Medical Billing or Coding: Key Insights into Which Path to Choose?
Medical billing and coding are vital components of the healthcare system. While they may sound similar, these roles are distinct yet complementary. Medical billing focuses on the administrative processes involved in submitting and following up on insurance claims to ensure healthcare providers receive payment for their services. Medical coding, on the other hand, involves converting diagnoses, treatments, procedures, and equipment into standardized alphanumeric codes. These codes are used for documentation, insurance claims, and reimbursement.
Medical coding professionals are responsible for accurately translating medical data from patient records into codes using systems like ICD-10 and CPT. This standardization ensures consistent communication across different healthcare facilities. Coders with medical billing and coding certification from AMBCI also help finance departments understand the specific medical reasons for treatments, making it easier to process payments and maintain accurate records.
Medical billing involves more than just sending invoices. Billers manage a patient's insurance information, verify coverage, and begin the claims process. The process is generally divided into front-end and back-end tasks. Front-end billing includes verifying patient eligibility and obtaining pre-authorizations before services are rendered. Back-end billing involves creating itemized claims and following up with insurance providers or government agencies to secure payment.
Both roles require strong organizational skills, attention to detail, and knowledge of healthcare laws like HIPAA. Medical billers often serve as a bridge between patients, providers, and insurance companies, while coders ensure the accuracy and completeness of patient documentation.
Education, Training, and Certification
Many entry-level positions in medical billing and coding require only a high school diploma or GED. However, having a degree or certification in health information technology or a related field significantly boosts employability. Online programs now offer flexible training options, including associate degrees and specialized certificates.
Certifications such as Certified Professional Coder (CPC), Certified Coding Associate (CCA), and Certified Billing and Coding Specialist (CBCS) are well-regarded in the industry. These credentials are offered by organizations like the American Health Information Management Association (AHIMA) and the American Academy of Professional Coders (AAPC). Being certified increases job prospects, salary potential, and industry credibility.
Career Outlook and Salary Expectations
As of 2025, medical billing and coding continue to be in high demand. According to updated statistics from the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, employment for medical records and health information technicians is expected to grow by 15% from 2024 to 2034, much faster than average. On average, certified medical coders can earn about $60,150 annually, while medical billers average around $58,800.
These roles offer stability, remote work flexibility, and opportunities for advancement. Professionals can work in hospitals, private practices, insurance companies, or even start their own medical billing businesses.
Technology and Automation in 2025
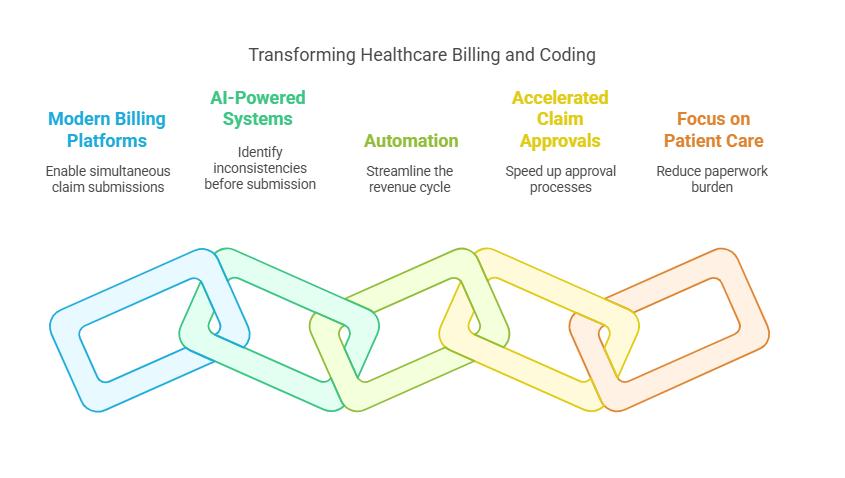
Technology has significantly transformed the billing and coding landscape. Modern billing platforms allow providers to create and submit multiple claims simultaneously, reducing human error. AI-powered systems can identify inconsistencies and potential denials before claims are submitted, increasing reimbursement rates.
Automation has also streamlined the revenue cycle by accelerating the claim approval process. These tools have freed up time for providers to focus more on patient care and less on paperwork.
Outsourcing as a Growing Trend
In 2025, outsourcing medical billing and coding is becoming increasingly common. Many healthcare providers, especially smaller clinics, are opting to partner with external billing services to reduce overhead costs and increase efficiency. These third-party vendors often have highly trained staff and require minimal onboarding, making them an attractive solution for busy practices.
Is Medical Billing or Coding Right for You?
If you are detail-oriented, tech-savvy, and interested in the healthcare industry, either career path can be fulfilling. Medical billing leans more toward administrative and customer-facing responsibilities, while medical coding is ideal for those who enjoy working with data and medical terminology. Both careers offer job flexibility, good salaries, and meaningful contributions to patient care.
To get started, enroll in an accredited training program, gain hands-on experience, and pursue certification. With the right skills and credentials, you can build a stable and rewarding career in this growing field.
6 Lesser-Known Facts About Medical Billing and Coding
Coders are essential in legal investigations: Forensic medical coders assist in investigations related to insurance fraud, wrongful death, and other legal matters by meticulously reviewing medical records to identify discrepancies or potential evidence of malpractice or negligence. Association of Forensic Medical Coders
Coders can specialize by body system: Advanced medical coders often focus on specific medical specialties such as cardiology, orthopedics, or oncology to ensure precision and compliance in coding practices.
Telemedicine coding has its own complexities: The rise of virtual healthcare services, especially after the COVID-19 pandemic, introduced specific modifiers and codes for telemedicine, adding complexity to medical coding practices.
Medical coders can work for the government: Government agencies like the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) employ medical coders to analyze national healthcare trends and ensure compliance with federal regulations.
Medical billing errors cost billions: Medical billing errors are a significant issue in the U.S. healthcare system, with estimates indicating that inaccuracies and fraud cost billions annually. For instance, some reports suggest that healthcare fraud, including billing errors, costs the U.S. approximately $68 billion each year. Prognocis
AI doesn’t replace coders—it assists them: While automation and AI handle repetitive tasks, human coders remain essential for interpreting nuanced clinical information, ensuring accuracy, and reducing medical billing errors. MedTech Intelligence
FAQs About Medical Billing and Coding
-
No, but certifications from AHIMA or AAPC significantly increase job prospects and pay.
-
Yes. Many employers offer fully remote or hybrid positions, especially after the pandemic shifted many jobs online.
-
Most certification programs take 4 to 12 months, depending on whether you're studying full-time or part-time.
-
They're different. Billing involves dealing with patients and insurance, while coding requires interpreting medical data. Coding is more technical, whereas billing is more administrative.
-
For coders: Certified Professional Coder (CPC).
For billers: Certified Billing and Coding Specialist (CBCS) or Certified Professional Biller (CPB).