrative tasks ensuring healthcare providers are reimbursed for their services. Codingtranslates patient diagnoses and procedures into codes, while billing prepares and submits claims to insurance companies for payment processing.
6. What is healthcare coding?
Healthcare coding refers to the use of standardized systems, like ICD and CPT, to classify and code patient diagnoses, medical services, and procedures. This ensures uniform documentation across the industry and supports billing, insurance claims, and statistical health data analysis.
7. How long is medical billing and coding school?
The duration depends on the program chosen:
Certificate programs take 4–12 months.
Associate degrees require 18–24 months.
Accelerated courses can be completed in as little as 8 weeks but may cover fewer advanced topics.
8. How to find medical bills online?
To locate your medical bills online:
Use patient portals through your healthcare provider’s website or app.
Contact the billing department of the provider to request digital records.
Check insurance portals, where Explanation of Benefits (EOBs) may list your bill details.
9. What do medical billing and coding professionals do?
Their responsibilities include:
Assigning medical codes to patient records.
Preparing and submitting insurance claims.
Communicating with insurance companies to address errors or rejections.
Managing patient invoices and payments.
Ensuring compliance with healthcare regulations and coding accuracy.
10. How can I get certified in medical billing and coding?
Follow these steps to become certified:
Enroll in a training program, focusing on ICD-10, CPT, and billing software.
Choose a certification, such as CPC (by AAPC) or CCA (by AHIMA), that aligns with your goals.
Apply for the exam, study using prep materials, and pass the test.
Maintain certification through continuing education requirements.
11. How to learn medical coding?
Take online or in-person classes on medical coding from reputable organizations like AAPC or AHIMA.
Use coding textbooks and apps to familiarize yourself with ICD-10, CPT, and HCPCS standards.
Practice coding scenarios, often available through educational programs and free tools.
Participate in internships or work experience to refine real-world coding skills.
12. How long is medical coding school?
Programs vary in length:
Most certificate programs take 4–12 months.
An associate degree in medical coding usually requires 18 to 24 months.
Accelerated programs may take as little as 8–10 weeks.
13. How to get a certificate in medical billing and coding?
Complete a recognized training program covering coding systems and billing practices.
Select a certification exam, such as CPC or CCS.
Register for the exam, prepare with study guides, and pass the test.
After obtaining your certificate, ensure you fulfill continuing education requirements as needed.
14. How hard is medical billing and coding?
It depends on your aptitude for detail, organization, and learning medical terminology. While the coursework may seem challenging at first, many find it manageable with proper study and preparation. Staying updated on coding standards is a continual process, but worthwhile for career progression.
15. How to become a medical biller and coder online?
Enroll in an online program from an accredited institution.
Participate in virtual classes covering medical codes, billing systems, and insurance processes.
Complete simulations or internships for practical experience (many programs include these).
Study and obtain certification like CPC or CCA.
16. How to start a medical coding business?
Gain experience and certification in medical coding.
Develop a business plan, outlining your services, pricing, and target clients (e.g., small clinics).
Secure the necessary technology like coding software or billing platforms.
Market your services through networking, online platforms, or healthcare job boards.
Maintain compliance with healthcare laws and client confidentiality.
17. What classes are required for medical billing and coding?
Typical coursework includes:
Medical terminology and anatomy
Coding systems (ICD-10, CPT, HCPCS)
Billing processes and insurance claims
Revenue cycle management
Health information systems and compliance
18. What is the job description for medical billing and coding?
A medical billing and coding specialist:
Analyzes patient data to assign accurate diagnostic and procedural codes.
Prepares and submits insurance claims.
Resolves billing discrepancies with insurers and patients.
Maintains patient records and ensures the accuracy of billing information.
Stays up-to-date with coding rules, regulations, and healthcare law.
19. How to become a certified medical coder online?
Enroll in an accredited online coding program.
Complete necessary coursework on coding systems and billing practices.
Register for a certification exam, such as CPC or CCS, which you can take remotely.
Prepare with exam-specific study materials and practice tests.
Pass the exam and stay certified through continuing education.
20. How to get started in medical billing and coding?
Research training programs (online or in-person) and enroll in one that fits your needs.
Acquire certifications, such as CPC or CCA, to boost your job prospects.
Secure an entry-level position in a clinic, hospital, or billing company.
Continue learning through hands-on experience and optional advanced certifications.
21. How do you get a medical coding certificate?
To get a medical coding certificate:
Enroll in a coding program through an accredited institution or online provider.
Complete coursework covering coding systems (ICD-10, CPT, HCPCS) and medical terminology.
Choose a certification exam, such as CPC (Certified Professional Coder) or CCS (Certified Coding Specialist).
Study using practice exams and coding manuals.
Pass the certification exam and maintain your credential through continuing education.
22. How much are medical billing and coding classes?
The cost of classes varies depending on the program type:
Certificate programs range from $1,000 to $4,000.
Associate degrees may cost between $5,000 and $15,000.
Online courses can be more affordable, starting around $500. Some schools also offer payment plans or financial aid.
23. How long is a medical coding course?
Medical coding courses typically last:
4–12 months for certificate programs.
18–24 months for associate degrees.
Accelerated programs can be completed in a shorter timeframe, often 8–10 weeks, but may not offer as much depth.
24. How hard is medical billing and coding?
The difficulty largely depends on how comfortable you are with learning medical terminology, anatomy, and coding rules. Attention to detail and strong organizational skills are a must. While challenging for some, many people can master it with disciplined study and practice.
25. Can you teach yourself medical coding?
Yes, it’s possible to self-study medical coding by:
Using coding guides like ICD-10 and CPT manuals.
Accessing free online resources, practice tests, and tutorials.
Joining coding forums or communities for peer support.
However, earning certification and completing a formal program may improve career prospects.
26. What is the definition of medical coding?
Medical coding is the process of assigning standardized codes to diagnoses, procedures, and treatments provided by healthcare professionals. Codes like ICD-10, CPT, and HCPCS are used to ensure accurate documentation, billing, and compliance.
27. What degree do you need for medical billing and coding?
You don’t need a degree to begin working in medical billing and coding; a certificate or diploma is often sufficient. However, an associate degree in health information management or a related field can help in advancing your career.
28. How difficult is medical coding certification?
Certification exams like the CPC or CCA are rigorous and require a solid grasp of coding systems, medical terminology, and guidelines. Preparation through a training program and practice exams is essential to pass on the first attempt.
29. How long does it take to get CPC certification?
CPC certification typically takes:
4–12 months of training to complete coursework.
An additional few weeks to months of preparation before passing the exam, depending on your study schedule.
30. How to learn medical billing and coding for free?
To learn for free:
Explore free resources from organizations like AAPC and AHIMA.
Watch tutorial videos on platforms like YouTube.
Join free webinars and coding forums.
Use free practice exercises on coding and billing websites to build your skills.
31. How long does it take to get a medical coding certificate?
Earning a certificate can take as little as 4 months for an accelerated program or up to 12 months for a standard course. Preparation time for the certification exam may add a few weeks or months.
32. How do medical billing programs enter data?
Medical billing programs should enter data:
Accurately and comprehensively to avoid errors in claims.
Following coding guidelines and insurance compliance standards.
Using patient demographics, diagnosis codes, procedure codes, and insurance policy information to create detailed claims.
33. How to start a medical billing and coding business?
To start your own business:
Gain certifications (e.g., CPC) and industry experience.
Establish a business plan covering services like coding, billing, or claims management.
Get tools like HIPAA-compliant billing software.
Network with clinics and providers to build a client base.
Ensure compliance with legal and regulatory guidelines.
34. Which medical billing and coding certification is best?
The best certification depends on your goals:
CPC (Certified Professional Coder) by AAPC is ideal for outpatient settings.
CCS (Certified Coding Specialist) by AHIMA is suited for inpatient hospital coders.
CBCS (Certified Billing and Coding Specialist) by NHA combines skills for both billing and coding.
35. Where to learn medical billing and coding?
You can learn through:
Accredited colleges offering in-person or online programs.
Reputable organizations like AAPC or AHIMA.
Online platforms such as Coursera and Udemy for affordable courses.
36. How much does medical billing and coding training cost?
Training costs depend on the course type:
Certificate programs typically cost between $1,000 and $4,000.
Associate degrees range from $5,000 to $15,000.
Some free or low-cost options are available online, but formal certification exams will require payment.
37. How long is medical billing training?
Training is generally:
4 to 12 months for a certificate or diploma.
Longer for an associate degree, lasting 18 to 24 months.
38. What does medical billing and coding look like?
This work involves using:
Specialized billing software to process claims.
Coding manuals for assigning proper ICD-10 or CPT codes.
Communication tools for liaising with insurers and resolving claim issues.
39. How fast can I get a coding certification?
Accelerated programs and intensive study can allow you to be certified in 6–12 months. CPC and CCA are often chosen for their straightforward preparation paths.
40. How to get medical coding certification online?
To achieve certification online:
Enroll in an online training program.
Study using online resources, coding manuals, and mock exams.
Register for a remote exam (offered by organizations like AAPC).
Take and pass the test using a proctored online setup.
41. How to become a medical billing and coding specialist?
To become a specialist in medical billing and coding:
Complete a training program, either online or in-person, offered by accredited institutions.
Gain certification through exams like CPC (AAPC) or CCS (AHIMA), which validate your expertise.
Build hands-on experience by working in healthcare facilities or through internships.
Stay updated on new coding practices and healthcare regulations to advance your career.
42. How to become a billing and coding specialist?
Follow these steps:
Learn medical terminology and anatomy, as background knowledge is essential.
Enroll in a billing and coding program to gain formal training.
Earn certification, such as CBCS or CCA, to qualify for specialist roles.
Apply to entry-level positions and grow professionally through continuing education.
43. How to become a medical coder online?
Enroll in accredited online courses that offer flexible schedules and focused coding training.
Study coding systems like ICD-10, CPT, and HCPCS widely used in the industry.
Pursue certification exams online through organizations like AAPC or AHIMA.
44. How to get into medical billing and coding?
Research the career path to understand roles and responsibilities.
Complete a training course to learn coding systems like ICD-10 and billing processes.
Obtain relevant certifications to meet employer requirements.
Apply for entry-level roles to start gaining experience.
45. How to get medical billing certification?
To obtain certification:
Enroll in a program that prepares you for certification exams.
Choose certifications like CBCS, which focus on fundamental billing knowledge.
Study diligently and practice using mock exams.
Pass the certification exam to receive credentials recognized by employers.
46. How to get a billing and coding certificate?
Complete a recognized training program.
Prepare for certificates like CPC (Certified Professional Coder) or CHAP (Certified Healthcare Access Professional).
Schedule and take the corresponding exam to earn your certificate.
47. How to start a medical billing and coding business?
Here’s a step-by-step guide:
Gain coding/billing experience and certification.
Write a detailed business plan for offering billing services to clinics.
Invest in HIPAA-compliant software and tools.
Market your services to healthcare providers in need of billing support.
48. What are the certifications for medical billing and coding?
Common certifications include:
CPC (Certified Professional Coder) for outpatient coding.
CCA (Certified Coding Associate) for entry-level coding skills.
CBCS (Certified Billing and Coding Specialist) for focusing on both billing and coding services.
CCS (Certified Coding Specialist) suitable for advanced hospital-based coding professionals.
49. How to get a coding certification?
Choose reliable organizations like AAPC or AHIMA for training.
Complete the training that aligns with the certification (e.g., CPC, CCS).
Register for the certification exam and use study resources like flashcards or practice exams.
Take and pass the exam to earn your credential.
50. What classes are needed for medical billing and coding?
Typical classes include:
Medical Terminology and Anatomy
Medical Coding Systems (ICD-10, CPT, HCPCS)
Health Insurance Principles and Billing Processes
Medical Software and Healthcare Compliance
51. What degree is medical billing and coding?
While a bachelor’s degree isn’t required, a specialized certificate program or an associate degree in fields like Health Information Management is ideal for entering the profession.
52. How to get a medical billing and coding certification?
Enroll in an accredited training program to learn coding and billing fundamentals.
Practice coding scenarios using ICD-10 and CPT codes.
Sign up for an exam, such as the CPC or CCA, offered by AAPC or AHIMA.
Pass the exam and fulfill any continuing education requirements to maintain your certification.
53. What is meant by medical coding?
Medical coding involves the systematic assignment of standardized codes to healthcare diagnoses, treatments, and procedures. This ensures proper documentation, billing accuracy, and insurance claims processing.
54. What is medical coding?
Medical coding is the process of translating medical diagnoses and treatments into industry-standard codes (like ICD-10, CPT, and HCPCS). These codes are used to bill insurance companies and ensure accurate healthcare documentation.
55. What medical coding certification is best?
The best certification depends on your career goals:
CPC is ideal for outpatient coding roles.
CCS is better suited for inpatient or hospital coding professionals.
CCA provides a foundational certification that is versatile for beginners.
56. How long does it take for medical billing and coding?
Entry-level programs range from 4 to 12 months.
Advanced courses, like associate degrees, typically take 18 to 24 months to complete.
57. How long does it take to get medical coding certification?
The timeline generally includes:
4–12 months of education in a training program.
A few weeks to months of exam prep before taking certification tests such as CPC or CCS.
58. How long is a medical billing and coding program?
The length depends on the depth of study:
Certificate programs: 4–12 months.
Associate degrees: 18–24 months.
59. How to get into medical coding and billing?
Learn the career basics by researching online resources and programs.
Take a formal training course to master coding systems.
Obtain certification to enhance job opportunities.
Apply for beginner roles like medical coder or billing assistant.
60. How long is medical billing training?
Medical billing training lasts:
4 to 12 months for certifications.
12 to 24 months for associate degrees.
61. How to get certified for medical billing and coding?
To get certified:
Enroll in a training program at an accredited institution or online platform.
Study coding systems such as ICD-10, CPT, and HCPCS, as well as medical billing practices.
Choose a certification, like CPC (Certified Professional Coder) or CCA (Certified Coding Associate).
Prepare for the exam using mock tests, study guides, and coding manuals.
Pass the certification exam and ensure you meet continuing education requirements to maintain your credential.
62. How to get ICD-10 certification?
To obtain ICD-10 certification:
Complete an ICD-10 training program offered by organizations like AHIMA or AAPC.
Practice using ICD-10 coding manuals and work on real-world scenarios.
Sign up for an ICD-10-focused certification exam, such as those from AAPC or AHIMA.
Pass the exam and keep up-to-date with ICD-10 code updates for accuracy.
63. How to get started in medical billing and coding?
To begin your career:
Research the field to understand responsibilities and expectations.
Enroll in a comprehensive training course, either online or in-person, to learn coding and billing systems.
Gain certification in coding (e.g., CPC, CCS) or billing (e.g., CBCS) to improve employability.
Apply for entry-level roles to build experience and grow your skills.
64. How to learn medical coding for free?
Here are some free learning options:
Access free resources like webinars, tutorials, and practice tests on sites like AAPC or AHIMA.
Use free online courses from platforms like Coursera or YouTube.
Practice with ICD-10, CPT, and HCPCS manuals available online or in libraries.
Join forums or communities for medical coders to learn from experts.
65. What degree do you need for medical billing and coding?
Most medical billing and coding positions require a certificate or diploma rather than a degree. For advanced roles, an associate degree in Health Information Management or a related field can be beneficial. A degree may also help for leadership or specialized roles.
66. What do you do in medical billing and coding?
Professionals in this field:
Translate medical diagnoses and procedures into standardized codes like ICD-10 and CPT.
Submit claims to insurance companies for reimbursement.
Handle billing disputes and errors by communicating with patients and insurers.
Ensure all medical records are accurately documented and compliant with regulations.
67. Where to learn medical billing and coding?
You can learn from:
Accredited schools like community colleges or universities offering in-person or online programs.
Reputable organizations like AAPC and AHIMA, which provide specialized coding and billing courses.
Online platforms, such as Udemy, Coursera, and LinkedIn Learning, which offer flexible options.
68. How to start a billing and coding business?
Follow these steps:
Gain industry experience by working as a certified professional.
Write a business plan detailing services like coding, billing, and claims management.
Invest in HIPAA-compliant billing software and administrative tools.
Register your business and ensure compliance with healthcare laws.
Market your services to healthcare facilities needing assistance with billing and coding.
69. Which medical billing and coding certification is best?
The "best" certification depends on your goals:
CPC (Certified Professional Coder) by AAPC is ideal for outpatient coding.
CCS (Certified Coding Specialist) by AHIMA suits those working in hospital settings.
CBCS (Certified Billing and Coding Specialist) is preferred for those focusing on billing and coding combined roles.
CCA (Certified Coding Associate) is great for entry-level coders.
70. Can I teach myself medical billing and coding?
Yes, you can teach yourself by:
Using online resources, study guides, and coding manuals like ICD-10 and CPT.
Watching instructional videos and tutorials on coding and billing processes.
Practicing with free coding tools and tests.
However, employers often require certification, which typically involves formal training or passing an exam.
71. How long does it take to learn medical coding?
Learning medical coding takes about 4 to 12 months for certificate programs. If pursuing an associate degree, it can take 18 to 24 months. However, mastering the skill depends on your study habits and prior familiarity with medical terminology and coding systems.
72. How long does medical billing and coding take?
Medical billing and coding training typically takes:
4 to 12 months for certificate programs.
18 to 24 months for associate degrees.
Additional certification preparation may extend this timeline by several weeks.
73. How to do medical coding?
To perform medical coding:
Familiarize yourself with coding systems like ICD-10, CPT, and HCPCS.
Assign correct codes to diagnoses, procedures, and treatments based on medical records.
Use coding software for accuracy and ensure compliance with healthcare regulations.
Validate codes against insurance and billing standards to avoid errors in claims.
74. How long is a medical coding course?
A standard medical coding course lasts:
4–12 months for a certificate or diploma program.
Around 24 months for an associate degree in Health Information Management.
75. How to get a medical coding certificate?
Follow these steps to earn a certificate:
Enroll in a training course tailored for medical coding.
Study medical terminology, coding systems, and relevant regulations.
Practice using coding manuals and take mock exams.
Register for and pass a certification exam like CPC, CCA, or CCS.
76. How to learn billing and coding?
You can learn billing and coding by:
Taking courses at community colleges or online platforms like AAPC.
Studying coding systems like ICD-10 and medical billing software.
Practicing with real-world scenarios and sample codes.
Pursuing certifications to ensure employment readiness.
77. How long is a medical coding program?
The duration varies:
Certificate programs typically take 4–12 months.
Associate degrees require 18–24 months, offering more in-depth knowledge and broader career opportunities.
78. What does medical billing and coding look like?
The work involves:
Translating diagnoses and treatments into standardized codes.
Submitting claims through billing software to insurance providers.
Resolving claim disputes and ensuring all data is accurately documented.
Using tools like HIPAA-compliant software and coding manuals daily.
79. What is a medical billing and coding job?
A medical billing and coding job focuses on:
Assigning codes to treatments, procedures, and diagnoses for accurate billing.
Managing insurance claims and ensuring they comply with regulations.
Handling patient billing questions and errors in claims.
Supporting healthcare providers by maintaining accurate medical records.
80. What is a billing and coding job in medical?
This role includes:
Coding patient records using ICD-10, CPT, and HCPCS systems.
Preparing and submitting medical claims to insurance providers.
Verifying patient insurance policies and processing disputes.
Maintaining compliance with legal and regulatory standards in healthcare billing.
81. What is the role of a medical coder?
A medical coder translates healthcare services, diagnoses, and procedures into standardized codes like ICD-10, CPT, and HCPCS. These codes help healthcare providers document patient care accurately and ensure proper billing and reimbursement from insurance companies.
82. What is the role of a medical biller?
Medical billers are responsible for processing and submitting insurance claims. They:
Review coded medical records for billing accuracy.
Communicate with insurance providers to ensure compliance.
Handle patient billing inquiries and payment processing.
83. How to become a medical billing and coding specialist online?
Enroll in a reputable online certificate or diploma program in medical billing and coding.
Learn coding systems like ICD-10, CPT, and HCPCS and billing processes.
Obtain certification, such as CPC, CCA, or CBCS, through online exams.
Build experience with internships or entry-level remote positions.
84. How to get a job in medical billing and coding?
Earn certification to stand out to employers (e.g., CPC, CCS).
Build your resume by completing training programs or internships.
Apply to hospitals, clinics, and insurance companies seeking entry-level coders or billers.
Use job boards like Indeed or AAPC’s career portal to find opportunities.
85. What skills are needed for medical billing and coding?
Professionals in this field need skills like:
Proficiency in medical terminology and coding systems.
Strong attention to detail to avoid coding or billing errors.
Knowledge of billing software and healthcare compliance regulations.
Problem-solving skills to handle denied claims and queries.
86. How to advance in a medical billing and coding career?
To grow in your career:
Pursue advanced certifications like CCS-P or CPC-I for specialized roles.
Gain experience in high-demand fields like hospital coding or auditing.
Consider earning an associate degree or moving into healthcare management.
Stay updated with rapidly evolving coding standards like ICD-11.
87. What are the challenges in medical billing and coding?
Common challenges include:
Adapting to frequent changes in coding standards and regulations.
Managing complex claims and handling denied reimbursements.
Preventing errors due to misinterpretation of medical records.
Balancing high workloads while maintaining accuracy.
88. How to stay updated in medical billing and coding?
Attend webinars, workshops, or events hosted by organizations like AAPC or AHIMA.
Subscribe to coding newsletters and industry publications.
Participate in forums and networking groups to exchange knowledge.
Complete continuing education courses to maintain certifications.
89. What is the future of medical billing and coding?
The field is expected to grow due to:
Increasing healthcare demands from an aging population.
Transition to new coding systems like ICD-11.
Greater adoption of technology, including AI-powered billing tools.
Rising demand for medical billing and coding professionals across remote and global roles.
90. How to network in the medical billing and coding industry?
Join professional organizations like AAPC, AHIMA, or regional coding associations.
Attend industry conferences, coding seminars, and job fairs.
Use online platforms like LinkedIn to connect with other professionals.
Participate in coding workshops or local chapter meetings for professional exposure.
91. How to find medical billing and coding jobs?
To find jobs in this field:
Use online job portals like Indeed, ZipRecruiter, and LinkedIn.
Check career sections on hospital, clinic, or insurance company websites.
Network through professional organizations like AAPCand AHIMA, which often have job boards.
Gain experience via internships or part-time roles to boost your qualifications.
92. What are the benefits of a career in medical billing and coding?
Benefits include:
High demand due to the growing healthcare industry.
Opportunities to work remotely or in flexible environments.
A clear path for career growth with certifications and experience.
Competitive salaries with potential for advancement in specialized roles.
The ability to contribute to accurate healthcare documentation and enhance patient care.
93. How to prepare for a medical billing and coding interview?
To prepare:
Research the job role and organization thoroughly.
Review relevant coding systems like ICD-10 and CPT, and practice coding scenarios.
Be ready to answer behavioral questions, like how you handle denied claims or errors.
Prepare questions to ask about the company’s software, workflows, or coding practices.
Highlight certifications, training, and prior experience during the interview.
94. What is the job outlook for medical billing and coding?
The job outlook is promising:
The Bureau of Labor Statistics projects job growth of 7% through 2031, faster than average for other fields.
Increased demand for healthcare services and data migration to electronic health records (EHRs) creates more opportunities.
Remote work options are expected to expand, making this career accessible globally.
95. How to choose the right medical billing and coding program?
Consider the following when selecting a program:
Accreditation by reputable organizations like AAPC or AHIMA.
Flexibility of learning modes, such as online or in-person classes.
Program length and whether it offers preparation for certifications like CPC or CCA.
Student reviews and job placement rates for graduates.
Access to resources like coding software, mock exams, and interactive practice.
96. What are common mistakes in medical billing and coding?
Mistakes include:
Using incorrect or outdated codes, leading to claim denials.
Misinterpreting medical records, causing discrepancies in documentation.
Omitting necessary modifiers or failing to check payer-specific requirements.
Overlooking compliance rules, which can result in audits or legal issues.
97. How to improve accuracy in medical billing and coding?
To enhance accuracy:
Stay updated on new codes and regulations through continuing education.
Double-check your work, especially complex codes or claims.
Use reliable coding software to reduce manual entry errors.
Maintain strong communication with healthcare providers for clarification.
Regularly attend training sessions and workshops to refresh your skills.
98. What are the ethical considerations in medical billing and coding?
Ethical responsibilities include:
Maintaining patient confidentiality and following HIPAA regulations.
Assigning codes accurately without intentional upcoding or fraud.
Ensuring honesty and transparency in billing practices.
Avoiding conflicts of interest and reporting any unethical behavior observed.
99. How to handle denied claims in medical billing?
Steps to resolve denied claims:
Review the denial code or reason provided by the payer.
Verify the claim details for errors, missing data, or unsupported codes.
Contact the insurance company for clarification or dispute the denial if necessary.
Correct the errors and resubmit the claim promptly.
Implement quality checks to prevent repeat errors in future claims.
100. What is the impact of technology on medical billing and coding?
Technology has significantly improved the field by:
Automating coding processes with AI, reducing manual workload and human errors.
Enabling real-time claim submissions and faster reimbursements via electronic systems.
Enhancing compliance through updates to coding software and EHR integration.
Allowing coders and billers to work remotely using cloud-based tools.
101. How to transition to a career in medical billing and coding?
To switch to this field:
Research training programs to acquire necessary skills and certifications.
Gain proficiency in coding systems like ICD-10, CPT, and HCPCS.
Obtain certifications such as CPC or CCA to boost your qualifications.
Look for entry-level positions or internships to gain practical experience.
Utilize online courses for flexibility if you're transitioning from another career.
102. What are the best resources for learning medical billing and coding?
Highly recommended resources include:
Online platforms like AAPC, AHIMA, and Coursera.
Textbooks such as ICD-10-CM Coding Handbook and Step-by-Step Medical Coding.
Coding software and tools like 3M CodeFinder or Encoder Pro.
Industry blogs, forums, and YouTube channels for practical tips and updates.
Practice exams and coding simulators available through certification organizations.
103. How to maintain certification in medical billing and coding?
To keep your certification active:
Complete required continuing education units (CEUs)annually or as required by the certifying body.
Stay informed about changes in coding standards and medical regulations.
Renew your certification by paying renewal fees and submitting proof of CEUs.
Attend industry events, webinars, and workshops to meet CEU requirements.
104. What are the differences between medical billing and medical coding?
Medical billing and coding are distinct yet interconnected roles:
Medical Coding: Focuses on translating medical procedures, treatments, and diagnoses into standardized codes (e.g., ICD, CPT).
Medical Billing: Uses those codes to create and submit insurance claims, resolve disputes, and manage patient billing.
105. How to handle patient inquiries in medical billing?
Steps to address patient concerns effectively:
Listen actively to understand their questions or complaints fully.
Provide clear explanations of the charges and coding used.
Verify their insurance details to clarify coverage and payments.
Offer solutions for billing or insurance issues, such as payment plans.
Maintain a professional and empathetic tone throughout the conversation.
106. What is the importance of compliance in medical billing and coding?
Compliance ensures:
Accurate and ethical billing practices, preventing fraud and legal issues.
Adherence to laws like HIPAA for patient privacy.
Avoidance of costly penalties or audits due to incorrect billing.
Trust between healthcare providers, payers, and patients.
107. How to manage workload in medical billing and coding?
To balance tasks effectively:
Use work management tools or EHR platforms to prioritize tasks.
Schedule regular breaks to maintain focus and prevent burnout.
Create a checklist for claims and coding tasks to stay organized.
Delegate non-essential tasks if you're part of a larger team.
Attend productivity training or workshops to enhance time management.
108. What are the career advancement opportunities in medical billing and coding?
Growth paths include:
Specializing in areas such as oncology coding or auditing.
Moving into leadership positions like coding supervisoror billing manager.
Transitioning to healthcare informatics or compliance roles.
Training or mentoring new billers and coders as an instructor or consultant.
109. How to choose between medical billing and coding as a career?
Factors to consider:
If you enjoy detail-oriented tasks and deciphering medical records, choose coding.
If you prefer financial processes or resolving payment issues, opt for billing.
Research demand in your region for each role and your long-term career goals.
Consider training programs that allow you to explore both fields before specializing.
110. What are the most common coding systems used in medical billing?
The primary coding systems include:
ICD-10 (International Classification of Diseases): For diagnoses and inpatient procedures.
CPT (Current Procedural Terminology): For medical services and procedures.
HCPCS (Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System): For services and supplies not covered by CPT codes.
DRG (Diagnosis-Related Groups): For hospital billing and resource categorization.
111. How to improve efficiency in medical billing and coding?
Enhance productivity by:
Utilizing advanced coding software for faster and more accurate coding.
Regularly updating knowledge on current regulationsand coding systems.
Streamlining workflows with clearly defined processesand task prioritization.
Conducting periodic training sessions for staff to ensure consistency.
Automating repetitive tasks, such as claims submissions or error checks.
112. What are the latest trends in medical billing and coding?
Key trends include:
Growing reliance on AI-powered tools for coding accuracy and efficiency.
Transitioning to ICD-11 for global standardization.
Increased demand for remote work options and cloud-based billing solutions.
Greater focus on compliance measures in light of evolving regulations.
Integration of machine learning for predictive analytics in claim processing.
113. How to handle complex medical coding scenarios?
To resolve challenging cases:
Consult the latest coding guidelines and payer-specific rules.
Use coding manuals, references, or online tools like Encoder Pro for clarity.
Work collaboratively with healthcare providers to interpret ambiguous documentation.
Seek advice from senior coders or join forums for peer input on difficult cases.
Regularly attend workshops to build expertise in complex coding areas.
114. What is the role of AI in medical billing and coding?
AI contributes by:
Automating code assignment, reducing errors, and saving time.
Identifying patterns to assist with denial managementand claim resolution.
Enhancing documentation with natural language processing (NLP) tools.
Providing real-time analytics for tracking productivity and performance.
Enabling predictive modeling for identifying potential compliance risks.
115. How to ensure data security in medical billing and coding?
To protect sensitive data:
Comply with HIPAA regulations for patient confidentiality.
Use encryption tools and implement secure access protocols like multi-factor authentication.
Train staff on recognizing phishing and other cybersecurity risks.
Conduct regular audits to identify and mitigate vulnerabilities.
Partner only with trusted vendors for cloud-based tools and data storage.
116. What are the best practices for medical billing and coding audits?
To conduct effective audits:
Schedule audits consistently to maintain accuracy over time.
Focus on common error areas like claim rejections, modifiers, or documentation quality.
Use audit results as a learning tool to improve processes and prevent future mistakes.
Ensure transparency by keeping open communication with the coding or billing team.
Leverage audit software to analyze large volumes of data efficiently.
117. How to deal with insurance companies in medical billing?
When negotiating or resolving issues:
Keep detailed records of all claims, denials, and communications.
Clearly understand and follow payer-specific policies and guidelines.
Be persistent when addressing denied claims or disputes, providing adequate documentation.
Build rapport with payer representatives to streamline communication.
Use online claims portals to track and manage claims efficiently.
118. What are the key performance indicators in medical billing and coding?
KPIs to monitor for performance include:
First-pass claim approval rate (quality of submissions).
Days in accounts receivable (A/R) to assess timely payments.
Claim denial rates, identifying areas for improvement.
Productivity metrics, such as claims processed per hour.
Compliance error rates to gauge adherence to coding and billing standards.
119. How to train new employees in medical billing and coding?
To onboard efficiently:
Provide comprehensive training on coding systems and billing processes.
Offer hands-on practice using industry-standard software.
Pair them with experienced staff for mentoring and real-time feedback.
Encourage participation in certification programs through AAPC or AHIMA.
Regularly assess knowledge with mock scenarios to ensure readiness.
120. What are the common software tools used in medical billing and coding?
Popular tools include:
Kareo and AdvancedMD for medical billing management.
3M CodeFinder and Encoder Pro for coding assistance.
Epic Systems and Cerner for electronic health records (EHR).
ClaimScrub for error-checking claims before submission.
Cloud-based solutions like AthenaHealth for remote accessibility.
121. How to handle patient billing disputes?
To address disputes effectively:
Listen actively to understand the patient’s concerns.
Review the billing records and insurance details to identify discrepancies.
Provide clear explanations of procedures, services, and charges.
Offer solutions such as payment plans or corrected bills if errors are found.
Maintain professionalism and empathy throughout the resolution process.
122. What are the ethical challenges in medical billing and coding?
Common challenges include:
Upcoding: Assigning higher-cost procedures intentionally for financial gains.
Unbundling: Separating bundled procedures to increase billing.
Patient privacy violations: Failing to protect sensitive health information.
Ensuring accuracy while avoiding intentional fraud or abuse in claims submissions.
Handling pressure to miscode to meet quotas or deadlines.
123. How to stay compliant with healthcare regulations?
Ensure compliance by:
Keeping up with changes in regulations like HIPAA and the Affordable Care Act.
Participating in training programs on legal and coding updates.
Using compliance-checking software to identify potential errors in claims.
Conducting regular audits of processes and documentation.
Following ethical coding and billing practices diligently.
124. What is the role of telemedicine in medical billing and coding?
Telemedicine has transformed billing and coding by:
Introducing new codes for virtual consultations and treatments.
Increasing the use of modifier codes to reflect remote services.
Requiring knowledge of payer-specific policies for telehealth claims.
Expanding access to healthcare reimbursement options for virtual practices.
Driving reliance on electronic systems for seamless claim processing.
125. How to improve patient satisfaction in billing processes?
Enhance satisfaction with these steps:
Simplify bills by using clear, itemized statements.
Offer multiple payment options, including online portals.
Educate patients on their insurance coverage to reduce confusion.
Provide prompt customer service for inquiries and complaints.
Implement proactive communication to address billing concerns early.
126. What are the differences between inpatient and outpatient coding?
Key differences include:
Inpatient Coding: Focuses on detailed diagnoses and procedures documented in hospital stays, relying on ICD-10-PCS codes.
Outpatient Coding: Covers minor procedures or consultations, primarily using CPT codes.
Documentation requirements and billing complexities tend to be higher for inpatient cases.
127. How to manage denied claims effectively?
To handle denials:
Identify the reason code or notes provided by the payer.
Cross-check documentation and coding inputs to locate errors.
Contact the payer for clarification if the denial seems unjustified.
Correct and resubmit claims promptly with accurate details.
Analyze trends in denials to prevent recurring issues.
128. What is the impact of healthcare reforms on billing and coding?
Reforms have driven changes like:
Updated codes and billing structures to reflect evolving care delivery systems.
Increased focus on patient accessibility and value-based care billing.
Greater emphasis on compliance with privacy laws and data management standards.
Expanded coverage for preventative and remote care services, requiring accurate coding.
129. How to choose the right coding certification?
Here are key considerations:
Match certifications with your career goals, e.g., CPC for professional coders or CCA for beginners.
Opt for certifications from recognized organizations like AAPC or AHIMA.
Check employer preferences for specific certifications in your region.
Consider the specialization offered, such as oncology coding or auditing.
Review preparatory resources and exam requirements to choose a manageable program.
What is Medical Billing and Medical Coding?
Medical billing and coding is the process of assigning medical codes to diagnoses and procedures for insurance reimbursement. Coding compliance is a critical aspect of the medical billing and coding process. Medical billers and coders play a crucial role in ensuring healthcare providers are quickly and accurately paid for their services. Medical billing involves creating claims based on the codes provided by medical coders, while medical coding involves translating patient care into current procedural terminology (CPT) codes. Medical coders use medical billing software and coding systems, such as ICD-10 and CPT, to assign codes.
Definition and Overview
Medical billing and coding is a crucial process in the healthcare industry that involves assigning medical codes to diagnoses and procedures for insurance reimbursement. Medical billing and coding professionals, also known as medical coders or coding specialists, play a vital role in ensuring that healthcare providers receive accurate and timely payment for their services. The process involves using standardized medical codes, such as ICD-10 and CPT, to assign codes to diagnoses and procedures, and then submitting claims to insurance companies for reimbursement. This meticulous work ensures that healthcare providers can focus on patient care while the billing and coding professionals handle the financial aspects.
Career Opportunities and Growth
Medical billing and coding is a growing field with a high demand for skilled professionals. Becoming a certified coding specialist can significantly enhance job prospects and earning potential. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, employment opportunities for medical records and health information technicians are expected to grow 13%
Job Prospects and Salary Range
The job prospects for medical billing and coding professionals are excellent, with the Bureau of Labor Statistics predicting a 13% growth in employment opportunities for medical records and health information technicians from 2020 to 2030. According to the AAPC 2023 Salary Survey results, certified medical records specialists earn 15% more than their non-certified colleagues. The median annual salary for medical records and health information technicians was $42,820 in May 2020, according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics. With experience and certification, medical billing and coding professionals can earn salaries ranging from $50,000 to over $70,000 per year. This promising outlook makes a career in medical billing and coding both stable and rewarding.
Education and Training Requirements
Overview of Certification Programs
Certification programs for medical billing and coding professionals are offered by several organizations, including the American Academy of Professional Coders (AAPC) and the American Health Information Management Association (AHIMA). The AAPC offers the Certified Professional Coder (CPC) certification, while AHIMA offers the Certified Coding Specialist (CCS) certification. These certifications demonstrate that an individual has met the competencies and standards required for medical billing and coding professionals. Certification programs typically include coursework, training, and a certification exam, and are designed to prepare individuals for a career in medical billing and coding. Earning these certifications not only validates your skills but also significantly enhances your employability and earning potential.
Online Medical Billing and Coding Programs
Online medical billing and coding programs are designed to provide students with the skills and knowledge needed to succeed in the medical billing and coding field. These programs typically include coursework in medical terminology, anatomy, and coding systems, as well as training in medical billing software and coding systems. Online programs are often flexible and can be completed in a short period of time, typically 12-18 months. Many online programs also include a voucher for a certification exam, such as the CPC or CCS exam. This flexibility allows students to balance their studies with other commitments, making it an ideal option for those looking to enter the healthcare industry quickly. At AMBCI we offer the strongest course for students with bite-sized learning tidbits as well as lifetime course access and AAPC examination.
Benefits and Features
Online medical billing and coding programs offer several benefits and features, including:
Flexibility: Online programs can be completed on a flexible schedule, allowing students to balance work and family responsibilities.
Convenience: Online programs can be completed from anywhere with an internet connection, eliminating the need for commuting.
Cost-effective: Online programs are often less expensive than traditional on-campus programs.
Career opportunities: Online programs can prepare students for a career in medical billing and coding, with job prospects and salary ranges varying depending on experience and certification.
Certification: Many online programs include a voucher for a certification exam, such as the CPC or CCS exam.
Taught by experienced instructors: Many online programs are taught by experienced instructors who have worked in the medical billing and coding field.
Comprehensive curriculum: Online programs typically include a comprehensive curriculum that covers all aspects of medical billing and coding, including medical terminology, anatomy, and coding systems.
These features make online medical billing and coding programs an attractive option for those looking to enter or advance in the healthcare industry.
Take the Next Step Toward Your Dream Career
This medical billing and coding online program is more than a course—it’s a pathway to professional success. From learning complex coding to mastering claims submission processes, this program equips you with real-world skills that employers value.
Don’t wait to start your career. Enroll today to access live mentorship, exclusive resources, and job placement assistance.