Billing and Coding Requirements
Essential Billing and Coding Requirements: A Guide for Healthcare Professionals
Searching for essential billing and coding requirements? This guide covers the education, certification, and skills you need to succeed in medical billing and coding.
Key Takeaways
Medical billing and coding specialists are essential for managing patient records and ensuring accurate insurance reimbursements in healthcare.
Pursuing accredited education and obtaining certifications, such as CBCS and CPC, significantly enhances job prospects and competitiveness in the field.
Continuous education and additional certifications are vital for career growth, enabling professionals to stay updated with industry standards and improve their earning potential.
Understanding Medical Billing and Coding
Medical billing and coding professionals are indispensable to the functionality of the healthcare system. They meticulously handle patient records and process insurance claims, guaranteeing that medical facilities receive proper compensation for their services. By maintaining precision in both billing practices and claim processing, these specialists ensure the seamless operation of healthcare provision.
Invoicing falls within the remit of medical billers who not only submit but also follow up on claims with insurance entities. Medical coders assist by interpreting clinical documentation into universally recognized alphanumeric codes which enable effective invoicing. While often intertwined, roles focused on billing or coding have distinct duties requiring specialized expertise.
Understanding the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) is crucial in the context of medical billing and coding careers, as it emphasizes the legal requirements and the need for professionals to protect patient information.
By collaborating closely, medical billers alongside coders facilitate streamlined management of patient health records as well as prompt settlement from insurers through accurate claims submission paired with exact code assignment – reinforcing a crucial link between care delivery and financial sustenance in healthcare operations.
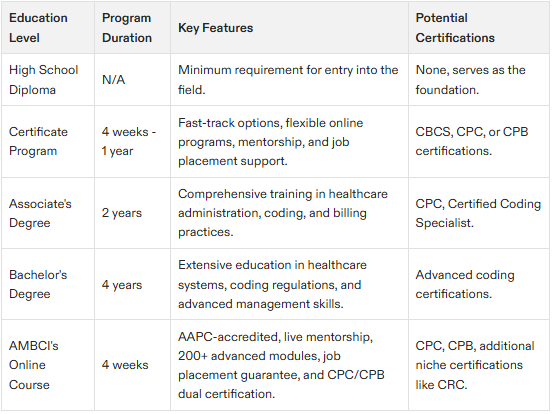
Educational Prerequisites for Medical Billing and Coding
To embark on a career in medical billing and coding, individuals must have at least completed their high school education or attained an equivalent credential. Enhancing one’s qualifications with specialized certificate programs or pursuing an associate degree can significantly bolster employability and distinguish job seekers in the competitive healthcare sector. The demand for billing jobs is high due to a shortage of qualified professionals, and many of these positions can be done remotely. Educational requirements for entering the field include various options that cater to different career goals.
It is vital to enroll in accredited educational programs as they align with established industry benchmarks and equip students for certification examinations essential to this field. Educational pathways include expedited certificate courses that can be finalized within a year, as well as more extensive two- to four-year endeavors culminating in either associate’s or bachelor’s degrees focused on healthcare administration or similar disciplines.
Becoming a certified medical billing specialist is significant for those seeking a rewarding career in healthcare. Certification enhances earning potential, provides advanced knowledge, and opens up more job opportunities. Individuals aiming for positions that command higher salaries often opt for advanced studies via associate’s or bachelor’s degree programs. These avenues of study provide thorough training while also preparing candidates effectively for crucial industry certifications, thereby improving their standing within the job market. The timeline to attain proficiency in medical billing or coding varies between one to three years based upon the chosen educational trajectory.
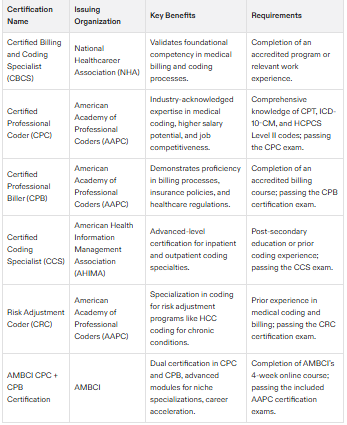
Certification Requirements for Medical Billers and Coders
Obtaining a coding certification in medical billing and coding is a crucial step toward becoming a medical biller and coder. It serves as proof of an individual’s proficiency in handling patient information and complying with healthcare regulations, both of which are essential for career progression. The time commitment involved in earning this certification includes passing specific exams and gaining relevant work experience.
A variety of recognized certifications exist within this professional domain. For instance, the Certified Billing and Coding Specialist (CBCS) credential conferred by the National Healthcareer Association (NHA) signifies specialized knowledge in medical billing and coding processes. Higher-level qualifications like the Certified Professional Coder (CPC) or certified coding specialist from organizations such as AAPC can augment a candidate’s appeal to potential employers.
The culmination of achieving status as a certified biller or coder involves passing a rigorous certification exam. These examinations typically necessitate prior completion of designated educational programs or courses that contribute significantly to vocational advancement. Certifying bodies mandate ongoing education credits to ensure certificate holders remain abreast with evolving standards within the industry.
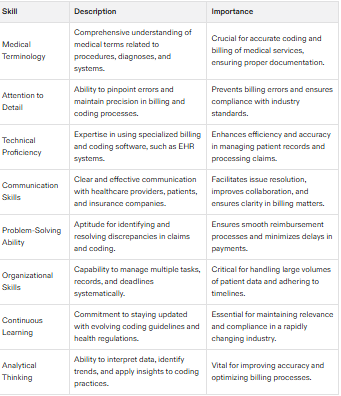
Key Skills for Medical Billing and Coding Professionals
Understanding medical terminology is crucial for precise coding and billing, as it allows professionals to accurately interpret medical documentation and allocate appropriate codes. This encompasses a thorough knowledge of common terms associated with bodily systems, diagnostic tests, nuclear medicine procedures, and medications.
To technical expertise in managing patient records and the intricacies of billing processes through specialized software systems, strong communication abilities are particularly important for billing specialists when discussing payment matters with patients. Meticulous attention to detail is imperative in this field.
To remain competent in medical billing and coding amid evolving healthcare regulations and standards for coding requires continuous education. Essential foundational skills that contribute to success include problem-solving aptitude, organizational capabilities, proficiency at multitasking effectively along with critical thinking skills.
Training Programs for Aspiring Medical Billers and Coders
Individuals aiming to become medical billers or professional coders have a variety of training programs at their disposal, from certifications obtained through technical or trade schools to in-depth associate’s and bachelor’s degree courses. CareerStep and AAPC are among the institutions offering specialized training, with some programs available online for added flexibility.
Medical records professionals have a growing job outlook due to increasing demands in the healthcare industry, driven by an aging population and the necessity for specialized coding and billing skills. A significant percentage of these professionals can work from home, making it an attractive career option.
For those seeking practical experience along with theoretical knowledge, hybrid programs that merge online coursework with classroom-based sessions can be invaluable. These medical coding educational paths typically range from six months to one year in duration and often incorporate internships or externships for hands-on practice in the field. Some pathways may culminate in obtaining a certification in coding.
The content covered within these courses covers topics such as healthcare regulations, medical terminology, and procedures related to coding. This comprehensive educational approach is designed not just to inform but also skillfully train individuals so they can adeptly navigate their future roles as proficient coders and medical billers within the healthcare industry.
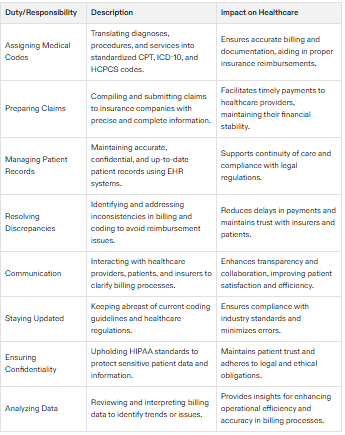
Job Duties and Responsibilities of Medical Billers and Coders
Medical billers and coders play a crucial role in the healthcare industry, ensuring that medical services are accurately documented and billed. Their primary job duties and responsibilities include:
Assigning Medical Codes: Medical coders translate diagnoses, procedures, and services into standardized medical codes. This requires a deep understanding of medical terminology and coding systems like ICD-10, CPT, and HCPCS.
Preparing and Submitting Claims: Medical billers prepare and submit claims to insurance companies, ensuring that all information is accurate and complete. This step is vital for securing timely reimbursements for healthcare providers.
Managing Patient Records: Maintaining accurate and confidential patient records is a core responsibility. Medical billers and coders must ensure that all patient information is correctly documented and securely stored.
Staying Up-to-Date with Coding Guidelines: The healthcare industry is constantly evolving, and medical billers and coders must stay current with the latest coding guidelines and regulations to ensure compliance and accuracy.
Communication: Effective communication with healthcare providers, patients, and insurance companies is essential. Medical billers and coders must be able to explain billing processes, resolve discrepancies, and provide clear information.
Resolving Billing and Coding Issues: Addressing and resolving any billing or coding discrepancies is a critical part of the job. This requires strong analytical and problem-solving skills.
Medical billers and coders must possess strong analytical and problem-solving skills, attention to detail, and excellent communication skills. They must also be knowledgeable about medical terminology, coding systems, and healthcare regulations.
Medical Billing and Coding Specializations
Medical billing and coding is a diverse field with various specializations, allowing professionals to focus on specific areas of interest and expertise. Some common specializations include:
Inpatient Coding: This specialization involves coding for hospital stays and procedures. Inpatient coders must be familiar with the complexities of hospital billing and the specific codes used for inpatient services.
Outpatient Coding: Outpatient coders focus on coding for clinic visits and procedures. This specialization requires knowledge of the codes used for outpatient services and the ability to handle a high volume of claims.
Surgical Coding: Surgical coders specialize in coding for surgical procedures and services. This requires a detailed understanding of surgical terminology and the specific codes associated with various surgical procedures.
Pediatric Coding: Pediatric coders focus on coding for pediatric patients and services. This specialization requires knowledge of the unique medical codes and terminology used in pediatric care.
Oncology Coding: Oncology coders specialize in coding for cancer diagnoses and treatments. This requires a deep understanding of oncology terminology and the specific codes used for cancer-related services.
Cardiology Coding: Cardiology coders focus on coding for heart-related diagnoses and treatments. This specialization requires knowledge of cardiology terminology and the specific codes used in cardiac care.
Medical billers and coders can also specialize in specific coding systems, such as ICD-10 or CPT. Specializing in a particular area can increase job prospects and earning potential.
The Role of Medical Codes in Billing and Coding
Medical billing requires an intricate understanding of different coding systems such as CPT, ICD-10, and HCPCS to ensure precise invoicing. The American Medical Association annually revises the CPT codes to reflect new medical procedures. Seven-character alphanumeric ICD-10-CM codes are employed for pinpointing exact diagnoses while updates to HCPCS codes occur quarterly to accommodate billing for various medical services and supplies.
These coding frameworks play a pivotal role in securing accurate insurance reimbursements during the medical billing process by guaranteeing that healthcare providers are compensated correctly. It is essential for those involved in coding and billing within healthcare to stay abreast with changes in coding guidelines regularly. Such vigilance guarantees that all aspects of medical procedures and services are coded accurately, thereby aiding proper insurance reimbursement while complying with regulatory mandates.
Navigating the Certification Exam
Getting ready for the certification exam might seem overwhelming, but having an understanding of what lies ahead can simplify your preparation. During the exam, participants are permitted to consult authorized print manuals. They must note that electronic devices are prohibited.
Typically, outcomes from the CPC exam become accessible within a period ranging from seven to ten working days. Achieving success in this examination permits individuals to incorporate the designation of CPC-A on their professional profile, which serves as a significant boost for their vocational advancement opportunities.
Work Environment and Job Outlook
Medical billers and coders work in various settings, including hospitals, physician offices, dental clinics, and optometry offices. They can also be found in outpatient care centers and nursing care facilities, with many enjoying the flexibility of remote work.
The job outlook for medical billing and coding is promising, with an 8% projected growth rate from 2021 to 2031. In Texas, the growth rate is even higher at 18.5% from 2020 to 2030, driven by an aging population needing more medical care.
Salaries in this field vary based on experience and certifications. As of May 2021, the average annual salary for medical billing and coding specialists is $39,740. Those with certifications like CPC can earn around $56,109 on average, while professionals with multiple certifications can earn up to $70,000 per year.
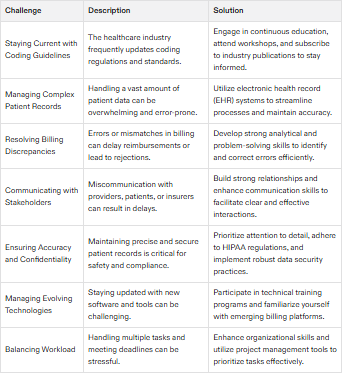
Common Challenges and Solutions
Medical billers and coders face various challenges in their daily work. Some common challenges include:
Staying Current with Coding Guidelines and Regulations: The healthcare industry is constantly evolving, and keeping up with the latest coding guidelines and regulations can be challenging. To overcome this, medical billers and coders should engage in continuous education and training to stay informed about industry changes.
Managing Complex Patient Records and Data: Handling large volumes of patient records and data can be overwhelming. Utilizing electronic health records (EHRs) and other technology can streamline processes and improve efficiency.
Resolving Billing and Coding Discrepancies: Discrepancies in billing and coding can lead to delays in reimbursement and other issues. Developing strong analytical and problem-solving skills can help medical billers and coders address and resolve these discrepancies effectively.
Communicating with Healthcare Providers and Insurance Companies: Effective communication is essential for resolving issues and ensuring accurate billing. Building strong relationships with healthcare providers and insurance companies can facilitate better communication and collaboration.
Maintaining Accuracy and Confidentiality of Patient Records: Ensuring the accuracy and confidentiality of patient records is a critical responsibility. Medical billers and coders must prioritize patient confidentiality and data security, adhering to all relevant regulations and guidelines.
By staying up-to-date with continuing education and training, using technology to streamline processes, and developing strong communication skills, medical billers and coders can overcome these challenges and excel in their roles.
Staying Current with Industry Developments
The medical billing and coding industry is constantly evolving, with new technologies, regulations, and coding systems emerging regularly. To stay current with industry developments, medical billers and coders can:
Attend Conferences and Workshops: Participating in industry conferences and workshops provides opportunities to learn about the latest trends, technologies, and best practices in medical billing and coding.
Participate in Online Forums and Discussion Groups: Engaging in online forums and discussion groups allows medical billers and coders to connect with peers, share knowledge, and stay informed about industry developments.
Read Industry Publications and News: Subscribing to industry publications and news sources can help medical billers and coders stay updated on the latest changes and trends in the field.
Pursue Continuing Education and Training: Enrolling in continuing education courses and training programs ensures that medical billers and coders remain knowledgeable about the latest coding guidelines, regulations, and technologies.
Join Professional Organizations: Becoming a member of professional organizations, such as the American Academy of Professional Coders (AAPC) or the American Health Information Management Association (AHIMA), provides access to valuable resources, networking opportunities, and professional development.
By staying current with industry developments, medical billers and coders can enhance their skills and knowledge, increase their job prospects, and provide high-quality services to healthcare providers and patients.
Continuing Education and Career Advancement
In the field of medical billing and coding, pursuing education and obtaining additional certifications are essential steps for career progression. Staying abreast with the latest changes within the industry through continuous learning can empower professionals to secure specialized positions that elevate their earning potential.
Certification from esteemed institutions such as CALRegional is strongly endorsed by employers who recognize it as a vital component of professional growth. Successfully navigating the certification exam grants individuals access to credentials like the CPC Apprentice certificate, which serves as an integral milestone in advancing one’s career trajectory in medical billing and coding.
Summary
In essence, pursuing a career in medical billing and coding holds the promise of ample growth opportunities. This guide outlines everything from grasping job responsibilities and educational requirements to achieving certification and honing essential skills needed for entry.
Commit to ongoing education and strive for higher-level certifications to unlock specialized positions that can enhance your earning prospects. The healthcare sector depends on the proficiency of medical billers and coders, marking it as a profession with substantial rewards.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the minimum educational requirement for a career in medical billing and coding?
The minimum educational requirement for a career in medical billing and coding is a high school diploma or equivalent. This foundational level of education is essential for entering the field.
How long does it take to become a proficient medical biller or coder?
To become a proficient medical biller or coder, it typically takes one to three years, depending on your educational path and experience level.
Consistent practice and exposure to real-world scenarios will further enhance your proficiency.
What certifications are valuable in medical billing and coding?
In the field of medical billing and coding, acquiring credentials like Certified Professional Coder (CPC) and Certified Billing and Coding Specialist (CBCS) can significantly bolster your professional prospects and reputation. These certifications serve as a testament to expertise in coding and billing, elevating both coders’ careers in medical billing as well as specialists in medical billing and coding.
Can medical billers and coders work remotely?
Yes, many medical billers and coders can work remotely, providing flexibility in their work environment.
This option has become increasingly common in the industry.
What is the job outlook for medical billing and coding professionals?
The job outlook for medical billing and coding professionals is promising, with a projected growth rate of 8% from 2021 to 2031. This indicates strong demand in the field, particularly in states like Texas.